PCells#
airbridge#
- qpdk.cells.airbridge(bridge_length=30.0, bridge_width=8.0, pad_width=15.0, pad_length=12.0, bridge_layer=<LayerMapQPDK.AB_DRAW: 49>, pad_layer=<LayerMapQPDK.AB_VIA: 50>)[source]#
Generate a superconducting airbridge component.
Creates an airbridge consisting of a suspended bridge span and landing pads on either side. The bridge allows transmission lines to cross over each other without electrical contact, which is essential for complex quantum circuit routing without crosstalk.
The bridge_layer (AB_DRAW) represents the elevated metal bridge structure, while the pad_layer (AB_VIA) represents the contact/landing pads that connect to the underlying circuit.
Note
To be used with
ComponentAlongPaththe unrotated version should be oriented for placement on a horizontal line.- Parameters:
bridge_length (float) – Total length of the airbridge span in µm.
bridge_width (float) – Width of the suspended bridge in µm.
pad_width (float) – Width of the landing pads in µm.
pad_length (float) – Length of each landing pad in µm.
bridge_layer (LayerSpec) – Layer for the suspended bridge metal (default: AB_DRAW).
pad_layer (LayerSpec) – Layer for the landing pads/contacts (default: AB_VIA).
- Returns:
Component containing the airbridge geometry with appropriate ports.
- Return type:
Component
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
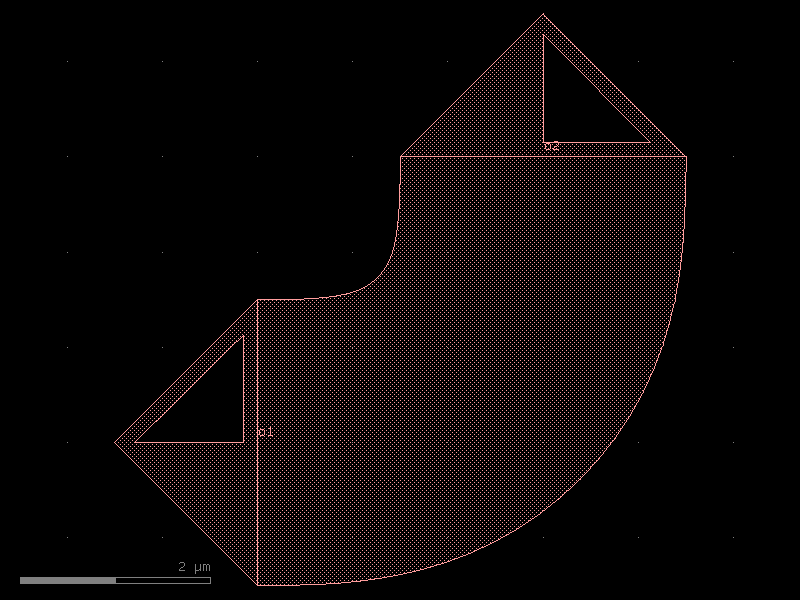
bend_circular#
- qpdk.cells.bend_circular(angle=90.0, radius=100.0, npoints=None, cross_section=<function coplanar_waveguide>, width=None, allow_min_radius_violation=True, **kwargs)[source]#
Returns circular bend.
Cross-sections have a minimum value of allowed bend radius, which is half their total width. If the user-specified radius is smaller than this value, it is adjusted to the minimum acceptable one.
- Parameters:
angle (float) – Angle of the bend in degrees.
radius (float) – Radius of the bend in μm.
npoints (int | None) – Number of points for the bend (optional, cannot be used with angular_step).
cross_section (CrossSection | str | dict[str, Any] | Callable[[...], CrossSection] | SymmetricalCrossSection | DCrossSection) – Cross-section specification.
width (float | None) – Optional width override in μm.
allow_min_radius_violation (bool) – Allow radius smaller than cross-section radius.
**kwargs – Additional arguments passed to gf.c.bend_circular (e.g., angular_step).
- Return type:
Component
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
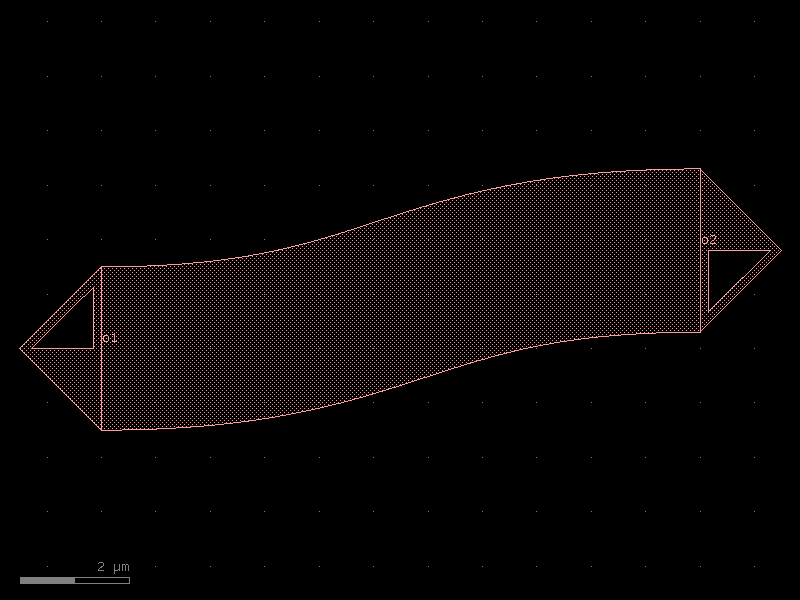
bend_circular_all_angle#
- qpdk.cells.bend_circular_all_angle(radius=100.0, angle=90.0, npoints=None, layer=None, width=None, cross_section=<function coplanar_waveguide>, allow_min_radius_violation=True)[source]#
Returns circular bend with arbitrary angle.
