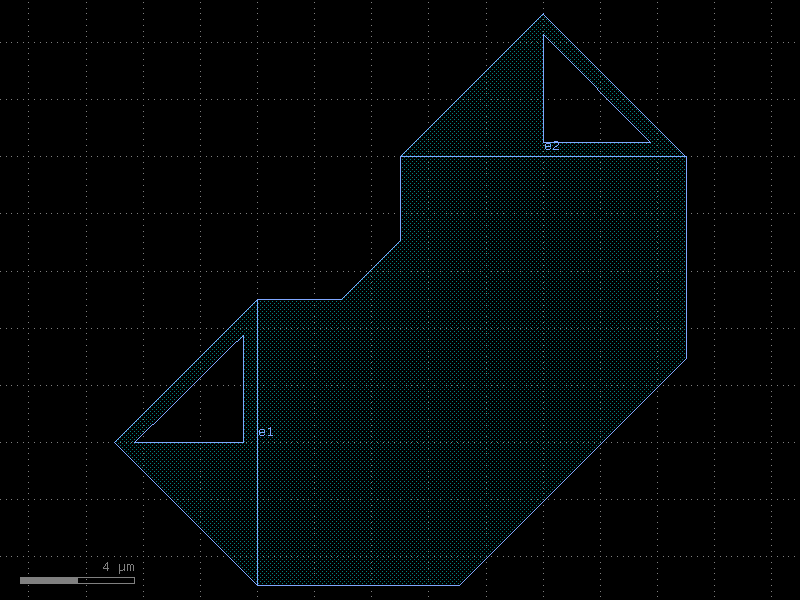
Cells Si SOI 220nm Cband#
add_fiber_array#
- cspdk.si220.cband.cells.add_fiber_array(component='straight', grating_coupler='grating_coupler_elliptical', gc_port_name='o1', component_name=None, cross_section='strip', gc_rotation=-90, radius_loopback=10, **kwargs)[source]#
Returns component with south routes and grating_couplers.
You can also use pads or other terminations instead of grating couplers.
- Parameters:
component (str | Callable[[...], Component] | dict[str, Any] | DKCell | partial[Component]) – component spec to connect to grating couplers.
grating_coupler – spec for route terminations.
gc_port_name (str) – grating coupler input port name.
component_name (str | None) – optional for the label.
cross_section (CrossSection | str | dict[str, Any] | Callable[[...], CrossSection] | SymmetricalCrossSection | DCrossSection) – cross_section function.
gc_rotation (float) – fiber coupler rotation in degrees. Defaults to -90.
radius_loopback (float) – optional radius of the loopback bend. Defaults to the cross_section.
kwargs – additional arguments.
- Keyword Arguments:
bend – bend spec.
straight – straight spec.
fanout_length – if None, automatic calculation of fanout length.
max_y0_optical – in um.
with_loopback – True, adds loopback structures.
with_loopback_inside – True, adds loopback structures inside the component.
straight_separation – from edge to edge.
list_port_labels – None, adds TM labels to port indices in this list.
connected_port_list_ids – names of ports only for type 0 optical routing.
nb_optical_ports_lines – number of grating coupler lines.
force_manhattan – False
excluded_ports – list of port names to exclude when adding gratings.
grating_indices – list of grating coupler indices.
routing_straight – function to route.
routing_method – route_single.
optical_routing_type – None: auto, 0: no extension, 1: standard, 2: check.
input_port_indexes – to connect.
pitch – in um.
radius – optional radius of the bend. Defaults to the cross_section.
route_backwards – route from component to grating coupler or vice-versa.
- Return type:
Component
import gdsfactory as gf c = gf.components.crossing() cc = gf.routing.add_fiber_array( component=c, optical_routing_type=2, grating_coupler=gf.components.grating_coupler_elliptical_te, with_loopback=False ) cc.plot()
import cspdk
c = cspdk.si220.cband.cells.add_fiber_array(component='straight', grating_coupler='grating_coupler_elliptical', gc_port_name='o1', cross_section='strip', gc_rotation=-90, radius_loopback=10).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
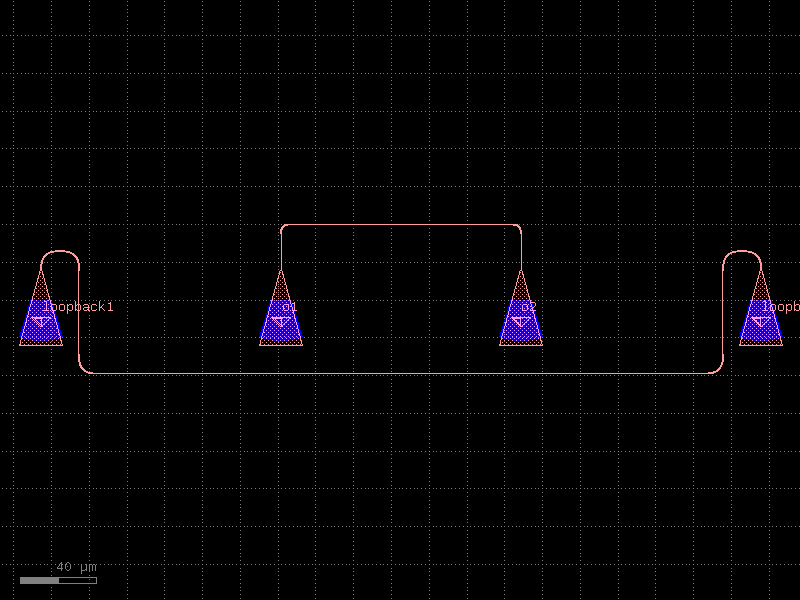
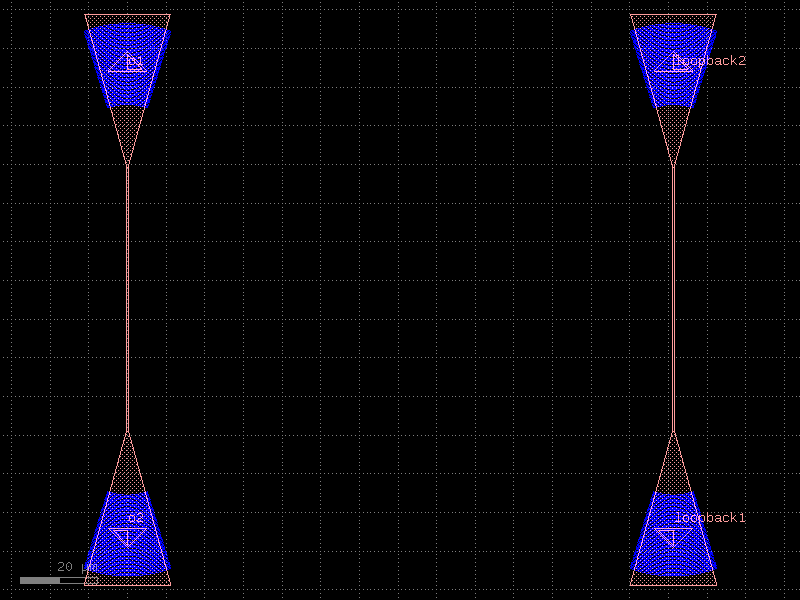
add_fiber_single#
- cspdk.si220.cband.cells.add_fiber_single(component='straight', grating_coupler='grating_coupler_elliptical', gc_port_name='o1', component_name=None, cross_section='strip', taper=None, input_port_names=None, pitch=70, with_loopback=True, loopback_spacing=100.0, **kwargs)[source]#
Returns component with south routes and grating_couplers.
You can also use pads or other terminations instead of grating couplers.
- Parameters:
component (str | Callable[[...], Component] | dict[str, Any] | DKCell | partial[Component]) – component spec to connect to grating couplers.
grating_coupler – spec for route terminations.
gc_port_name (str) – grating coupler input port name.
component_name (str | None) – optional for the label.
cross_section (CrossSection | str | dict[str, Any] | Callable[[...], CrossSection] | SymmetricalCrossSection | DCrossSection) – cross_section function.
taper (str | Callable[[...], Component] | dict[str, Any] | DKCell | partial[Component] | None) – taper spec.
input_port_names (list[str] | tuple[str, ...] | None) – list of input port names to connect to grating couplers.
pitch (float) – spacing between fibers.
with_loopback (bool) – adds loopback structures.
loopback_spacing (float) – spacing between loopback and test structure.
kwargs – additional arguments.
- Keyword Arguments:
bend – bend spec.
straight – straight spec.
fanout_length – if None, automatic calculation of fanout length.
max_y0_optical – in um.
with_loopback – True, adds loopback structures.
straight_separation – from edge to edge.
list_port_labels – None, adds TM labels to port indices in this list.
connected_port_list_ids – names of ports only for type 0 optical routing.
nb_optical_ports_lines – number of grating coupler lines.
force_manhattan – False
excluded_ports – list of port names to exclude when adding gratings.
grating_indices – list of grating coupler indices.
routing_straight – function to route.
routing_method – route_single.
optical_routing_type – None: auto, 0: no extension, 1: standard, 2: check.
gc_rotation – fiber coupler rotation in degrees. Defaults to -90.
input_port_indexes – to connect.
- Return type:
Component
import gdsfactory as gf c = gf.components.crossing() cc = gf.routing.add_fiber_array( component=c, optical_routing_type=2, grating_coupler=gf.components.grating_coupler_elliptical_te, with_loopback=False ) cc.plot()
import cspdk
c = cspdk.si220.cband.cells.add_fiber_single(component='straight', grating_coupler='grating_coupler_elliptical', gc_port_name='o1', cross_section='strip', pitch=70, with_loopback=True, loopback_spacing=100.0).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
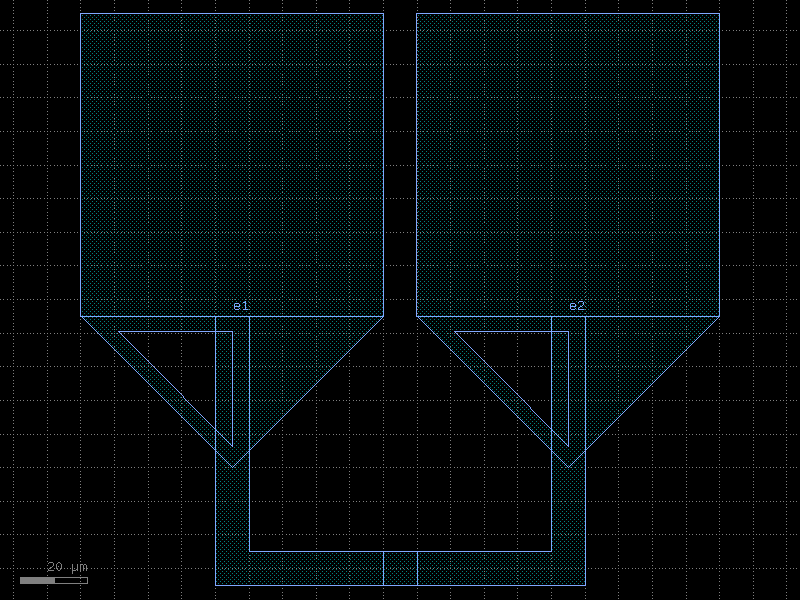
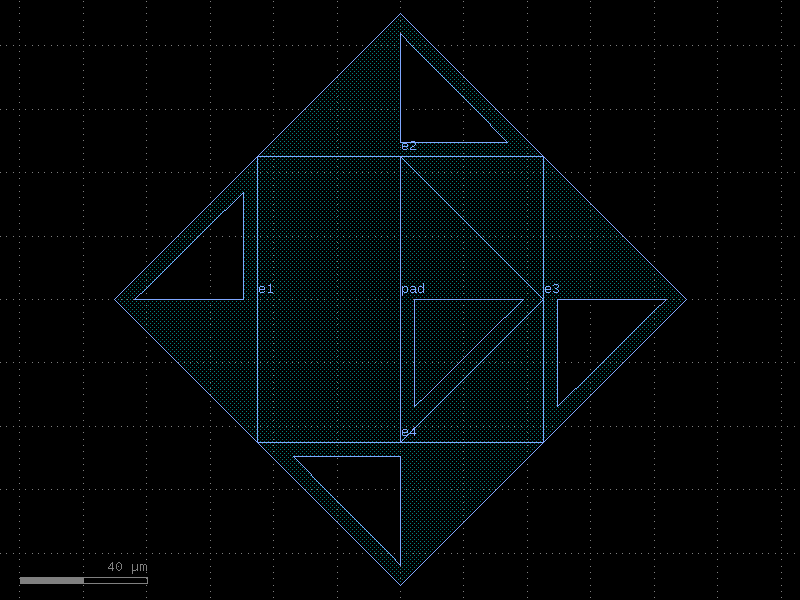
add_pads_top#
- cspdk.si220.cband.cells.add_pads_top(component='straight_metal', port_names=None, component_name=None, cross_section='metal_routing', pad_port_name='e1', pad='pad', bend='wire_corner', straight_separation=15.0, pad_pitch=100.0, taper=None, port_type='electrical', allow_width_mismatch=True, fanout_length=80, route_width=0, **kwargs)[source]#
Returns new component with ports connected top pads.
