The following condensed examples are going to be used in the gdsfactory photonics paper.
Please make sure to keep a maximum of approx. 20 lines of code per example.
For optimal rendering the examples should also avoid being too wide. If possible keep lines < 40 characters.
Fundamentals¶
You can add polygons to different layers. By default all units in gdsfactory are in um.
import gdsfactory as gfgf.CONF.plot_height = 300 / 400*350
gf.CONF.plot_width = 350
gf.CONF.plot_oversampling = 5.0import gdsfactory as gf
from gdsfactory.gpdk import PDK
PDK.activate()
# Create a blank component
# (essentially an empty GDS cell
# with some special features).
c = gf.Component()
# Add some geometry to it.
p1 = c.add_polygon(
[(-8, -1), (6, 8), (12, -6), (5, 3)],
layer=(1, 0)
)
c # Plot it in jupyter notebook.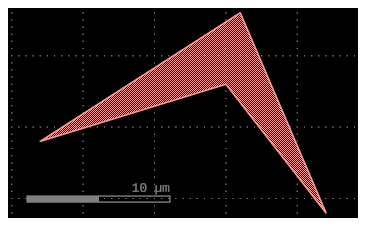
gf.CONF.plot_height = 420
gf.CONF.plot_width = 350c = gf.Component()
# Create new geometry from the functions
# available in the geometry library.
t = gf.components.text("Hello!")
r = gf.components.rectangle(
size=(5, 10), layer=(2, 0)
)
# Add references to the new geometry
# to c, our blank component.
text1 = c.add_ref(t)
# Using the << operator (identical to add_ref()),
# add the same geometry a second time.
text2 = c << t
r = c << r # Add the rectangle we created.
# Now that the geometry has been added to "c",
# we can move everything around:
text1.movey(25)
text2.move((5, 30))
text2.rotate(45)
r.movex(-15)
c
gf.CONF.plot_height = 330
gf.CONF.plot_width = 350@gf.cell
def mzi_with_bend(
radius: float = 10.0
) -> gf.Component:
c = gf.Component()
mzi = c << gf.components.mzi(length_y=35)
mzi.rotate(90)
bend = c << (
gf.components.bend_euler(radius=radius)
)
bend.connect("o1", mzi.ports["o2"])
c.add_port("o2", port=bend.ports["o2"])
c.add_port("o1", port=mzi.ports["o1"])
return c
c_mzi_with_bend = mzi_with_bend(radius=12)
c_mzi_with_bend.draw_ports()
c_mzi_with_bend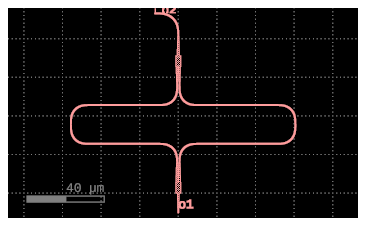
c_mzi_with_bend.pprint_ports()Loading...
gf.CONF.plot_height = 210
gf.CONF.plot_width = 350c = gf.Component()
mmi1 = c << gf.components.mmi1x2()
mmi2 = c << gf.components.mmi1x2()
mmi2.move((100, 40))
# Automatically route a waveguide
# between the two MMIs
route = gf.routing.route_single(
c,
port1=mmi1.ports["o2"],
port2=mmi2.ports["o1"],
cross_section=gf.cross_section.strip,
)
c