- Parameters:
radius (float | None) – Radius of the bend in μm.
angle (float) – Angle of the bend in degrees.
npoints (int | None) – Number of points for the bend.
layer (tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum | None) – Layer specification.
width (float | None) – Optional width override in μm.
cross_section (CrossSection | str | dict[str, Any] | Callable[[...], CrossSection] | SymmetricalCrossSection | DCrossSection) – Cross-section specification.
allow_min_radius_violation (bool) – Allow radius smaller than cross-section radius.
- Return type:
ComponentAllAngle
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
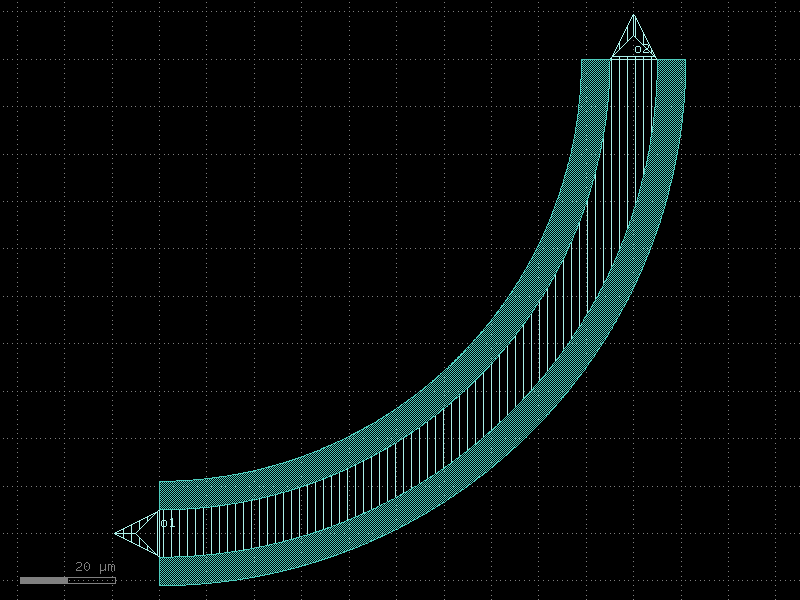
bend_euler#
- qpdk.cells.bend_euler(angle=90.0, p=0.5, with_arc_floorplan=True, npoints=720, cross_section=<function coplanar_waveguide>, allow_min_radius_violation=True, **kwargs)[source]#
Regular degree euler bend.
- Parameters:
angle (float) – Angle of the bend in degrees.
p (float) – Fraction of the bend that is curved (0-1).
with_arc_floorplan (bool) – Include arc floorplan.
npoints (int) – Number of points for the bend.
cross_section (CrossSection | str | dict[str, Any] | Callable[[...], CrossSection] | SymmetricalCrossSection | DCrossSection) – Cross-section specification.
allow_min_radius_violation (bool) – Allow radius smaller than cross-section radius.
**kwargs – Additional arguments passed to gf.c.bend_euler.
- Return type:
Component
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
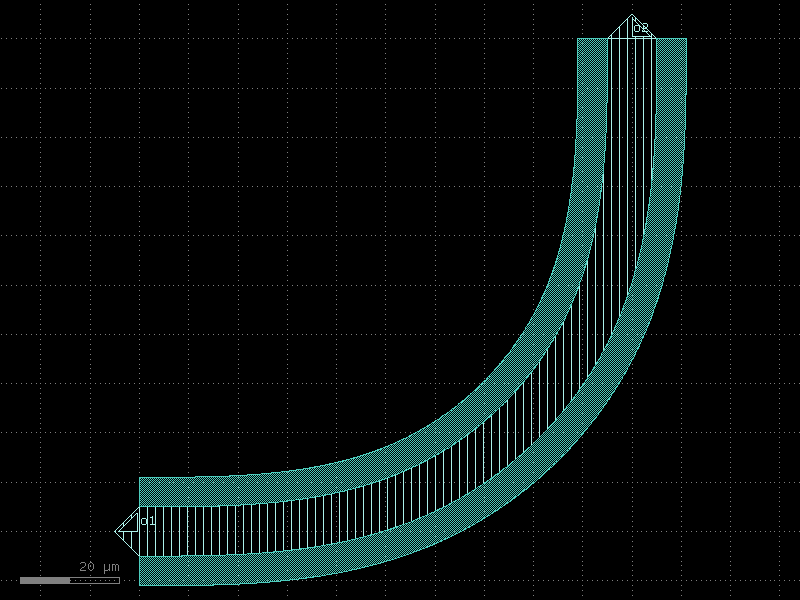
bend_euler_all_angle#
- qpdk.cells.bend_euler_all_angle(radius=None, angle=90.0, p=0.5, with_arc_floorplan=True, npoints=None, layer=None, width=None, cross_section=<function coplanar_waveguide>, allow_min_radius_violation=True)[source]#
Returns regular degree euler bend with arbitrary angle.
- Parameters:
radius (float | None) – Radius of the bend in μm.
angle (float) – Angle of the bend in degrees.
p (float) – Fraction of the bend that is curved (0-1).
with_arc_floorplan (bool) – Include arc floorplan.
npoints (int | None) – Number of points for the bend.
layer (tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum | None) – Layer specification.
width (float | None) – Optional width override in μm.
cross_section (CrossSection | str | dict[str, Any] | Callable[[...], CrossSection] | SymmetricalCrossSection | DCrossSection) – Cross-section specification.
allow_min_radius_violation (bool) – Allow radius smaller than cross-section radius.