- Parameters:
component (str | Callable[[...], Component] | dict[str, Any] | DKCell | partial[Component]) – component spec to connect to.
port_names (Sequence[str] | None) – list of port names to connect to pads.
component_name (str | None) – optional for the label.
cross_section (CrossSection | str | dict[str, Any] | Callable[[...], CrossSection] | SymmetricalCrossSection | DCrossSection) – cross_section function.
pad_port_name (str) – pad port name.
pad (str | Callable[[...], Component] | dict[str, Any] | DKCell | partial[Component]) – pad function.
bend (str | Callable[[...], Component] | dict[str, Any] | DKCell | partial[Component]) – bend function.
straight_separation (float) – from edge to edge.
pad_pitch (float) – spacing between pads.
taper (str | Callable[[...], Component] | dict[str, Any] | DKCell | partial[Component] | None) – taper function.
port_type (str) – port type.
allow_width_mismatch (bool) – if True, allows width mismatch.
fanout_length (float | None) – length of the fanout.
route_width (float | list[float]) – width of the route.
kwargs – additional arguments.
- Return type:
Component
import gdsfactory as gf c = gf.c.nxn( xsize=600, ysize=200, north=2, south=3, wg_width=10, layer="M3", port_type="electrical", ) cc = gf.routing.add_pads_top(component=c, port_names=("e1", "e4"), fanout_length=50) cc.plot()
import cspdk
c = cspdk.si220.cband.cells.add_pads_top(component='straight_metal', cross_section='metal_routing', pad_port_name='e1', pad='pad', bend='wire_corner', straight_separation=15.0, pad_pitch=100.0, port_type='electrical', allow_width_mismatch=True, fanout_length=80, route_width=0).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
bend_euler#
- cspdk.si220.cband.cells.bend_euler(radius=None, angle=90, p=0.5, width=None, cross_section='strip', allow_min_radius_violation=False)[source]#
Regular degree euler bend.
- Parameters:
radius (float | None) – in um. Defaults to cross_section_radius.
angle (float) – total angle of the curve.
p (float) – Proportion of the curve that is an Euler curve.
width (float | None) – width to use. Defaults to cross_section.width.
cross_section (CrossSection | str | dict[str, Any] | Callable[[...], CrossSection] | SymmetricalCrossSection | DCrossSection) – specification (CrossSection, string, CrossSectionFactory dict).
allow_min_radius_violation (bool) – if True allows radius to be smaller than cross_section radius.
- Return type:
Component
import cspdk
c = cspdk.si220.cband.cells.bend_euler(angle=90, p=0.5, cross_section='strip', allow_min_radius_violation=False).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
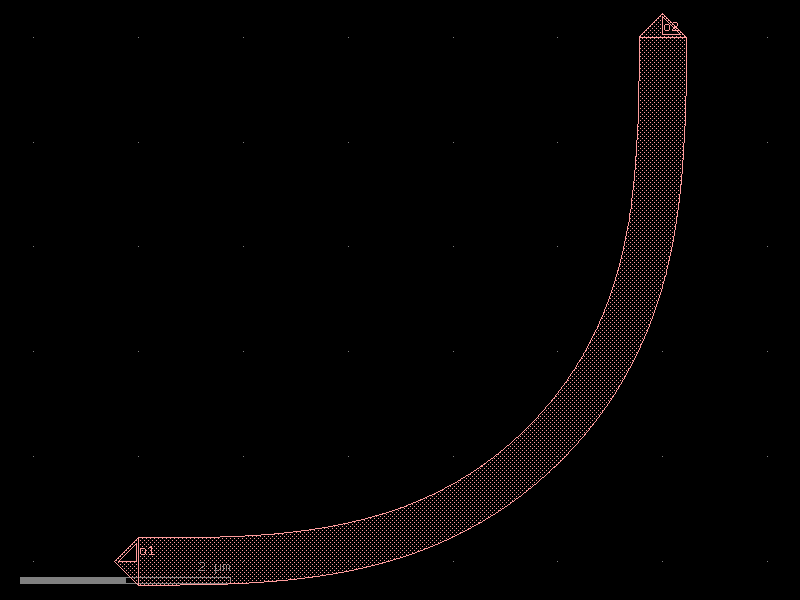
bend_metal#
- cspdk.si220.cband.cells.bend_metal(radius=None, angle=90, width=None, cross_section='metal_routing')[source]#
Regular degree euler bend.
- Parameters:
radius (float | None)
angle (float)
width (float | None)
cross_section (CrossSection | str | dict[str, Any] | Callable[[...], CrossSection] | SymmetricalCrossSection | DCrossSection)
- Return type:
Component
import cspdk
c = cspdk.si220.cband.cells.bend_metal(angle=90, cross_section='metal_routing').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
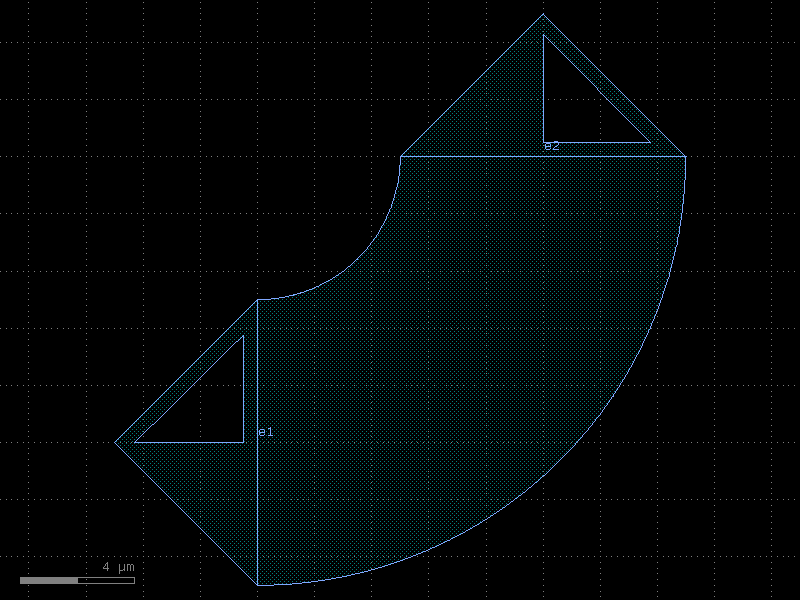
bend_s#
- cspdk.si220.cband.cells.bend_s(size=(11, 1.8), cross_section='strip', width=None, allow_min_radius_violation=False)[source]#
Return S bend with bezier curve.
stores min_bend_radius property in self.info[‘min_bend_radius’] min_bend_radius depends on height and length
- Parameters:
size (tuple[float, float]) – in x and y direction.
cross_section (CrossSection | str | dict[str, Any] | Callable[[...], CrossSection] | SymmetricalCrossSection | DCrossSection) – spec.
width (float | None) – width of the waveguide. If None, it will use the width of the cross_section.
allow_min_radius_violation (bool) – allows min radius violations.
- Return type:
Component
import cspdk
c = cspdk.si220.cband.cells.bend_s(size=(11, 1.8), cross_section='strip', allow_min_radius_violation=False).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
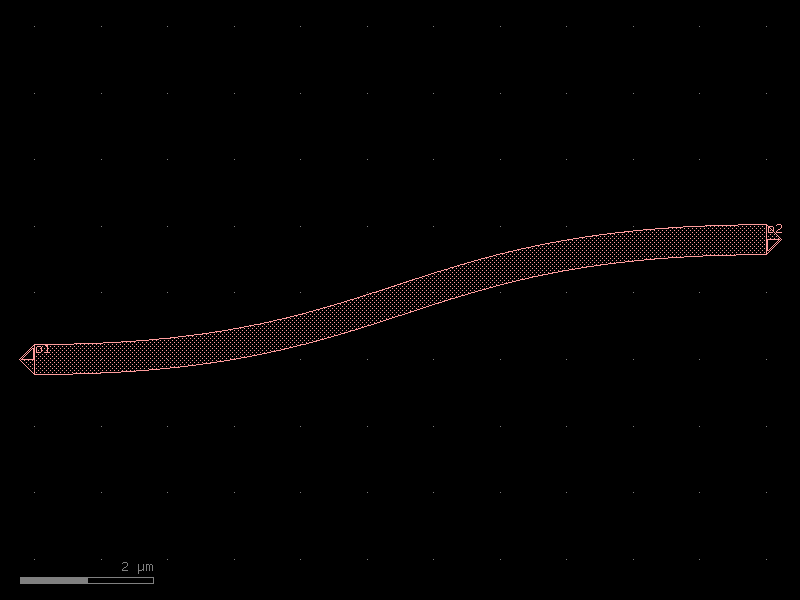

bend_s_metal#
- cspdk.si220.cband.cells.bend_s_metal(size=(11, 1.8), cross_section='metal_routing', width=None, allow_min_radius_violation=True)[source]#
Return S bend with bezier curve.
stores min_bend_radius property in self.info[‘min_bend_radius’] min_bend_radius depends on height and length
- Parameters:
size (tuple[float, float]) – in x and y direction.
cross_section (CrossSection | str | dict[str, Any] | Callable[[...], CrossSection] | SymmetricalCrossSection | DCrossSection) – spec.
width (float | None) – width of the waveguide. If None, it will use the width of the cross_section.
allow_min_radius_violation (bool) – allows min radius violations.
- Return type:
Component
import cspdk
c = cspdk.si220.cband.cells.bend_s_metal(size=(11, 1.8), cross_section='metal_routing', allow_min_radius_violation=True).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
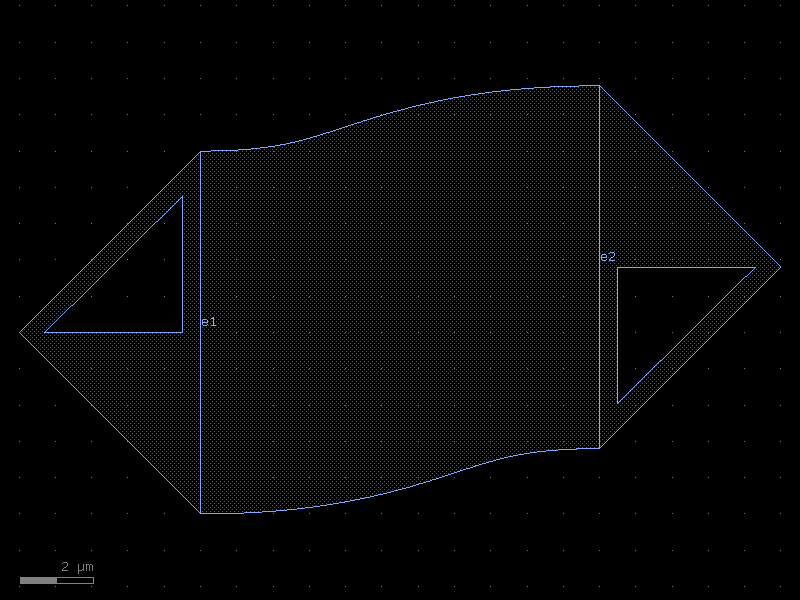
compass#
- cspdk.si220.cband.cells.compass(size=(4, 2), layer='PAD', port_type=None, port_inclusion=0.0, port_orientations=(180, 90, 0, -90), auto_rename_ports=True)[source]#
Rectangle with ports on each edge (north, south, east, and west).
- Parameters:
size (tuple[float, float]) – rectangle size.
layer (tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum) – tuple (int, int).
port_type (str | None) – optical, electrical.
port_inclusion (float) – from edge.
port_orientations (tuple[int, ...] | list[int] | None) – list of port_orientations to add. None does not add ports.
auto_rename_ports (bool) – auto rename ports.
- Return type:
Component
import cspdk
c = cspdk.si220.cband.cells.compass(size=(4, 2), layer='PAD', port_inclusion=0.0, port_orientations=(180, 90, 0, -90), auto_rename_ports=True).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)

coupler#
- cspdk.si220.cband.cells.coupler(length=14.5, gap=0.27)[source]#
Returns Symmetric coupler.
- Parameters:
length (float) – of coupling region in um.
gap (float) – of coupling region in um.
- Return type:
Component
import cspdk
c = cspdk.si220.cband.cells.coupler(length=14.5, gap=0.27).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
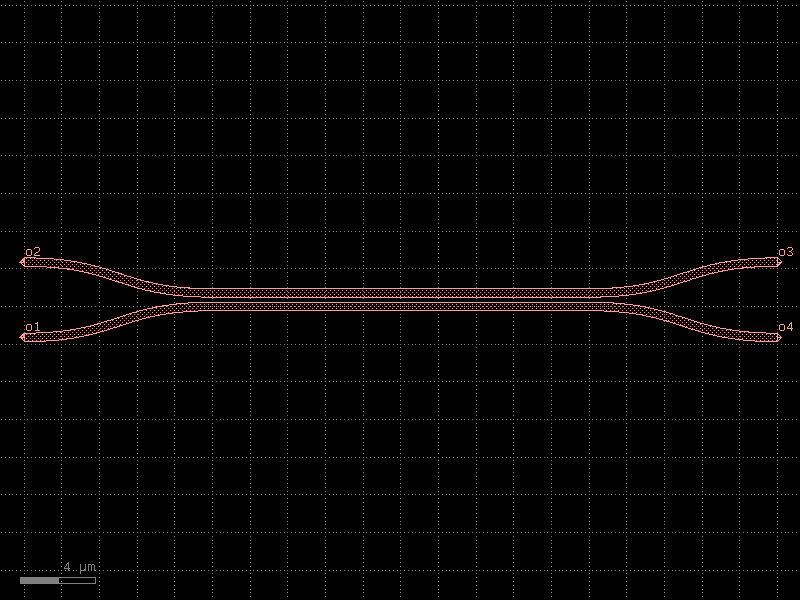
coupler_rib#
- cspdk.si220.cband.cells.coupler_rib(length=20, gap=0.27)[source]#
Returns Symmetric coupler.
- Parameters:
length (float) – of coupling region in um.
gap (float) – of coupling region in um.