- Return type:
ComponentAllAngle
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
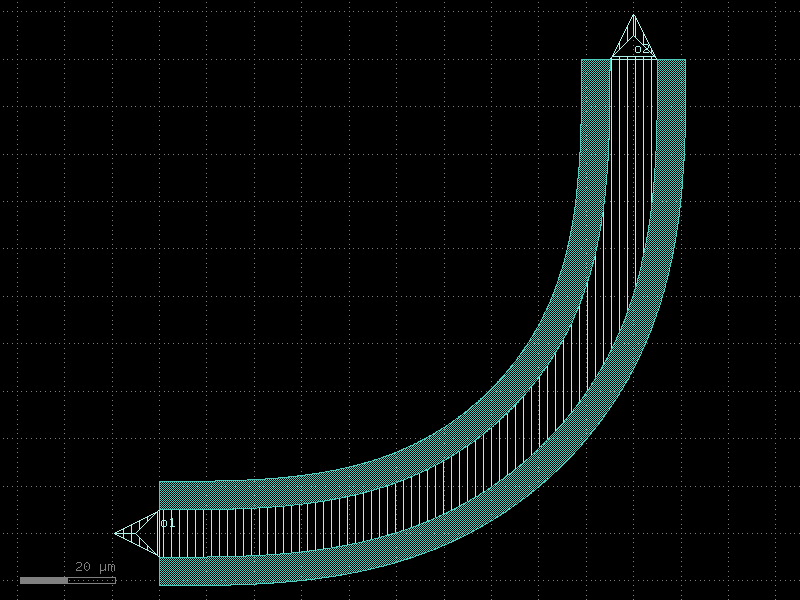
bend_s#
- qpdk.cells.bend_s(size=(20.0, 3.0), cross_section=<function coplanar_waveguide>, width=None, allow_min_radius_violation=True, **kwargs)[source]#
Return S bend with bezier curve.
stores min_bend_radius property in self.info[‘min_bend_radius’] min_bend_radius depends on height and length
- Parameters:
size (tuple[float, float]) – Tuple of (length, offset) for the S bend in μm.
cross_section (CrossSection | str | dict[str, Any] | Callable[[...], CrossSection] | SymmetricalCrossSection | DCrossSection) – Cross-section specification.
width (float | None) – Optional width override in μm.
allow_min_radius_violation (bool) – Allow radius smaller than cross-section radius.
**kwargs – Additional arguments passed to gf.c.bend_s.
- Return type:
Component
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
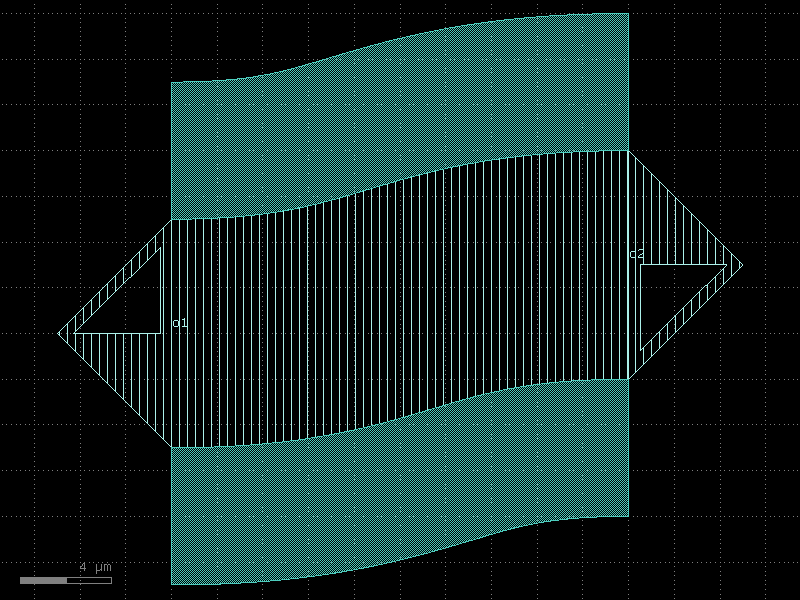
chip_edge#
- qpdk.cells.chip_edge(size=(10000.0, 10000.0), width=200.0, layer='M1_ETCH')[source]#
Returns a chip edge component with hollow rectangle frame.
Creates a rectangular frame (hollow rectangle) on an etched metal layer, typically used to define chip edge regions for proper fabrication.
- Parameters:
size (tuple[float, float]) – (tuple) Width and height of the chip edge area.
width (float) – Width/thickness of the etched frame border.
layer (tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum) – Layer to put the etched frame on.
- Return type:
Component
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)

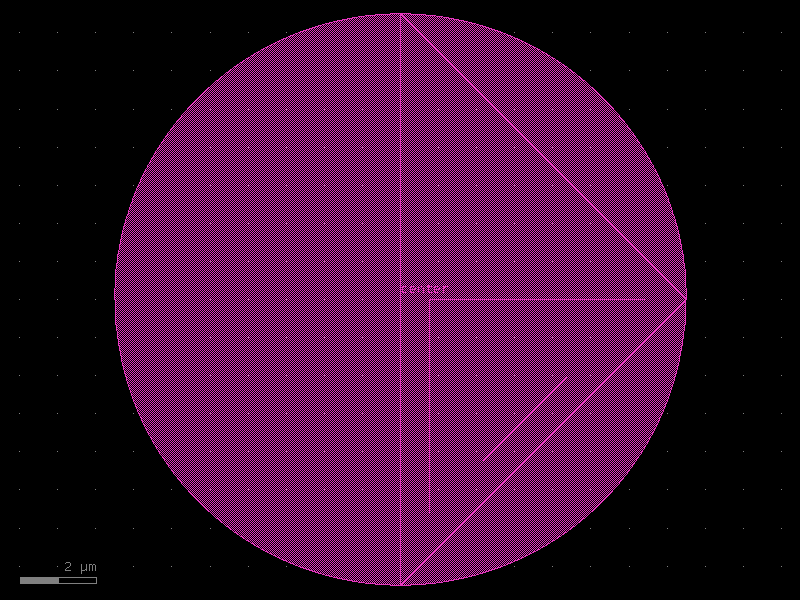
circle#
- qpdk.cells.circle(radius=10.0, angle_resolution=2.5, layer='WG')[source]#
Generate a circle geometry.
- Parameters:
radius (float) – of the circle.
angle_resolution (float) – number of degrees per point.
layer (LayerSpec) – layer.