- Return type:
Component
import cspdk
c = cspdk.si220.cband.cells.coupler_rib(length=20, gap=0.27).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
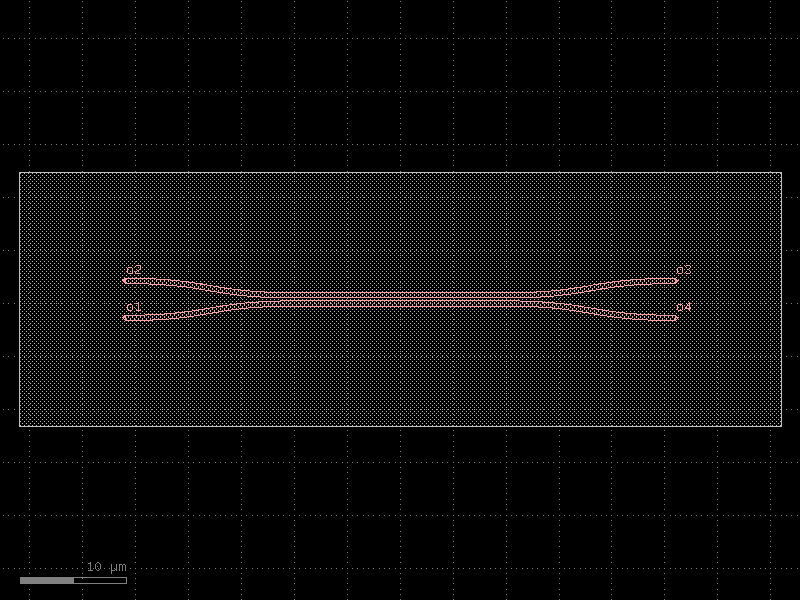
coupler_ring#
- cspdk.si220.cband.cells.coupler_ring(length_x=4, gap=0.27, radius=5, bend='bend_euler', straight='straight', cross_section='strip', length_extension=10)[source]#
Returns Coupler for ring.
- Parameters:
length_x (float) – length of the parallel coupled straight waveguides.
gap (float) – gap between for coupler.
radius (float) – for the bend and coupler.
bend (str | Callable[[...], Component] | dict[str, Any] | DKCell | partial[Component]) – 90 degrees bend spec.
straight (str | Callable[[...], Component] | dict[str, Any] | DKCell | partial[Component]) – straight spec.
cross_section (str) – cross_section spec.
length_extension (float) – length extension for the coupler.
- Return type:
Component
import cspdk
c = cspdk.si220.cband.cells.coupler_ring(length_x=4, gap=0.27, radius=5, bend='bend_euler', straight='straight', cross_section='strip', length_extension=10).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
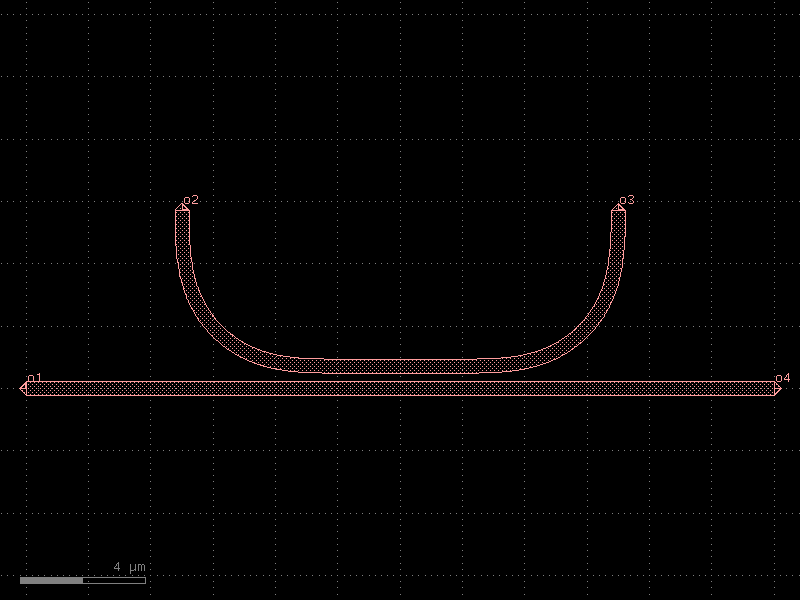
crossing#
- cspdk.si220.cband.cells.crossing()[source]#
SOI220nm_1550nm_TE_STRIP_Waveguide_Crossing fixed cell.
- Return type:
Component
import cspdk
c = cspdk.si220.cband.cells.crossing().copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
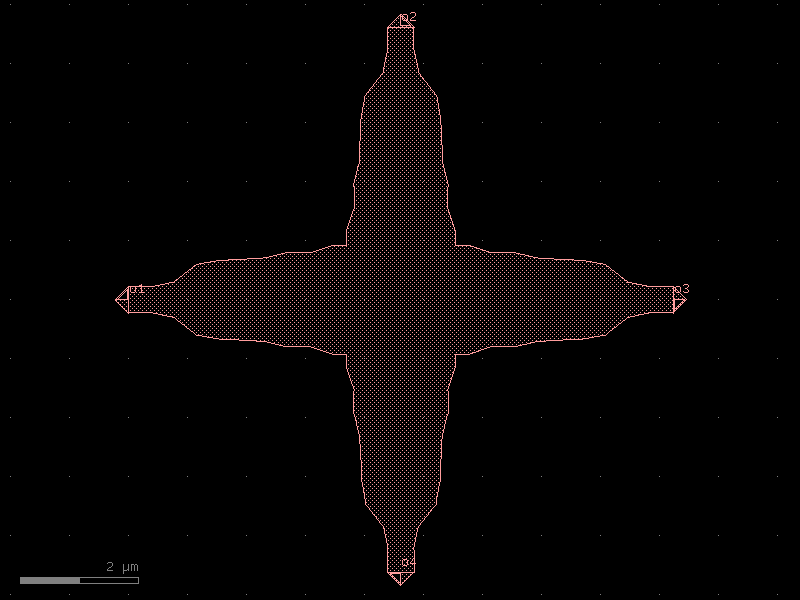

crossing_rib#
- cspdk.si220.cband.cells.crossing_rib()[source]#
SOI220nm_1550nm_TE_RIB_Waveguide_Crossing fixed cell.
- Return type:
Component
import cspdk
c = cspdk.si220.cband.cells.crossing_rib().copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
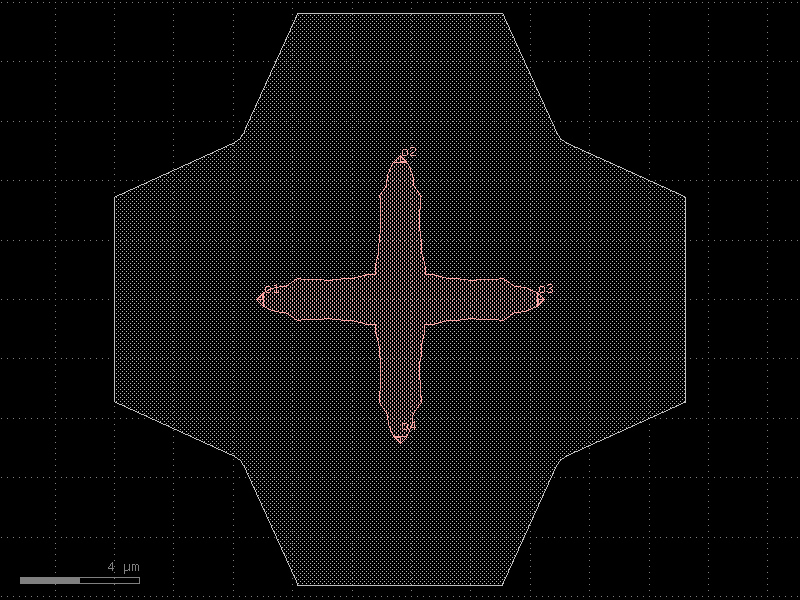
die#
- cspdk.si220.cband.cells.die(size=(16000.0, 3000.0))[source]#
A die.
- Parameters:
size (tuple[float, float])
- Return type:
Component
import cspdk
c = cspdk.si220.cband.cells.die(size=(16000.0, 3000.0)).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)

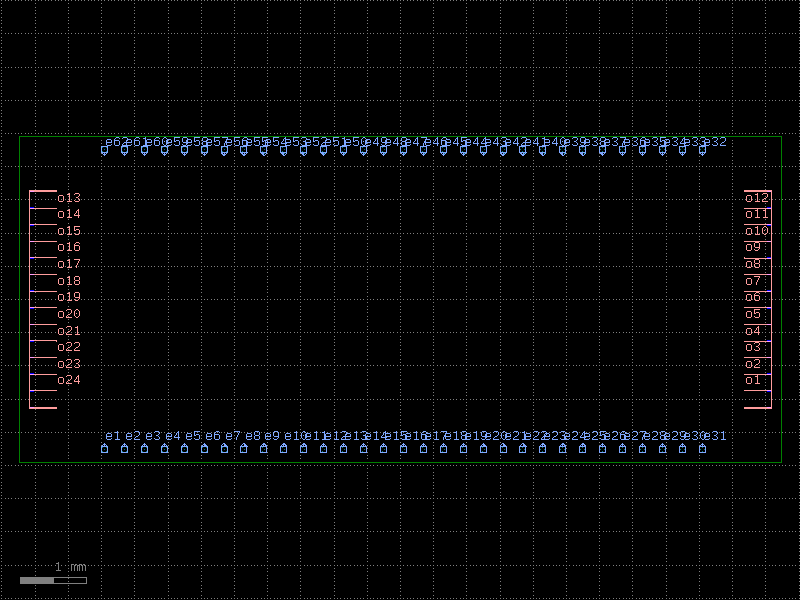
die_with_pads#
- cspdk.si220.cband.cells.die_with_pads(size=(11470.0, 4900.0), ngratings=14, npads=31, grating_pitch=250.0, pad_pitch=300.0, grating_coupler='grating_coupler_rectangular', cross_section='strip', pad='pad', layer_floorplan='FLOORPLAN', edge_to_pad_distance=150.0, edge_to_grating_distance=150.0, with_loopback=True)[source]#
A die with grating couplers and pads.
- Parameters:
size (tuple[float, float]) – the size of the die, in um.
ngratings (int) – the number of grating couplers.
npads (int) – the number of pads.
grating_pitch (float) – the pitch of the grating couplers, in um.
pad_pitch (float) – the pitch of the pads, in um.
grating_coupler (str | Callable[[...], Component] | dict[str, Any] | DKCell | partial[Component] | None) – the grating coupler component. None skips the grating couplers.
cross_section (CrossSection | str | dict[str, Any] | Callable[[...], CrossSection] | SymmetricalCrossSection | DCrossSection) – the cross section.
pad (str | Callable[[...], Component] | dict[str, Any] | DKCell | partial[Component]) – the pad component.
layer_floorplan (tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum) – the layer of the floorplan.
edge_to_pad_distance (float) – the distance from the edge to the pads, in um.
edge_to_grating_distance (float) – the distance from the edge to the grating couplers, in um.
with_loopback (bool) – if True, adds a loopback between edge GCs. Only works for rotation = 90 for now.
- Return type:
Component
import cspdk
c = cspdk.si220.cband.cells.die_with_pads(size=(11470.0, 4900.0), ngratings=14, npads=31, grating_pitch=250.0, pad_pitch=300.0, grating_coupler='grating_coupler_rectangular', cross_section='strip', pad='pad', layer_floorplan='FLOORPLAN', edge_to_pad_distance=150.0, edge_to_grating_distance=150.0, with_loopback=True).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
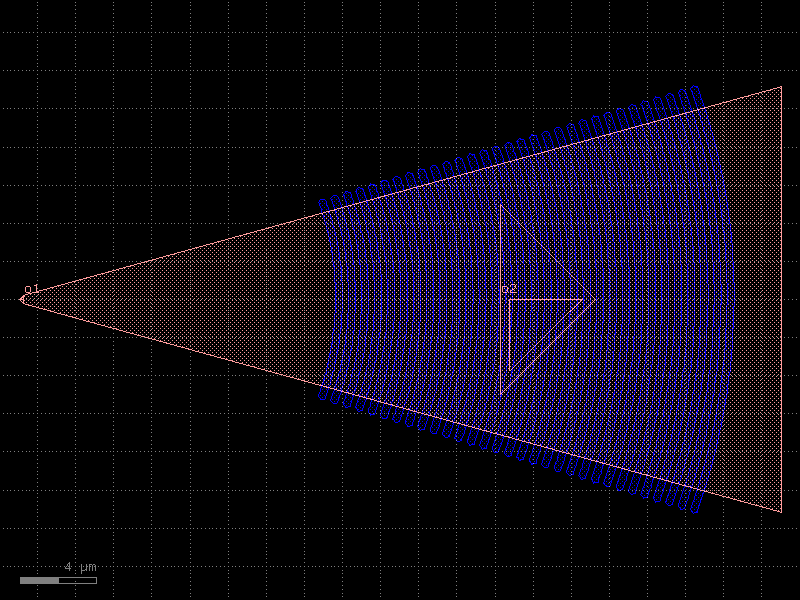
grating_coupler_elliptical#
- cspdk.si220.cband.cells.grating_coupler_elliptical(wavelength=1.55, grating_line_width=0.315, cross_section='strip')[source]#
A grating coupler with curved but parallel teeth.
- Parameters:
wavelength (float) – the center wavelength for which the grating is designed
grating_line_width – the line width of the grating
cross_section – a cross section or its name or a function generating a cross section.