- Return type:
Component
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
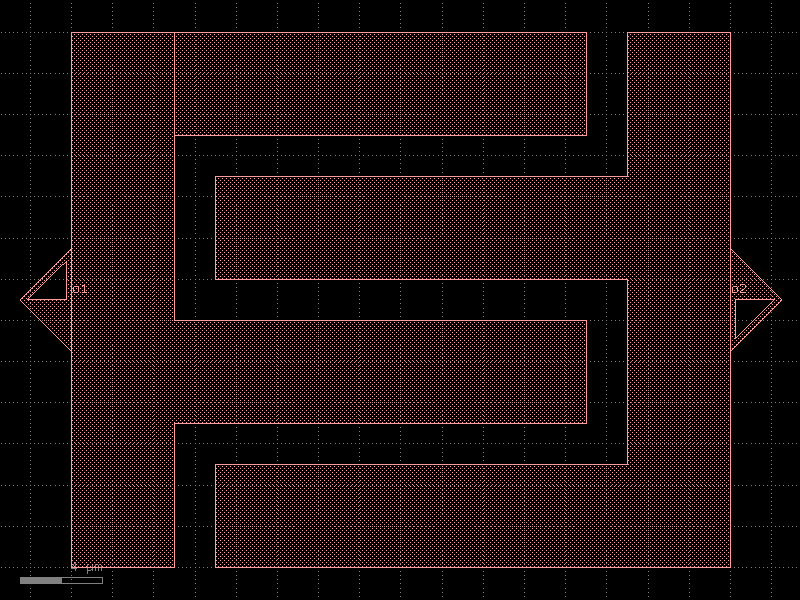
coupler_ring#
- qpdk.cells.coupler_ring(*, gap=16, radius=None, length_x=20, bend=<function bend_circular>, straight=<function straight>, cross_section='cpw', cross_section_bend=None, length_extension=None)#
Coupler for ring.
- Parameters:
gap (float) – spacing between parallel coupled straight waveguides.
radius (float | None) – of the bends. Default is None, which uses the default radius of the cross_section.
length_x (float) – length of the parallel coupled straight waveguides.
bend (ComponentSpec) – 90 degrees bend spec.
straight (ComponentSpec) – straight spec.
cross_section (CrossSectionSpec) – cross_section spec.
cross_section_bend (CrossSectionSpec | None) – optional bend cross_section spec.
length_extension (float | None) – straight length extension at the end of the coupler bottom ports.
- Return type:
Component
o2 o3 xx xx xx xx xx length_x x xx ◄───────────────► x xx xxx xx xxx xxx──────▲─────────xxx │gap o1──────▼─────────◄──────────────► o4 length_extension
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
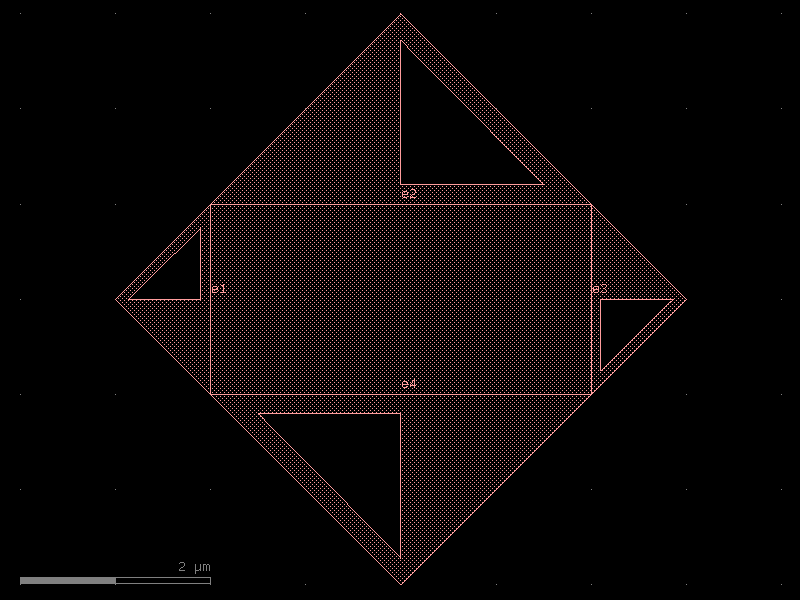
coupler_straight#
- qpdk.cells.coupler_straight(length=10.0, *, gap=16, cross_section='cpw')#
Coupler_straight with two parallel straights.
- Parameters:
length (float) – of straight.
gap (float) – between straights.
cross_section (CrossSectionSpec) – specification (CrossSection, string or dict).
- Return type:
Component
o2──────▲─────────o3 │gap o1──────▼─────────o4
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
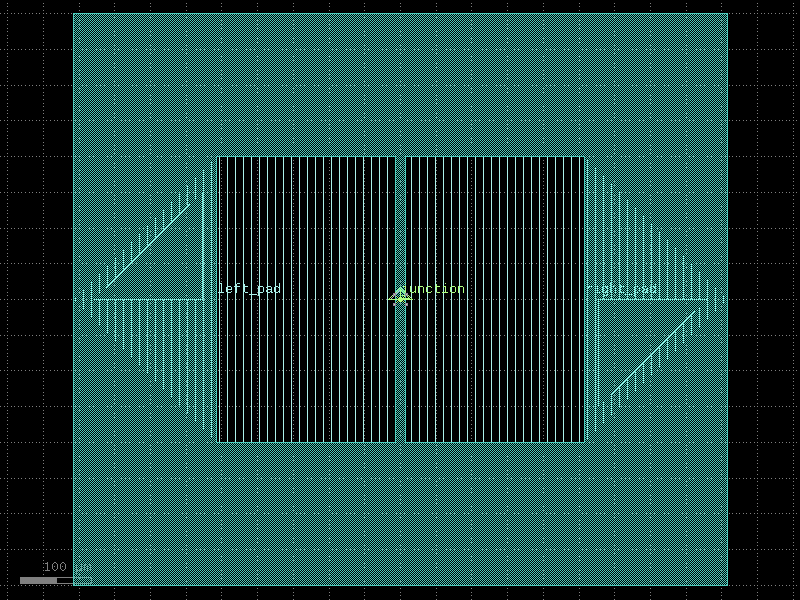
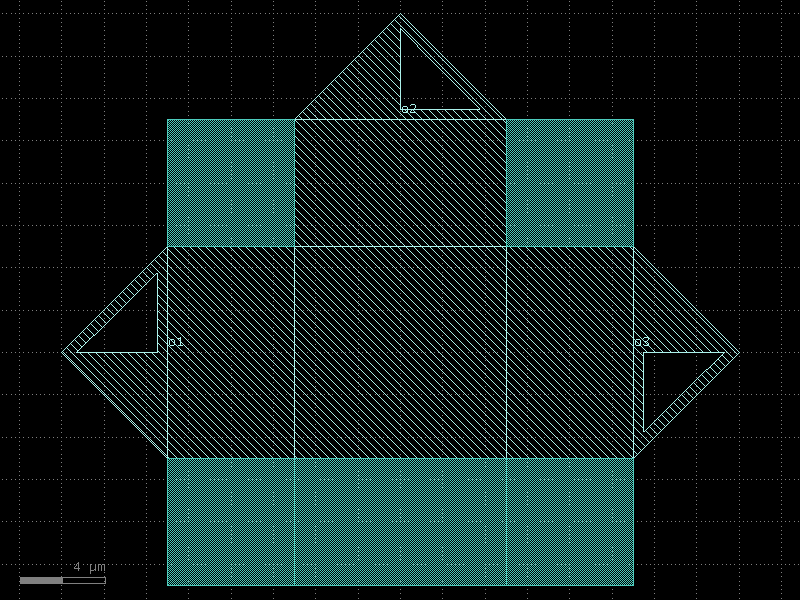
double_pad_transmon#
- qpdk.cells.double_pad_transmon(pad_size=(250.0, 400.0), pad_gap=15.0, junction_spec=<function squid_junction>, junction_displacement=None, layer_metal=<LayerMapQPDK.M1_DRAW: 1>)[source]#
Creates a double capacitor pad transmon qubit with Josephson junction.
A transmon qubit consists of two capacitor pads connected by a Josephson junction. The junction creates an anharmonic oscillator that can be used as a qubit.
See [KYG+07] for details.
- Parameters:
pad_size (tuple[float, float]) – (width, height) of each capacitor pad in μm.
pad_gap (float) – Gap between the two capacitor pads in μm.
junction_spec (ComponentSpec) – Component specification for the Josephson junction component.
junction_displacement (DCplxTrans | None) – Optional complex transformation to apply to the junction.
layer_metal (LayerSpec) – Layer for the metal pads.
- Returns:
A gdsfactory component with the transmon geometry.
- Return type:
Component
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
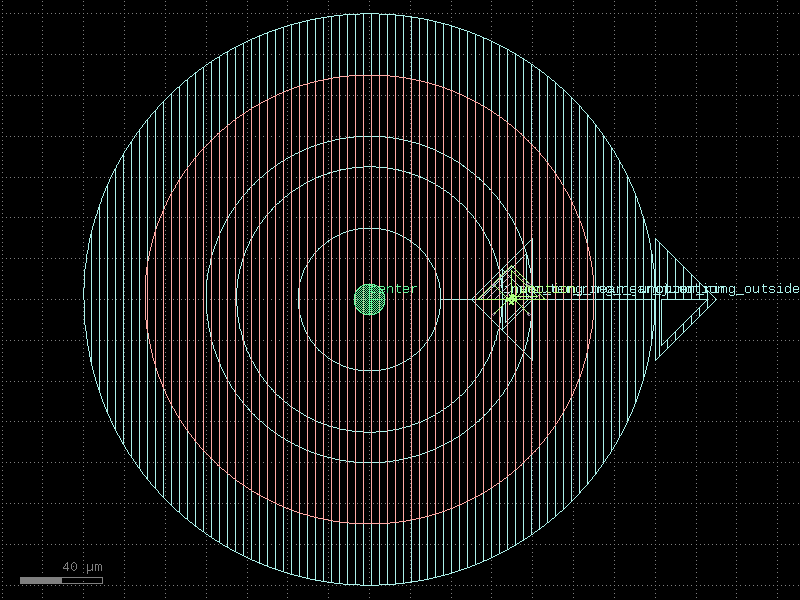
double_pad_transmon_with_bbox#
- qpdk.cells.double_pad_transmon_with_bbox(bbox_extension=200.0, pad_size=(250.0, 400.0), pad_gap=15.0, junction_spec=<function squid_junction>, junction_displacement=None, layer_metal=<LayerMapQPDK.M1_DRAW: 1>)[source]#
Creates a double capacitor pad transmon qubit with Josephson junction and an etched bounding box.
See
double_pad_transmon()for more details.- Parameters:
bbox_extension (float) – Extension size for the bounding box in μm.
pad_size (tuple[float, float]) – (width, height) of each capacitor pad in μm.
pad_gap (float) – Gap between the two capacitor pads in μm.
junction_spec (ComponentSpec) – Component specification for the Josephson junction component.
junction_displacement (DCplxTrans | None) – Optional complex transformation to apply to the junction.
layer_metal (LayerSpec) – Layer for the metal pads.
- Returns:
A gdsfactory component with the transmon geometry and etched box.