- Return type:
Component
import cspdk
c = cspdk.si220.cband.cells.grating_coupler_elliptical(wavelength=1.55, grating_line_width=0.315, cross_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
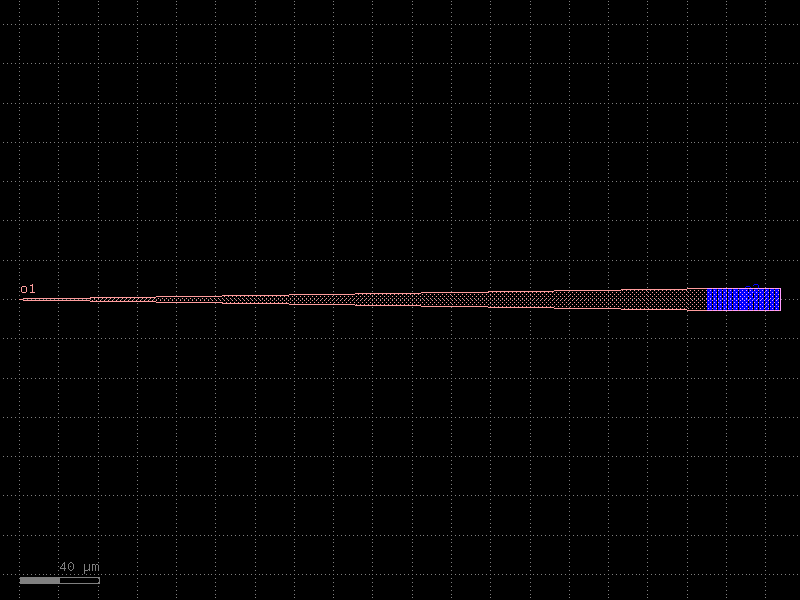
grating_coupler_rectangular#
- cspdk.si220.cband.cells.grating_coupler_rectangular(period=0.63, n_periods=60, length_taper=350.0, wavelength=1.55, cross_section='strip')[source]#
A grating coupler with straight and parallel teeth.
- Parameters:
period – the period of the grating
n_periods (int) – the number of grating teeth
length_taper (float) – the length of the taper tapering up to the grating
wavelength (float) – the center wavelength for which the grating is designed
cross_section – a cross section or its name or a function generating a cross section.
- Return type:
Component
import cspdk
c = cspdk.si220.cband.cells.grating_coupler_rectangular(period=0.63, n_periods=60, length_taper=350.0, wavelength=1.55, cross_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
grating_coupler_rectangular_rib#
- cspdk.si220.cband.cells.grating_coupler_rectangular_rib(*, period=0.5, n_periods=60, length_taper=350.0, wavelength=1.55, cross_section='rib')#
A grating coupler with straight and parallel teeth.
- Parameters:
period – the period of the grating
n_periods (int) – the number of grating teeth
length_taper (float) – the length of the taper tapering up to the grating
wavelength (float) – the center wavelength for which the grating is designed
cross_section – a cross section or its name or a function generating a cross section.
- Return type:
Component
import cspdk
c = cspdk.si220.cband.cells.grating_coupler_rectangular_rib(period=0.5, n_periods=60, length_taper=350.0, wavelength=1.55, cross_section='rib').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
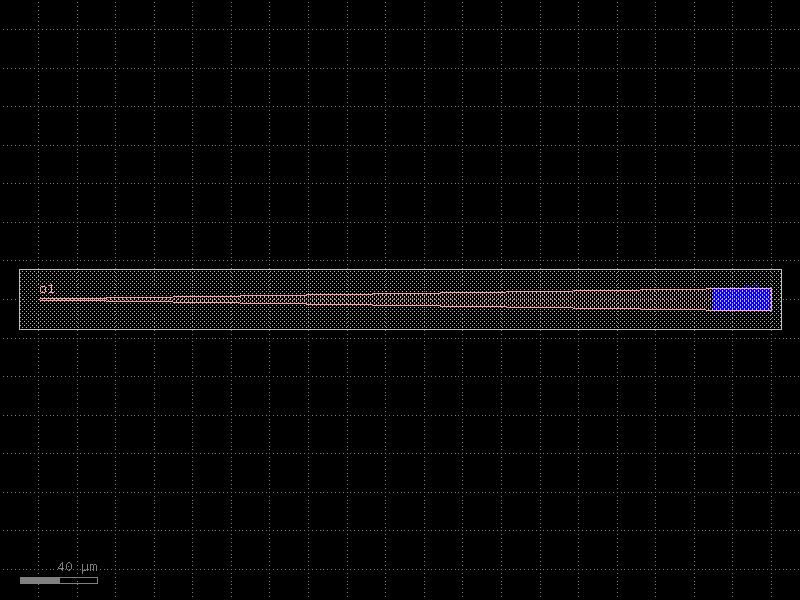

heater#
import cspdk
c = cspdk.si220.cband.cells.heater().copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
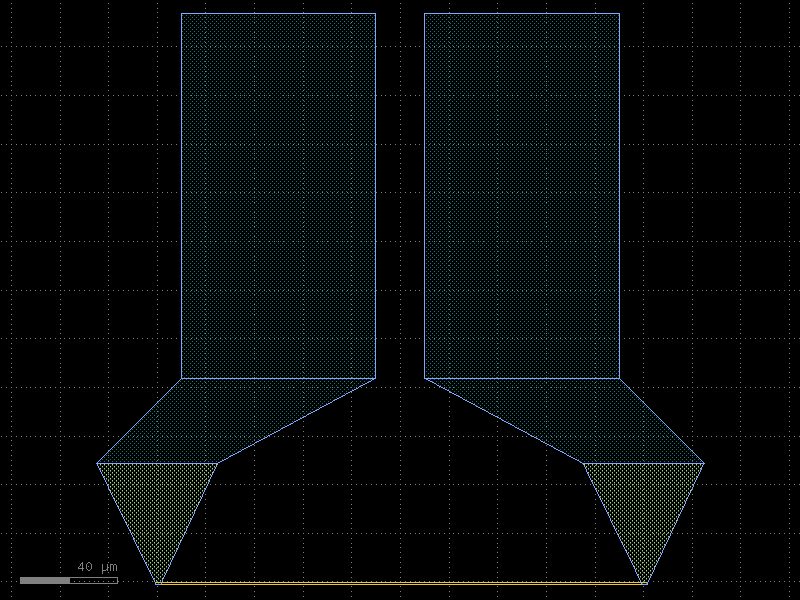
mmi1x2#
- cspdk.si220.cband.cells.mmi1x2(width=None, width_taper=1.5, length_taper=20.0, length_mmi=31.0, width_mmi=6.0, gap_mmi=1.64, cross_section='strip')[source]#
An mmi1x2.
An mmi1x2 is a splitter that splits a single input to two outputs
- Parameters:
width (float | None) – the width of the waveguides connecting at the mmi ports.
width_taper (float) – the width at the base of the mmi body.
length_taper (float) – the length of the tapers going towards the mmi body.
length_mmi (float) – the length of the mmi body.
width_mmi (float) – the width of the mmi body.
gap_mmi (float) – the gap between the tapers at the mmi body.
cross_section (CrossSection | str | dict[str, Any] | Callable[[...], CrossSection] | SymmetricalCrossSection | DCrossSection) – a cross section or its name or a function generating a cross section.
- Return type:
Component
import cspdk
c = cspdk.si220.cband.cells.mmi1x2(width_taper=1.5, length_taper=20.0, length_mmi=31.0, width_mmi=6.0, gap_mmi=1.64, cross_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
mmi1x2_rib#
- cspdk.si220.cband.cells.mmi1x2_rib(width=None, width_taper=1.5, length_taper=20.0, *, length_mmi=32.7, width_mmi=6.0, gap_mmi=1.64, cross_section='rib')#
An mmi1x2.
An mmi1x2 is a splitter that splits a single input to two outputs
- Parameters:
width (float | None) – the width of the waveguides connecting at the mmi ports.
width_taper (float) – the width at the base of the mmi body.
length_taper (float) – the length of the tapers going towards the mmi body.
length_mmi (float) – the length of the mmi body.
width_mmi (float) – the width of the mmi body.
gap_mmi (float) – the gap between the tapers at the mmi body.
cross_section (CrossSection | str | dict[str, Any] | Callable[[...], CrossSection] | SymmetricalCrossSection | DCrossSection) – a cross section or its name or a function generating a cross section.
- Return type:
Component
import cspdk
c = cspdk.si220.cband.cells.mmi1x2_rib(width_taper=1.5, length_taper=20.0, length_mmi=32.7, width_mmi=6.0, gap_mmi=1.64, cross_section='rib').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
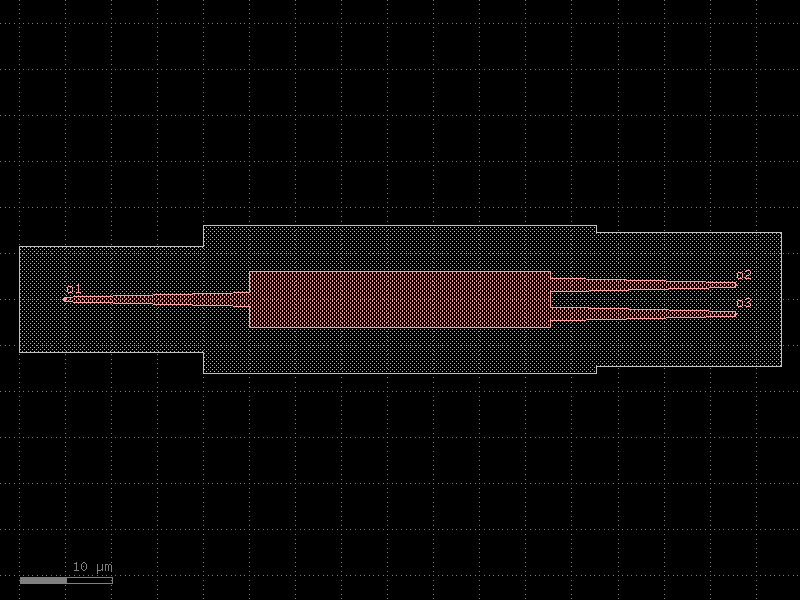
mmi2x2#
- cspdk.si220.cband.cells.mmi2x2(width=None, width_taper=1.5, length_taper=20.0, length_mmi=42.5, width_mmi=6.0, gap_mmi=0.5, cross_section='strip')[source]#
An mmi2x2.
An mmi2x2 is a 2x2 splitter
- Parameters:
width (float | None) – the width of the waveguides connecting at the mmi ports
width_taper (float) – the width at the base of the mmi body
length_taper (float) – the length of the tapers going towards the mmi body
length_mmi (float) – the length of the mmi body
width_mmi (float) – the width of the mmi body
gap_mmi (float) – the gap between the tapers at the mmi body
cross_section (CrossSection | str | dict[str, Any] | Callable[[...], CrossSection] | SymmetricalCrossSection | DCrossSection) – a cross section or its name or a function generating a cross section.
- Return type:
Component
import cspdk
c = cspdk.si220.cband.cells.mmi2x2(width_taper=1.5, length_taper=20.0, length_mmi=42.5, width_mmi=6.0, gap_mmi=0.5, cross_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
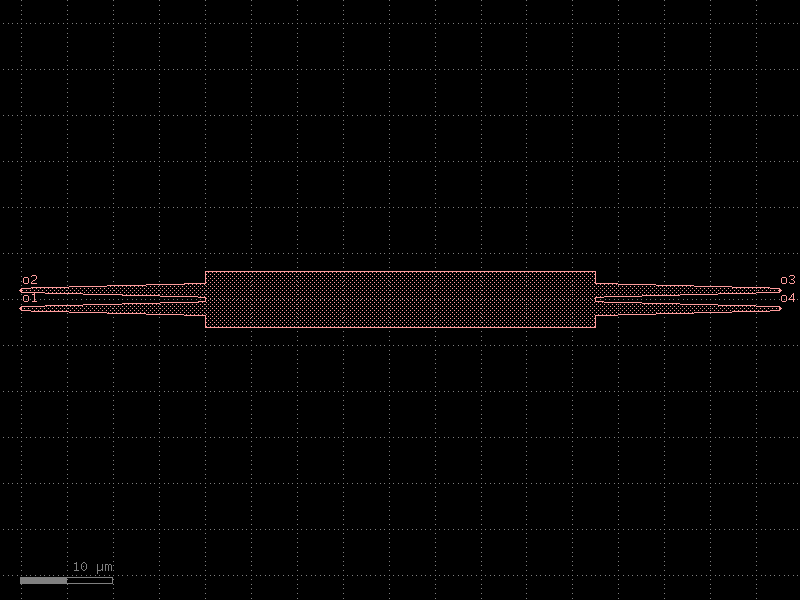
mmi2x2_rib#
- cspdk.si220.cband.cells.mmi2x2_rib(width=None, width_taper=1.5, length_taper=20.0, *, length_mmi=44.8, width_mmi=6.0, gap_mmi=0.53, cross_section='rib')#
An mmi2x2.
An mmi2x2 is a 2x2 splitter
- Parameters:
width (float | None) – the width of the waveguides connecting at the mmi ports
width_taper (float) – the width at the base of the mmi body
length_taper (float) – the length of the tapers going towards the mmi body
length_mmi (float) – the length of the mmi body
width_mmi (float) – the width of the mmi body
gap_mmi (float) – the gap between the tapers at the mmi body
cross_section (CrossSection | str | dict[str, Any] | Callable[[...], CrossSection] | SymmetricalCrossSection | DCrossSection) – a cross section or its name or a function generating a cross section.
- Return type:
Component
import cspdk
c = cspdk.si220.cband.cells.mmi2x2_rib(width_taper=1.5, length_taper=20.0, length_mmi=44.8, width_mmi=6.0, gap_mmi=0.53, cross_section='rib').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
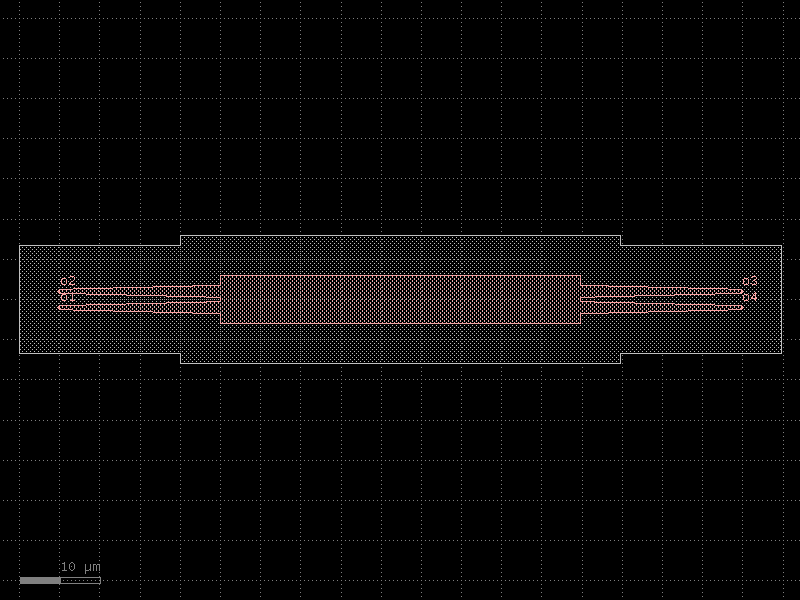
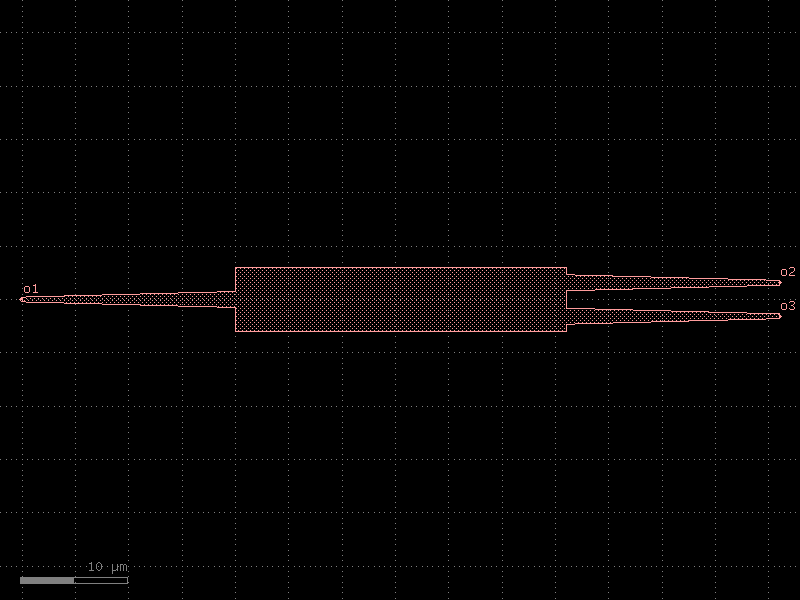
mzi#
- cspdk.si220.cband.cells.mzi(delta_length=10, bend='bend_euler', straight='straight', splitter='coupler', combiner=None, port_e1_splitter='o3', port_e0_splitter='o4', port_e1_combiner='o3', port_e0_combiner='o4', cross_section='strip')[source]#
Mzi.
- Parameters:
delta_length (float) – bottom arm vertical extra length.
bend (str | Callable[[...], Component] | dict[str, Any] | DKCell | partial[Component]) – 90 degrees bend library.
straight (str | Callable[[...], Component] | dict[str, Any] | DKCell | partial[Component]) – straight function.
splitter (str | Callable[[...], Component] | dict[str, Any] | DKCell | partial[Component]) – splitter function.
combiner (str | Callable[[...], Component] | dict[str, Any] | DKCell | partial[Component] | None) – combiner function.
port_e1_splitter (str) – east top splitter port.
port_e0_splitter (str) – east bot splitter port.
port_e1_combiner (str) – east top combiner port.
port_e0_combiner (str) – east bot combiner port.
cross_section (CrossSection | str | dict[str, Any] | Callable[[...], CrossSection] | SymmetricalCrossSection | DCrossSection) – for routing (sxtop/sxbot to combiner).
- Return type:
Component
import cspdk
c = cspdk.si220.cband.cells.mzi(delta_length=10, bend='bend_euler', straight='straight', splitter='coupler', port_e1_splitter='o3', port_e0_splitter='o4', port_e1_combiner='o3', port_e0_combiner='o4', cross_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
pack_doe#
- cspdk.si220.cband.cells.pack_doe(doe=None, settings=None, do_permutations=False, function=None, **kwargs)[source]#
Packs a component DOE (Design of Experiment) using pack.
- Parameters:
doe (ComponentSpec | None) – function to return Components.
settings (Mapping[str, Sequence[kf.typings.MetaData]] | None) – component settings.
do_permutations (bool) – for each setting.
function (CellSpec | None) – to apply (add padding, grating couplers).
kwargs (Any) – for pack.
- Keyword Arguments:
spacing – Minimum distance between adjacent shapes.
aspect_ratio – (width, height) ratio of the rectangular bin.
max_size – Limits the size into which the shapes will be packed.
sort_by_area – Pre-sorts the shapes by area.
density – Values closer to 1 pack tighter but require more computation.
precision – Desired precision for rounding vertex coordinates.
text – Optional function to add text labels.
text_prefix – for labels. For example. ‘A’ for ‘A1’, ‘A2’…
text_offsets – relative to component size info anchor. Defaults to center.
text_anchors – relative to component (ce cw nc ne nw sc se sw center cc).
name_prefix – for each packed component (avoids the Unnamed cells warning). Note that the suffix contains a uuid so the name will not be deterministic.
rotation – for each component in degrees.
h_mirror – horizontal mirror in y axis (x, 1) (1, 0). This is the most common.
v_mirror – vertical mirror using x axis (1, y) (0, y).
- Return type:
Component
import cspdk
c = cspdk.si220.cband.cells.pack_doe(do_permutations=False).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)

pack_doe_grid#
- cspdk.si220.cband.cells.pack_doe_grid(doe=None, settings=None, do_permutations=False, function=None, with_text=False, **kwargs)[source]#
Packs a component DOE (Design of Experiment) using grid.
- Parameters:
doe (ComponentSpec | None) – function to return Components.
settings (Mapping[str, Sequence[kf.typings.MetaData]] | None) – component settings.
do_permutations (bool) – for each setting.
function (CellSpec | None) – to apply to component (add padding, grating couplers).
with_text (bool) – includes text label.
kwargs (Any) – for grid.
- Keyword Arguments:
spacing – between adjacent elements on the grid, can be a tuple for
width. (different distances in height and)
separation – If True, guarantees elements are separated with fixed spacing
grid. (if False, elements are spaced evenly along a)
shape – x, y shape of the grid (see np.reshape).
with (If no shape and the list is 1D, if np.reshape were run)
align_x – {‘x’, ‘xmin’, ‘xmax’} for x (column) alignment along.
align_y – {‘y’, ‘ymin’, ‘ymax’} for y (row) alignment along.
edge_x – {‘x’, ‘xmin’, ‘xmax’} for x (column) (ignored if separation = True).
edge_y – {‘y’, ‘ymin’, ‘ymax’} for y (row) (ignored if separation = True).
rotation – for each component in degrees.
h_mirror – horizontal mirror y axis (x, 1) (1, 0). most common mirror.
v_mirror – vertical mirror using x axis (1, y) (0, y).
- Return type:
Component
import cspdk
c = cspdk.si220.cband.cells.pack_doe_grid(do_permutations=False, with_text=False).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)

pad#
- cspdk.si220.cband.cells.pad(size=(90.0, 90.0), layer='PAD', port_inclusion=0, port_orientation=0)[source]#
Returns rectangular pad with ports.
- Parameters:
size (tuple[float, float]) – x, y size.
layer (tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum) – pad layer.
bbox_layers – list of layers.
bbox_offsets – Optional offsets for each layer with respect to size. positive grows, negative shrinks the size.
port_inclusion (float) – from edge.
port_orientation (float) – in degrees.
- Return type:
Component
import cspdk
c = cspdk.si220.cband.cells.pad(size=(90.0, 90.0), layer='PAD', port_inclusion=0, port_orientation=0).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
rectangle#
- cspdk.si220.cband.cells.rectangle(size=(4, 2), layer='PAD', centered=False, port_type=None, port_orientations=(180, 90, 0, -90))[source]#
Returns a rectangle.
- Parameters:
size (tuple[float, float]) – (tuple) Width and height of rectangle.
layer (tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum) – Specific layer to put polygon geometry on.
centered (bool) – True sets center to (0, 0), False sets south-west to (0, 0).
port_type (str | None) – optical, electrical.
port_orientations (tuple[int, ...] | list[int] | None) – list of port_orientations to add. None adds no ports.
- Return type:
Component
import cspdk
c = cspdk.si220.cband.cells.rectangle(size=(4, 2), layer='PAD', centered=False, port_orientations=(180, 90, 0, -90)).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
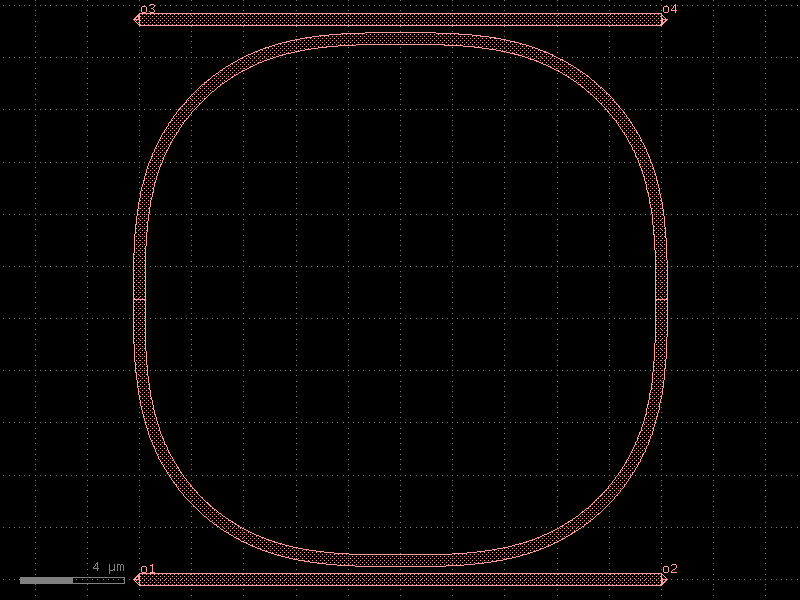
ring_double#
- cspdk.si220.cband.cells.ring_double(gap=0.27, gap_top=None, gap_bot=None, radius=10.0, length_x=0.01, length_y=0.01, cross_section='strip', length_extension=10.0)[source]#
Returns a double bus ring.
two couplers (ct: top, cb: bottom) connected with two vertical straights (sl: left, sr: right)
- Parameters:
gap (float) – gap between for coupler.
gap_top (float | None) – gap for the top coupler. Defaults to gap.
gap_bot (float | None) – gap for the bottom coupler. Defaults to gap.
radius (float) – for the bend and coupler.
length_x (float) – ring coupler length.
length_y (float) – vertical straight length.
bend – 90 degrees bend spec.
straight – straight spec.
coupler_ring – ring coupler spec.
coupler_ring_top – top ring coupler spec. Defaults to coupler_ring.
cross_section (CrossSection | str | dict[str, Any] | Callable[[...], CrossSection] | SymmetricalCrossSection | DCrossSection) – cross_section spec.
length_extension (float) – straight length extension at the end of the coupler bottom ports.
- Return type:
Component
import cspdk
c = cspdk.si220.cband.cells.ring_double(gap=0.27, radius=10.0, length_x=0.01, length_y=0.01, cross_section='strip', length_extension=10.0).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
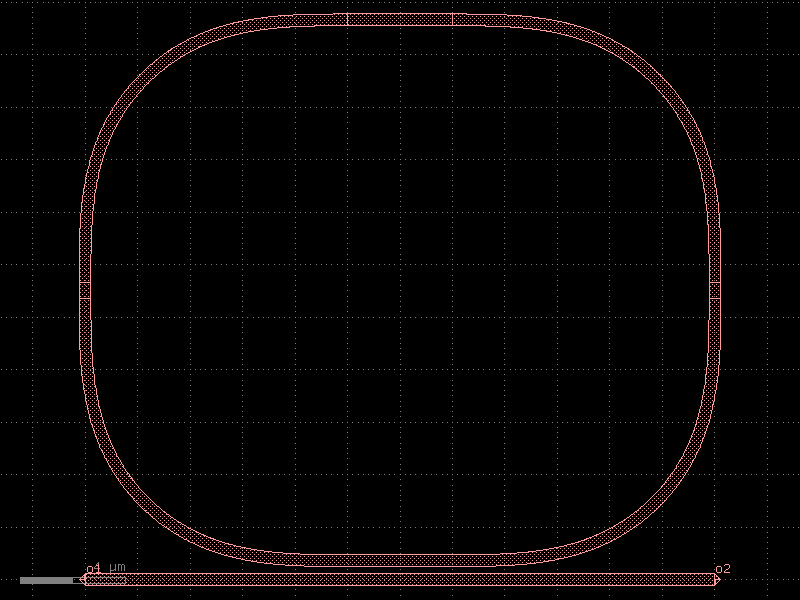
ring_single#
- cspdk.si220.cband.cells.ring_single(gap=0.27, radius=10.0, length_x=4.0, length_y=0.6, cross_section='strip', length_extension=10.0)[source]#
Returns a single ring.
ring coupler (cb: bottom) connects to two vertical straights (sl: left, sr: right), two bends (bl, br) and horizontal straight (wg: top)
- Parameters:
gap (float) – gap between for coupler.
radius (float) – for the bend and coupler.
length_x (float) – ring coupler length.
length_y (float) – vertical straight length.
coupler_ring – ring coupler spec.
bend – 90 degrees bend spec.
straight – straight spec.
coupler_ring – ring coupler spec.
cross_section (CrossSection | str | dict[str, Any] | Callable[[...], CrossSection] | SymmetricalCrossSection | DCrossSection) – cross_section spec.
length_extension (float) – straight length extension at the end of the coupler bottom ports.