- Return type:
Component
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
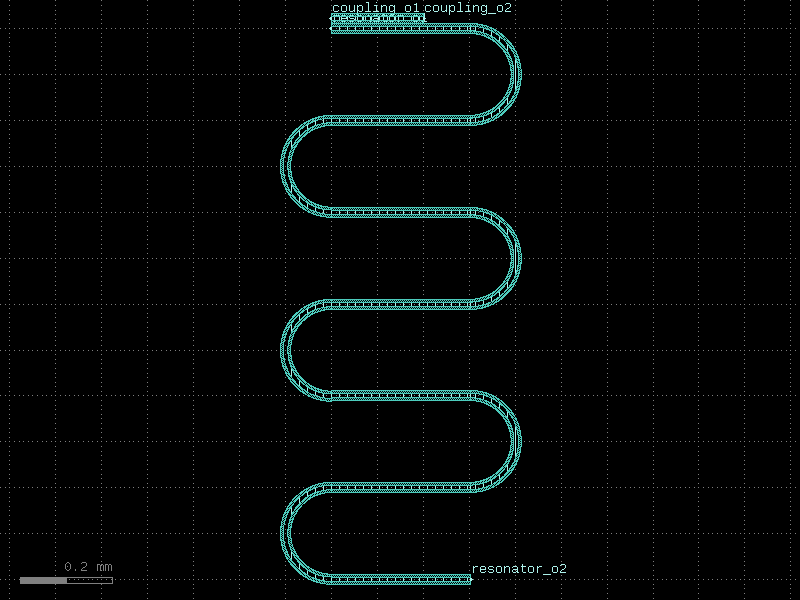
double_pad_transmon_with_resonator#
- qpdk.cells.double_pad_transmon_with_resonator(*, qubit='double_pad_transmon_with_bbox', resonator=functools.partial(<function resonator>, open_start=False, open_end=True, start_with_bend=True, length=4000, meanders=6), resonator_meander_start=(-900, -1200), resonator_length=5000.0, resonator_meanders=5, resonator_bend_spec='bend_circular', resonator_cross_section='cpw', resonator_open_start=False, resonator_open_end=True, coupler=functools.partial(<function plate_capacitor_single>, width=20, length=394), qubit_rotation=90, coupler_port='left_pad', coupler_offset=(-45, 0))#
Returns a transmon qubit coupled to a quarter wave resonator.
- Parameters:
qubit (ComponentSpec) – Qubit component.
resonator (ComponentSpec) – Resonator component.
resonator_meander_start (tuple[float, float]) – (x, y) position of the start of the resonator meander.
resonator_length (float) – Length of the resonator in µm.
resonator_meanders (int) – Number of meander sections for the resonator.
resonator_bend_spec (ComponentSpec) – Specification for the bend component used in meanders.
resonator_cross_section (CrossSectionSpec) – Cross-section specification for the resonator.
resonator_open_start (bool) – If True, adds an etch section at the start of the resonator.
resonator_open_end (bool) – If True, adds an etch section at the end of the resonator.
coupler (ComponentSpec) – Coupler spec.
qubit_rotation (float) – Rotation angle for the qubit in degrees.
coupler_port (str) – Name of the qubit port to position the coupler relative to.
coupler_offset (tuple[float, float]) – (x, y) offset for the coupler position.
- Return type:
Component
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
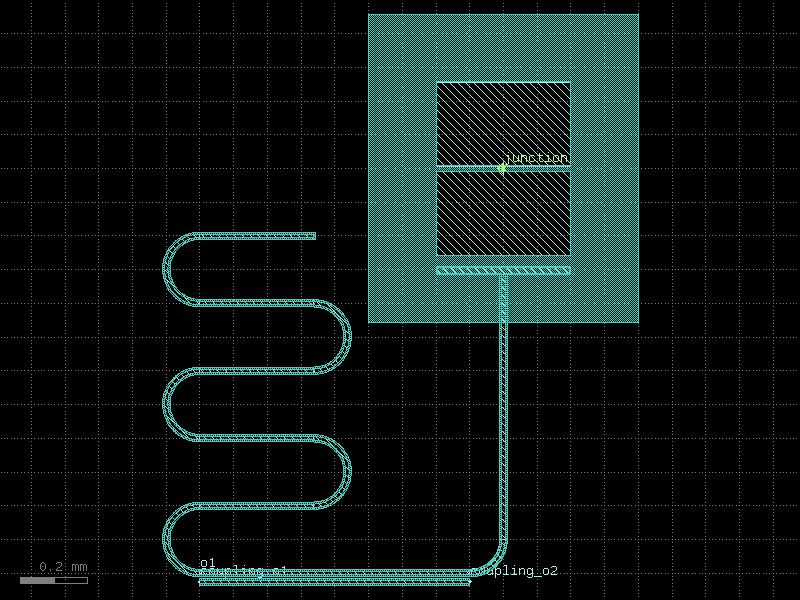
double_pad_transmon_with_resonator_and_probeline#
- qpdk.cells.double_pad_transmon_with_resonator_and_probeline(*, qubit='double_pad_transmon_with_bbox', resonator=functools.partial(<function resonator>, open_start=False, open_end=True, start_with_bend=True, length=4000, meanders=6), resonator_meander_start=(-900, -1200), resonator_length=5000.0, resonator_meanders=5, resonator_bend_spec='bend_circular', resonator_cross_section='cpw', resonator_open_start=False, resonator_open_end=True, coupler=functools.partial(<function plate_capacitor_single>, width=20, length=394), qubit_rotation=90, coupler_port='left_pad', coupler_offset=(-45, 0), probeline_coupler=functools.partial(<function coupler_straight>, cross_section='cpw', gap=16), probeline_coupling_gap=16.0, probeline_coupling_length=None)#
Returns a transmon qubit coupled to a quarter wave resonator and a probeline.
Uses a
coupler_straight()to couple the resonator to a probeline. The coupling section is inserted at the start of the resonator meander, with one waveguide carrying the resonator signal and the other providing ports for probeline routing.- Parameters:
qubit (ComponentSpec) – Qubit component.
resonator (ComponentSpec) – Resonator component.
resonator_meander_start (tuple[float, float]) – (x, y) position of the start of the resonator meander.
resonator_length (float) – Length of the resonator in µm.
resonator_meanders (int) – Number of meander sections for the resonator.
resonator_bend_spec (ComponentSpec) – Specification for the bend component used in meanders.
resonator_cross_section (CrossSectionSpec) – Cross-section specification for the resonator.
resonator_open_start (bool) – If True, adds an etch section at the start of the resonator.
resonator_open_end (bool) – If True, adds an etch section at the end of the resonator.
coupler (ComponentSpec) – Coupler spec.
qubit_rotation (float) – Rotation angle for the qubit in degrees.
coupler_port (str) – Name of the qubit port to position the coupler relative to.
coupler_offset (tuple[float, float]) – (x, y) offset for the coupler position.
probeline_coupler (ComponentSpec) – Component spec for the probeline coupling section.
probeline_coupling_gap (float) – Gap between the resonator and probeline waveguides in the coupling section in µm.
probeline_coupling_length (float | None) – Length of the coupling section in µm.