- Return type:
Component
xxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxx xxxx xxx xxx xxx xxx xx xxx x xxx xx xx▲ xx xx│length_y xx xx▼ xx xx xx length_x x xx ◄───────────────► x xx xxx xx xxx xxx──────▲─────────xxx │gap o1──────▼─────────o2
import cspdk
c = cspdk.si220.cband.cells.ring_single(gap=0.27, radius=10.0, length_x=4.0, length_y=0.6, cross_section='strip', length_extension=10.0).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
spiral#
- cspdk.si220.cband.cells.spiral(length=100, cross_section='strip', spacing=3, n_loops=6)[source]#
Returns a spiral double (spiral in, and then out).
- Parameters:
length (float) – length of the spiral straight section.
cross_section (CrossSection | str | dict[str, Any] | Callable[[...], CrossSection] | SymmetricalCrossSection | DCrossSection) – cross_section component.
spacing (float) – spacing between the spiral loops.
n_loops (int) – number of loops.
- Return type:
Component
import cspdk
c = cspdk.si220.cband.cells.spiral(length=100, cross_section='strip', spacing=3, n_loops=6).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
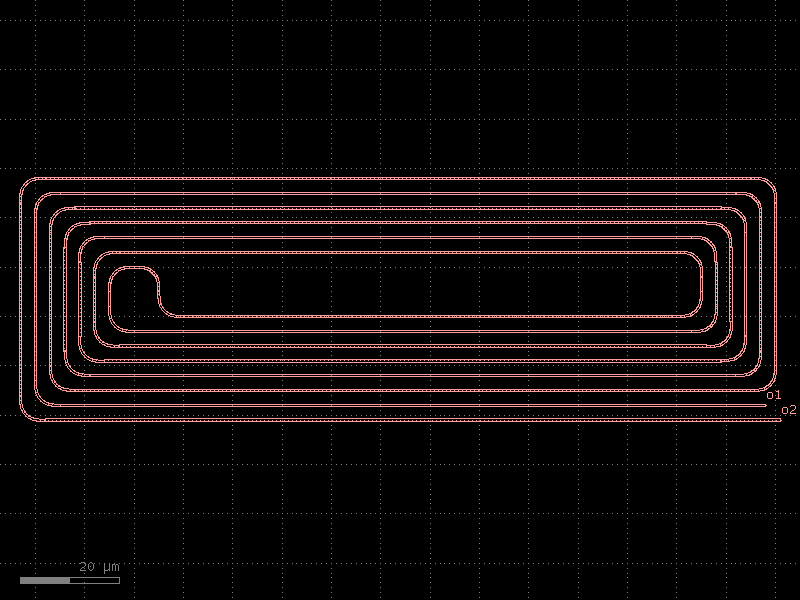
spiral_racetrack#
- cspdk.si220.cband.cells.spiral_racetrack(min_radius=None, straight_length=20.0, spacings=(2, 2, 3, 3, 2, 2), straight='straight', bend='bend_euler', bend_s='bend_s', cross_section='strip', cross_section_s=None, extra_90_deg_bend=False, allow_min_radius_violation=False)[source]#
Returns Racetrack-Spiral.
- Parameters:
min_radius (float | None) – smallest radius in um.
straight_length (float) – length of the straight segments in um.
spacings (Sequence[float]) – space between the center of neighboring waveguides in um.
straight (str | Callable[[...], Component] | dict[str, Any] | DKCell | partial[Component]) – factory to generate the straight segments.
bend (str | Callable[[...], Component] | dict[str, Any] | DKCell | partial[Component]) – factory to generate the bend segments.
bend_s (str | Callable[[...], Component] | dict[str, Any] | DKCell | partial[Component]) – factory to generate the s-bend segments.
cross_section (CrossSection | str | dict[str, Any] | Callable[[...], CrossSection] | SymmetricalCrossSection | DCrossSection) – cross-section of the waveguides.
cross_section_s (CrossSection | str | dict[str, Any] | Callable[[...], CrossSection] | SymmetricalCrossSection | DCrossSection | None) – cross-section of the s bend waveguide (optional).
extra_90_deg_bend (bool) – if True, we add an additional straight + 90 degree bent at the output, so the output port is looking down.
allow_min_radius_violation (bool) – if True, will allow the s-bend to have a smaller radius than the minimum radius.
- Return type:
Component
import cspdk
c = cspdk.si220.cband.cells.spiral_racetrack(straight_length=20.0, spacings=(2, 2, 3, 3, 2, 2), straight='straight', bend='bend_euler', bend_s='bend_s', cross_section='strip', extra_90_deg_bend=False, allow_min_radius_violation=False).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
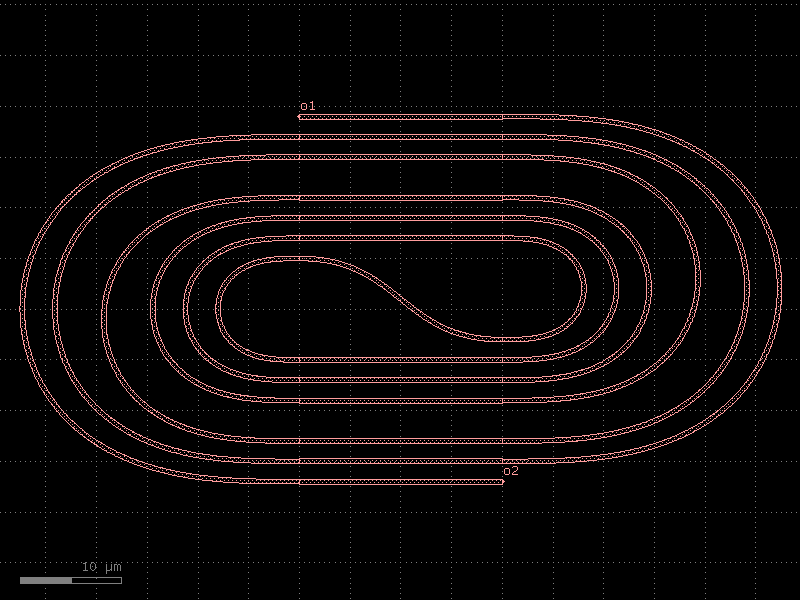
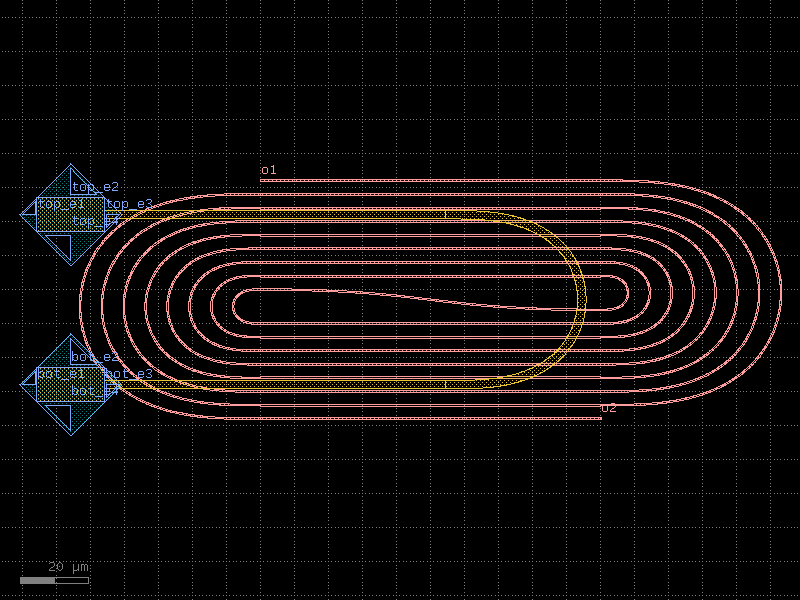
spiral_racetrack_heater#
- cspdk.si220.cband.cells.spiral_racetrack_heater(spacing=4.0, num=8, straight_length=100, cross_section='strip')[source]#
Returns spiral racetrack with a heater above.
based on https://doi.org/10.1364/OL.400230 .
- Parameters:
spacing (float) – center to center spacing between the waveguides.
num (int) – number of spiral loops.
straight_length (float) – length of the straight segments.
cross_section (CrossSection | str | dict[str, Any] | Callable[[...], CrossSection] | SymmetricalCrossSection | DCrossSection) – cross_section.
- Return type:
Component
import cspdk
c = cspdk.si220.cband.cells.spiral_racetrack_heater(spacing=4.0, num=8, straight_length=100, cross_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
straight#
- cspdk.si220.cband.cells.straight(length=10, cross_section='strip', width=None, npoints=2)[source]#
Returns a Straight waveguide.
- Parameters:
length (float) – straight length (um).
cross_section (CrossSection | str | dict[str, Any] | Callable[[...], CrossSection] | SymmetricalCrossSection | DCrossSection) – specification (CrossSection, string or dict).
width (float | None) – width of the waveguide. If None, it will use the width of the cross_section.
npoints (int) – number of points.
- Return type:
Component
import cspdk
c = cspdk.si220.cband.cells.straight(length=10, cross_section='strip', npoints=2).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)

straight_heater_meander#
- cspdk.si220.cband.cells.straight_heater_meander(length=320.0, heater_width=2.5, spacing=2, cross_section='strip', layer_heater='HEATER', via_stack='via_stack_heater_mtop', n=3, port_orientation1=90, port_orientation2=90, radius=None)[source]#
Returns a meander based heater.
based on SungWon Chung, Makoto Nakai, and Hossein Hashemi, Low-power thermo-optic silicon modulator for large-scale photonic integrated systems Opt. Express 27, 13430-13459 (2019) https://www.osapublishing.org/oe/abstract.cfm?URI=oe-27-9-13430
- Parameters:
length (float) – phase shifter length.
heater_width (float) – width of the heater.
spacing (float) – waveguide spacing (center to center).
cross_section (CrossSection | str | dict[str, Any] | Callable[[...], CrossSection] | SymmetricalCrossSection | DCrossSection) – for waveguide.
layer_heater (tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum) – for top heater, if None, it does not add a heater.
via_stack (str | Callable[[...], Component] | dict[str, Any] | DKCell | partial[Component] | None) – for the heater to via_stack metal.
n (int | None) – number of meanders.
port_orientation1 (float | None) – orientation of the first port. None for all orientations.
port_orientation2 (float | None) – orientation of the second port. None for all orientations.
radius (float | None) – radius of the meander.
- Return type:
Component
import cspdk
c = cspdk.si220.cband.cells.straight_heater_meander(length=320.0, heater_width=2.5, spacing=2, cross_section='strip', layer_heater='HEATER', via_stack='via_stack_heater_mtop', n=3, port_orientation1=90, port_orientation2=90).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
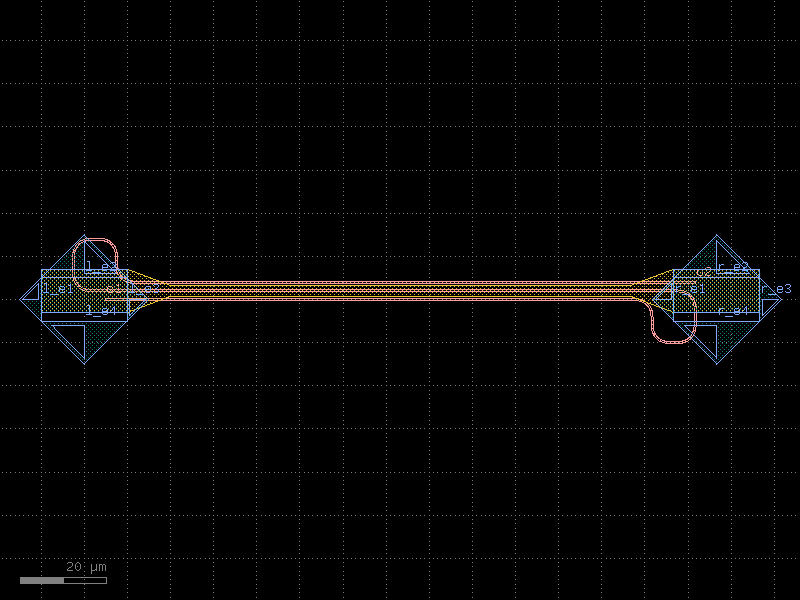
straight_heater_metal#
- cspdk.si220.cband.cells.straight_heater_metal(length=320.0, length_undercut_spacing=6.0, length_undercut=30.0, length_straight=0.1, length_straight_input=15.0, with_undercut=False, port_orientation1=90, port_orientation2=90)[source]#
Returns a thermal phase shifter.
dimensions from https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.27.010456
- Parameters:
length (float) – phase shifter length.
length_undercut_spacing (float) – spacing between the waveguide and the undercut.
length_undercut (float) – undercut length.
length_straight (float) – straight length.
length_straight_input (float) – straight length input.
with_undercut (bool) – isolation trenches for higher efficiency.
port_orientation1 (int | None) – orientation of the first port. None for all orientations.
port_orientation2 (int | None) – orientation of the second port. None for all orientations.
- Return type:
Component
import cspdk
c = cspdk.si220.cband.cells.straight_heater_metal(length=320.0, length_undercut_spacing=6.0, length_undercut=30.0, length_straight=0.1, length_straight_input=15.0, with_undercut=False, port_orientation1=90, port_orientation2=90).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
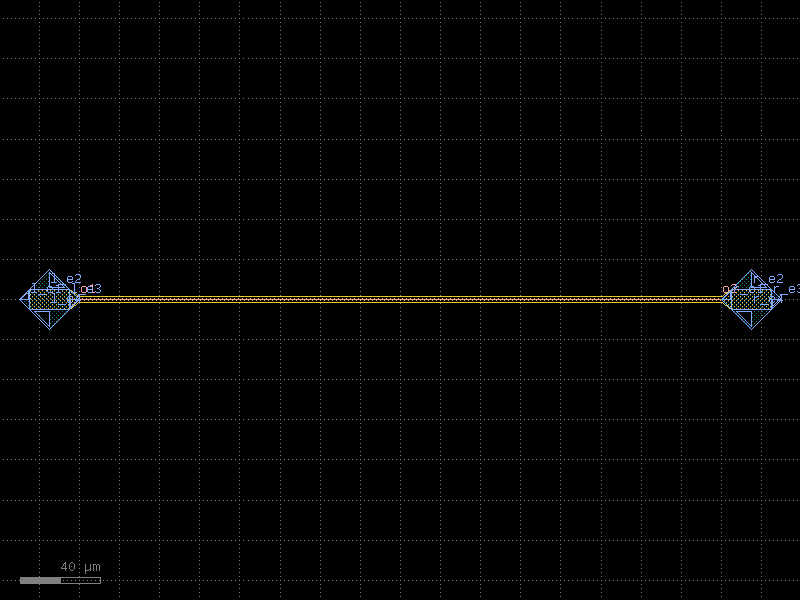
straight_metal#
- cspdk.si220.cband.cells.straight_metal(length=10, cross_section='metal_routing', width=None)[source]#
Returns a Straight waveguide.
- Parameters:
length (float) – straight length (um).
cross_section (CrossSection | str | dict[str, Any] | Callable[[...], CrossSection] | SymmetricalCrossSection | DCrossSection) – specification (CrossSection, string or dict).
width (float | None) – width of the waveguide. If None, it will use the width of the cross_section.
- Return type:
Component
import cspdk
c = cspdk.si220.cband.cells.straight_metal(length=10, cross_section='metal_routing').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
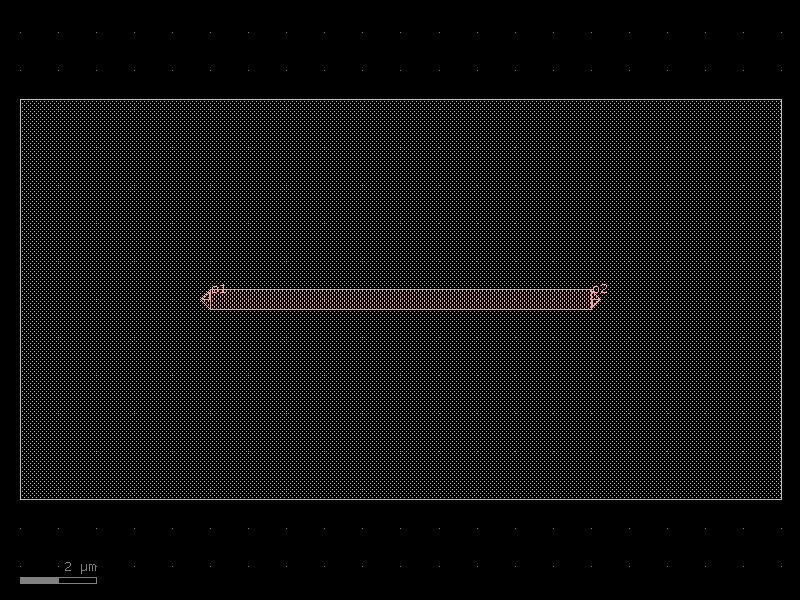
straight_rib#
- cspdk.si220.cband.cells.straight_rib(length=10, cross_section='rib', width=None)[source]#
Returns a Straight waveguide.
- Parameters:
length (float) – straight length (um).
cross_section (CrossSection | str | dict[str, Any] | Callable[[...], CrossSection] | SymmetricalCrossSection | DCrossSection) – specification (CrossSection, string or dict).
width (float | None) – width of the waveguide. If None, it will use the width of the cross_section.
- Return type:
Component
import cspdk
c = cspdk.si220.cband.cells.straight_rib(length=10, cross_section='rib').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
straight_strip#
- cspdk.si220.cband.cells.straight_strip(length=10, cross_section='strip', width=None, npoints=2)[source]#
Returns a Straight waveguide.
- Parameters:
length (float) – straight length (um).
cross_section (CrossSection | str | dict[str, Any] | Callable[[...], CrossSection] | SymmetricalCrossSection | DCrossSection) – specification (CrossSection, string or dict).
width (float | None) – width of the waveguide. If None, it will use the width of the cross_section.
npoints (int) – number of points.
- Return type:
Component
import cspdk
c = cspdk.si220.cband.cells.straight_strip(length=10, cross_section='strip', npoints=2).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)

taper#
- cspdk.si220.cband.cells.taper(length=10.0, width1=0.45, width2=None, cross_section='strip')[source]#
Linear taper, which tapers only the main cross section section.
- Parameters:
length (float) – taper length.
width1 (float) – width of the west/left port.
width2 (float | None) – width of the east/right port. Defaults to width1.
cross_section (CrossSection | str | dict[str, Any] | Callable[[...], CrossSection] | SymmetricalCrossSection | DCrossSection) – specification (CrossSection, string, CrossSectionFactory dict).
- Return type:
Component
import cspdk
c = cspdk.si220.cband.cells.taper(length=10.0, width1=0.45, cross_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)

taper_metal#
- cspdk.si220.cband.cells.taper_metal(length=10.0, width1=10, width2=None, cross_section='metal_routing')[source]#
Linear taper, which tapers only the main cross section section.
- Parameters:
length (float) – taper length.
width1 (float) – width of the west/left port.
width2 (float | None) – width of the east/right port. Defaults to width1.
cross_section (CrossSection | str | dict[str, Any] | Callable[[...], CrossSection] | SymmetricalCrossSection | DCrossSection) – specification (CrossSection, string, CrossSectionFactory dict).
- Return type:
Component
import cspdk
c = cspdk.si220.cband.cells.taper_metal(length=10.0, width1=10, cross_section='metal_routing').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
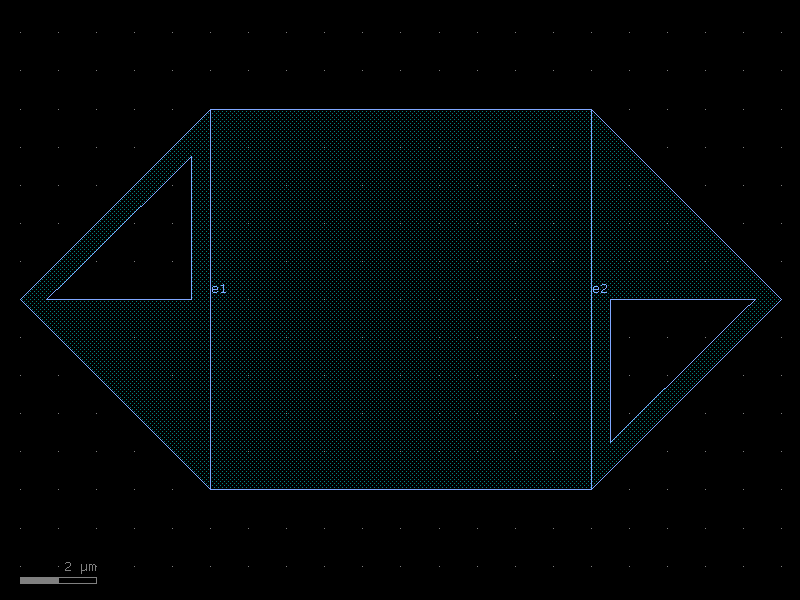
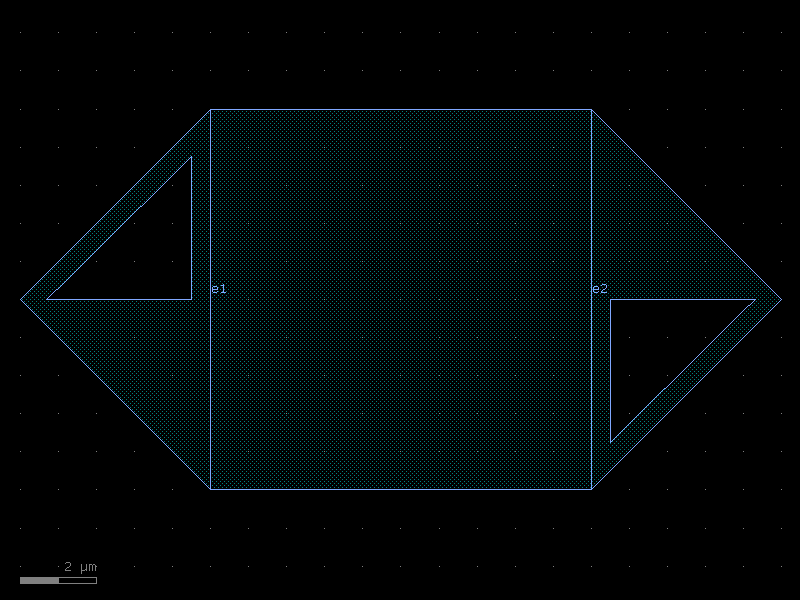
taper_strip_to_ridge#
- cspdk.si220.cband.cells.taper_strip_to_ridge(length=10.0, width1=0.5, width2=0.5, w_slab1=0.2, w_slab2=10.45, cross_section='strip')[source]#
A taper between strip and ridge.
This is a transition between two distinct cross sections
- Parameters:
length (float) – the length of the taper.
width1 (float) – the input width of the taper.
width2 (float) – the output width of the taper.
w_slab1 (float) – the input slab width of the taper.
w_slab2 (float) – the output slab width of the taper.
cross_section (CrossSection | str | dict[str, Any] | Callable[[...], CrossSection] | SymmetricalCrossSection | DCrossSection) – a cross section or its name or a function generating a cross section.
- Return type:
Component
import cspdk
c = cspdk.si220.cband.cells.taper_strip_to_ridge(length=10.0, width1=0.5, width2=0.5, w_slab1=0.2, w_slab2=10.45, cross_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
text_rectangular#
- cspdk.si220.cband.cells.text_rectangular(text='abc', size=3, justify='left', layer='PAD')[source]#
Pixel based font, guaranteed to be manhattan, without acute angles.
- Parameters:
text (str) – string.
size (float) – pixel size.
justify (str) – left, right or center.
layer (tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum) – for text.
- Return type:
Component
import cspdk
c = cspdk.si220.cband.cells.text_rectangular(text='abc', size=3, justify='left', layer='PAD').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)

text_rectangular_multi_layer#
- cspdk.si220.cband.cells.text_rectangular_multi_layer(text='abc', layers=('WG', 'PAD'), text_factory='text_rectangular', **kwargs)[source]#
Returns rectangular text in different layers.
- Parameters:
text (str) – string of text.
layers (Sequence[tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum]) – list of layers to replicate the text.
text_factory (str | Callable[[...], Component] | dict[str, Any] | DKCell | partial[Component]) – function to create the text Components.
kwargs (Any) – keyword arguments for text_factory.
- Return type:
Component
import cspdk
c = cspdk.si220.cband.cells.text_rectangular_multi_layer(text='abc', layers=('WG', 'PAD'), text_factory='text_rectangular').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)

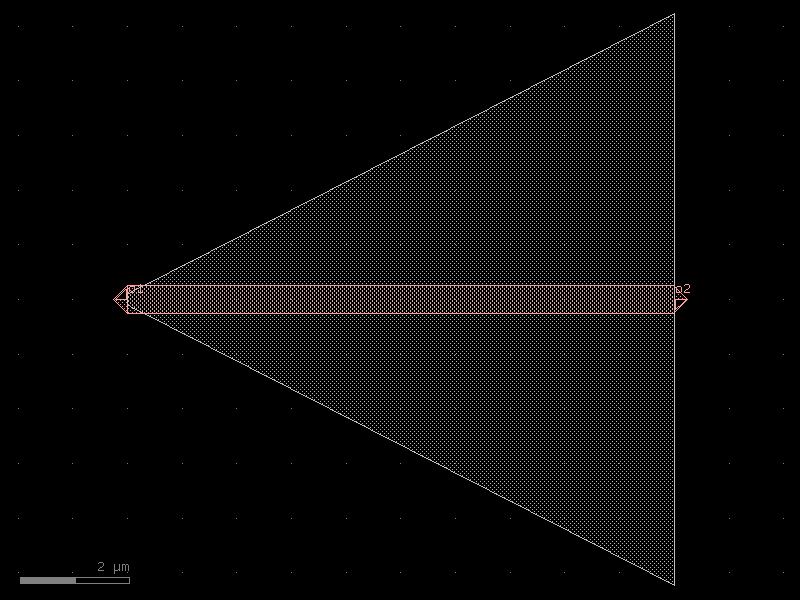
trans_rib10#
- cspdk.si220.cband.cells.trans_rib10(*, length=10, width1=0.5, width2=0.5, w_slab1=0.2, w_slab2=10.45, cross_section='strip')#
A taper between strip and ridge.