- Return type:
Component
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
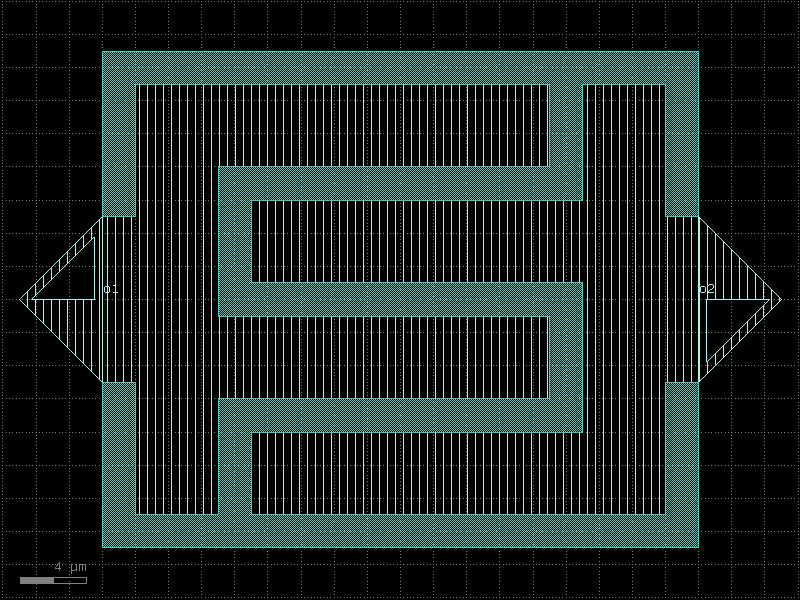
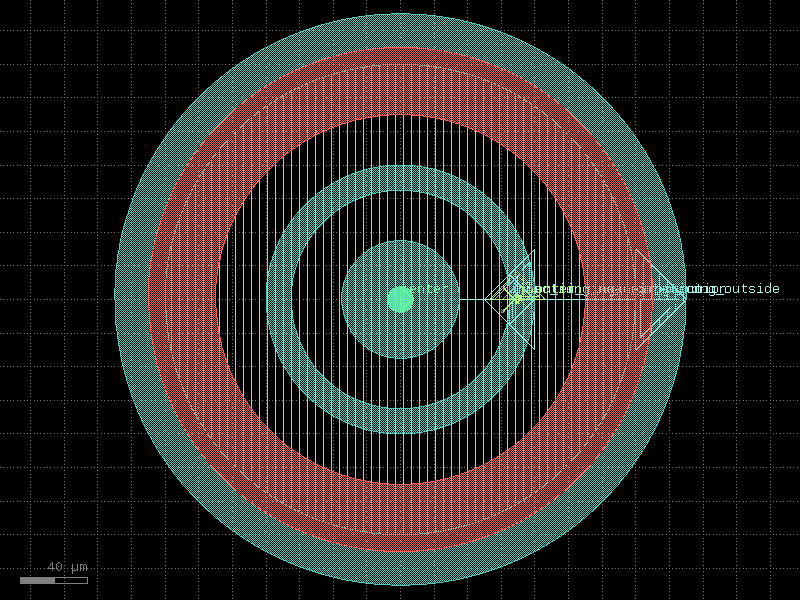
flipmon#
- qpdk.cells.flipmon(inner_circle_radius=60.0, outer_ring_radius=110.0, outer_ring_width=60.0, top_circle_radius=110.0, junction_spec=<function squid_junction_long>, junction_displacement=None, layer_metal=<LayerMapQPDK.M1_DRAW: 1>, layer_metal_top=<LayerMapQPDK.M2_DRAW: 3>)[source]#
Creates a circular transmon qubit with flipmon geometry.
A circular variant of the transmon qubit with another circle as the inner pad.
See [LWJ+25, LZY+21] for details about the flipmon design.
- Parameters:
inner_circle_radius (float) – Central radius of the inner circular capacitor pad in μm.
outer_ring_radius (float) – Central radius of the outer circular capacitor pad in μm.
outer_ring_width (float) – Width of the outer circular capacitor pad in μm.
top_circle_radius (float) – Central radius of the top circular capacitor pad in μm. There is no separate width as the filled circle is not a ring.
junction_spec (ComponentSpec) – Component specification for the Josephson junction component.
junction_displacement (DCplxTrans | None) – Optional complex transformation to apply to the junction.
layer_metal (LayerSpec) – Layer for the metal pads.
layer_metal_top (LayerSpec) – Layer for the other metal layer pad for flip-chip.
- Returns:
A gdsfactory component with the circular transmon geometry.
- Return type:
Component
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
flipmon_with_bbox#
- qpdk.cells.flipmon_with_bbox(inner_circle_radius=60.0, outer_ring_radius=110.0, outer_ring_width=60.0, top_circle_radius=110.0, junction_spec=<function squid_junction_long>, junction_displacement=None, layer_metal=<LayerMapQPDK.M1_DRAW: 1>, layer_metal_top=<LayerMapQPDK.M2_DRAW: 3>, m1_etch_extension_gap=30.0, m2_etch_extension_gap=40.0)[source]#
Creates a circular transmon qubit with flipmon geometry and a circular etched bounding box.
See
flipmon()for more details.- Parameters:
inner_circle_radius (float) – Central radius of the inner circular capacitor pad in μm.
outer_ring_radius (float) – Central radius of the outer circular capacitor pad in μm.
outer_ring_width (float) – Width of the outer circular capacitor pad in μm.
top_circle_radius (float) – Central radius of the top circular capacitor pad in μm.
junction_spec (ComponentSpec) – Component specification for the Josephson junction component.
junction_displacement (DCplxTrans | None) – Optional complex transformation to apply to the junction.
layer_metal (LayerSpec) – Layer for the metal pads.
layer_metal_top (LayerSpec) – Layer for the other metal layer pad for flip-chip.
m1_etch_extension_gap (float) – Radius extension length for the M1 etch bounding box in μm.
m2_etch_extension_gap (float) – Radius extension length for the M2 etch bounding box in μm.