This is a transition between two distinct cross sections
- Parameters:
length (float) – the length of the taper.
width1 (float) – the input width of the taper.
width2 (float) – the output width of the taper.
w_slab1 (float) – the input slab width of the taper.
w_slab2 (float) – the output slab width of the taper.
cross_section (CrossSection | str | dict[str, Any] | Callable[[...], CrossSection] | SymmetricalCrossSection | DCrossSection) – a cross section or its name or a function generating a cross section.
- Return type:
Component
import cspdk
c = cspdk.si220.cband.cells.trans_rib10(length=10, width1=0.5, width2=0.5, w_slab1=0.2, w_slab2=10.45, cross_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
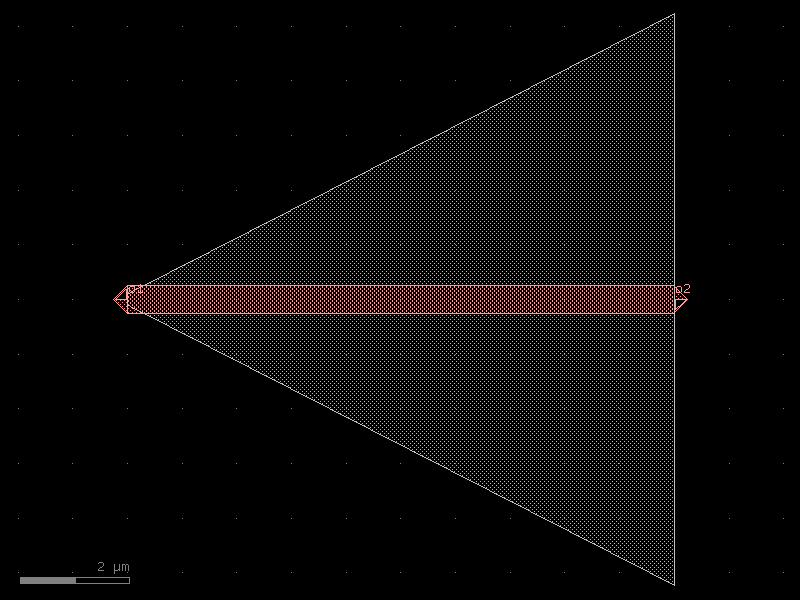
trans_rib20#
- cspdk.si220.cband.cells.trans_rib20(*, length=20, width1=0.5, width2=0.5, w_slab1=0.2, w_slab2=10.45, cross_section='strip')#
A taper between strip and ridge.
This is a transition between two distinct cross sections
- Parameters:
length (float) – the length of the taper.
width1 (float) – the input width of the taper.
width2 (float) – the output width of the taper.
w_slab1 (float) – the input slab width of the taper.
w_slab2 (float) – the output slab width of the taper.
cross_section (CrossSection | str | dict[str, Any] | Callable[[...], CrossSection] | SymmetricalCrossSection | DCrossSection) – a cross section or its name or a function generating a cross section.
- Return type:
Component
import cspdk
c = cspdk.si220.cband.cells.trans_rib20(length=20, width1=0.5, width2=0.5, w_slab1=0.2, w_slab2=10.45, cross_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
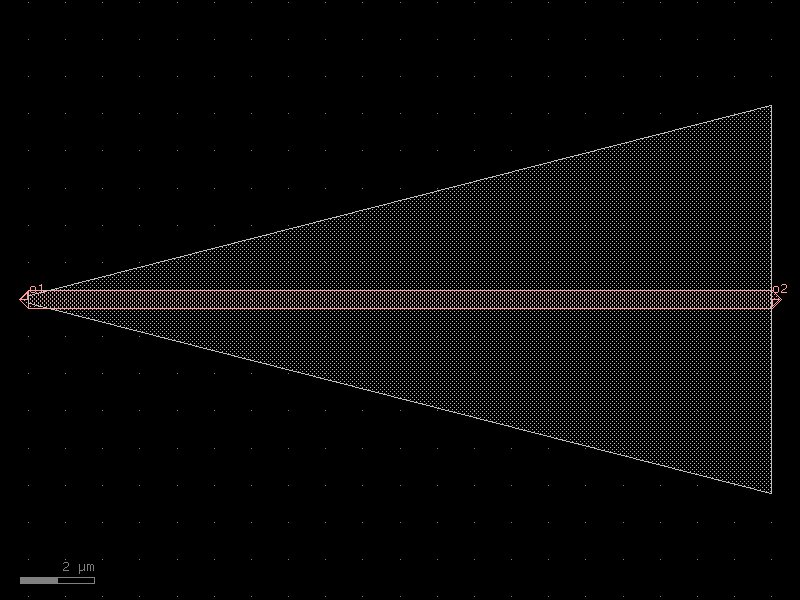
trans_rib50#
- cspdk.si220.cband.cells.trans_rib50(*, length=50, width1=0.5, width2=0.5, w_slab1=0.2, w_slab2=10.45, cross_section='strip')#
A taper between strip and ridge.
This is a transition between two distinct cross sections
- Parameters:
length (float) – the length of the taper.
width1 (float) – the input width of the taper.
width2 (float) – the output width of the taper.
w_slab1 (float) – the input slab width of the taper.
w_slab2 (float) – the output slab width of the taper.
cross_section (CrossSection | str | dict[str, Any] | Callable[[...], CrossSection] | SymmetricalCrossSection | DCrossSection) – a cross section or its name or a function generating a cross section.
- Return type:
Component
import cspdk
c = cspdk.si220.cband.cells.trans_rib50(length=50, width1=0.5, width2=0.5, w_slab1=0.2, w_slab2=10.45, cross_section='strip').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
via_stack_heater_mtop#
- cspdk.si220.cband.cells.via_stack_heater_mtop(size=(20.0, 10.0))[source]#
Rectangular via array stack.
You can use it to connect different metal layers or metals to silicon. You can use the naming convention via_stack_layerSource_layerDestination contains 4 ports (e1, e2, e3, e4)
also know as Via array http://www.vlsi-expert.com/2017/12/vias.html
- Parameters:
size (tuple[float, float]) – of the layers.
- Return type:
Component
import cspdk
c = cspdk.si220.cband.cells.via_stack_heater_mtop(size=(20.0, 10.0)).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
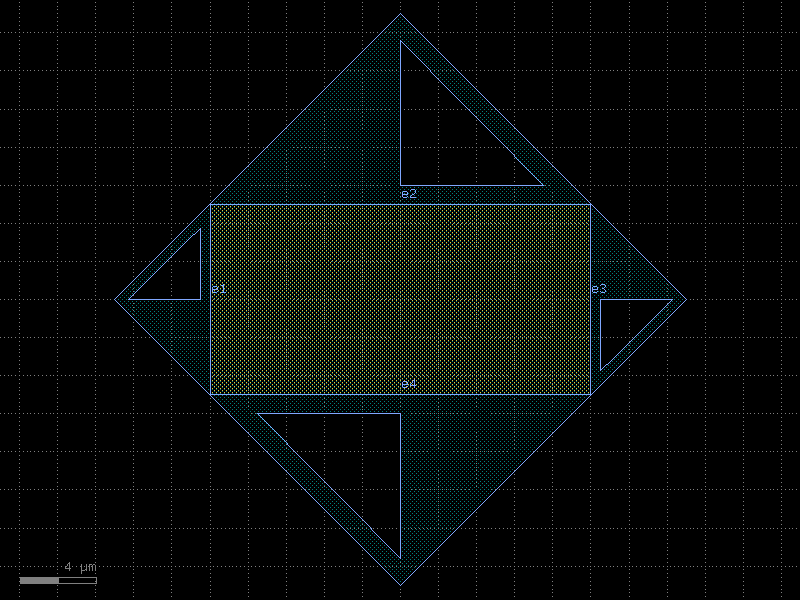
wire_corner#
- cspdk.si220.cband.cells.wire_corner(cross_section='metal_routing', width=None, radius=None)[source]#
Returns 45 degrees electrical corner wire.
- Parameters:
cross_section (CrossSection | str | dict[str, Any] | Callable[[...], CrossSection] | SymmetricalCrossSection | DCrossSection) – spec.
width (float | None) – optional width. Defaults to cross_section width.
radius (float | None) – ignored.
- Return type:
Component
import cspdk
c = cspdk.si220.cband.cells.wire_corner(cross_section='metal_routing').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
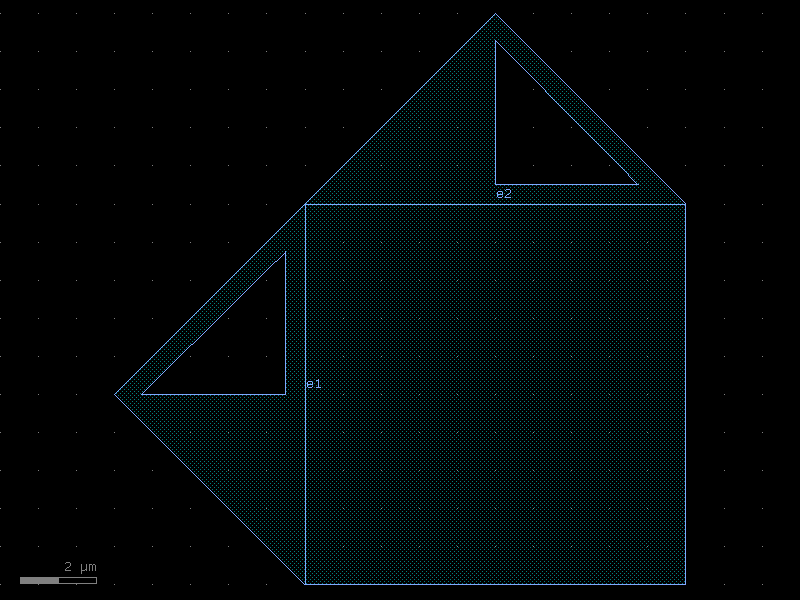
wire_corner45#
- cspdk.si220.cband.cells.wire_corner45(cross_section='metal_routing', radius=10, width=None, layer=None, with_corner90_ports=True)[source]#
Returns 90 degrees electrical corner wire.
- Parameters:
cross_section (CrossSection | str | dict[str, Any] | Callable[[...], CrossSection] | SymmetricalCrossSection | DCrossSection) – spec.
radius (float) – in um.
width (float | None) – optional width. Defaults to cross_section width.
layer (tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum | None) – optional layer.
with_corner90_ports (bool) – if True, adds ports at 90 degrees.
- Return type:
Component
import cspdk
c = cspdk.si220.cband.cells.wire_corner45(cross_section='metal_routing', radius=10, with_corner90_ports=True).copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
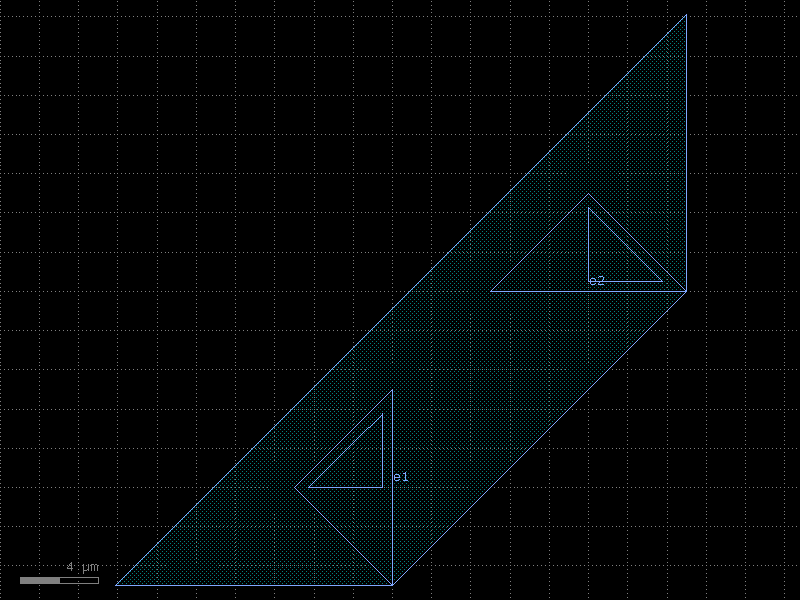
wire_corner45_straight#
- cspdk.si220.cband.cells.wire_corner45_straight(width=None, radius=None, cross_section='metal_routing')[source]#
Returns 90 degrees electrical corner wire.
- Parameters:
width (float | None) – of the wire.
radius (float | None) – of the corner. Defaults to width.
cross_section (CrossSection | str | dict[str, Any] | Callable[[...], CrossSection] | SymmetricalCrossSection | DCrossSection) – metal_routing.
- Return type:
Component
import cspdk
c = cspdk.si220.cband.cells.wire_corner45_straight(cross_section='metal_routing').copy()
c.draw_ports()
c.plot()
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)