- Returns:
A gdsfactory component with the flipmon geometry and etched box.
- Return type:
Component
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
flipmon_with_resonator#
- qpdk.cells.flipmon_with_resonator(*, qubit='flipmon_with_bbox', resonator=functools.partial(<function resonator>, open_start=False, open_end=True, start_with_bend=True, length=4000, meanders=6), resonator_meander_start=(-900, -1200), resonator_length=5000.0, resonator_meanders=5, resonator_bend_spec='bend_circular', resonator_cross_section='cpw', resonator_open_start=False, resonator_open_end=True, coupler=functools.partial(<function plate_capacitor_single>, width=10, length=58), qubit_rotation=-90, coupler_port='outer_ring_outside', coupler_offset=(-10, 0))#
Returns a transmon qubit coupled to a quarter wave resonator.
- Parameters:
qubit (ComponentSpec) – Qubit component.
resonator (ComponentSpec) – Resonator component.
resonator_meander_start (tuple[float, float]) – (x, y) position of the start of the resonator meander.
resonator_length (float) – Length of the resonator in µm.
resonator_meanders (int) – Number of meander sections for the resonator.
resonator_bend_spec (ComponentSpec) – Specification for the bend component used in meanders.
resonator_cross_section (CrossSectionSpec) – Cross-section specification for the resonator.
resonator_open_start (bool) – If True, adds an etch section at the start of the resonator.
resonator_open_end (bool) – If True, adds an etch section at the end of the resonator.
coupler (ComponentSpec) – Coupler spec.
qubit_rotation (float) – Rotation angle for the qubit in degrees.
coupler_port (str) – Name of the qubit port to position the coupler relative to.
coupler_offset (tuple[float, float]) – (x, y) offset for the coupler position.
- Return type:
Component
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
flipmon_with_resonator_and_probeline#
- qpdk.cells.flipmon_with_resonator_and_probeline(*, qubit='flipmon_with_bbox', resonator=functools.partial(<function resonator>, open_start=False, open_end=True, start_with_bend=True, length=4000, meanders=6), resonator_meander_start=(-900, -1200), resonator_length=5000.0, resonator_meanders=5, resonator_bend_spec='bend_circular', resonator_cross_section='cpw', resonator_open_start=False, resonator_open_end=True, coupler=functools.partial(<function plate_capacitor_single>, width=10, length=58), qubit_rotation=-90, coupler_port='outer_ring_outside', coupler_offset=(-10, 0), probeline_coupler=functools.partial(<function coupler_straight>, cross_section='cpw', gap=16), probeline_coupling_gap=16.0, probeline_coupling_length=None)#
Returns a transmon qubit coupled to a quarter wave resonator and a probeline.
Uses a
coupler_straight()to couple the resonator to a probeline. The coupling section is inserted at the start of the resonator meander, with one waveguide carrying the resonator signal and the other providing ports for probeline routing.- Parameters:
qubit (ComponentSpec) – Qubit component.
resonator (ComponentSpec) – Resonator component.
resonator_meander_start (tuple[float, float]) – (x, y) position of the start of the resonator meander.
resonator_length (float) – Length of the resonator in µm.
resonator_meanders (int) – Number of meander sections for the resonator.
resonator_bend_spec (ComponentSpec) – Specification for the bend component used in meanders.
resonator_cross_section (CrossSectionSpec) – Cross-section specification for the resonator.
resonator_open_start (bool) – If True, adds an etch section at the start of the resonator.
resonator_open_end (bool) – If True, adds an etch section at the end of the resonator.
coupler (ComponentSpec) – Coupler spec.
qubit_rotation (float) – Rotation angle for the qubit in degrees.
coupler_port (str) – Name of the qubit port to position the coupler relative to.
coupler_offset (tuple[float, float]) – (x, y) offset for the coupler position.
probeline_coupler (ComponentSpec) – Component spec for the probeline coupling section.
probeline_coupling_gap (float) – Gap between the resonator and probeline waveguides in the coupling section in µm.
probeline_coupling_length (float | None) – Length of the coupling section in µm.
- Return type:
Component
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
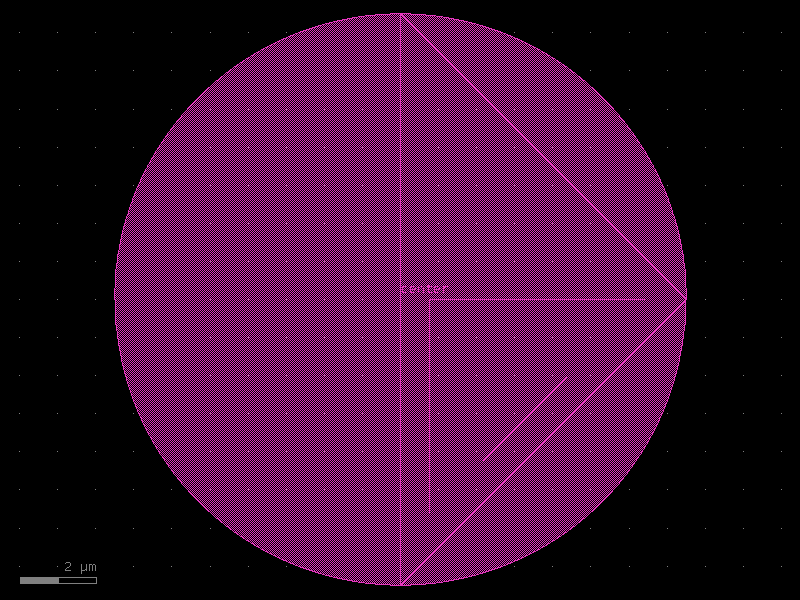
indium_bump#
- qpdk.cells.indium_bump(diameter=15.0)[source]#
Creates an indium bump component for 3D integration.
See [RKD+17] for details.
- Parameters:
diameter (float) – Diameter of the indium bump in µm.
- Returns:
A gdsfactory Component representing the indium bump.
- Return type:
Component
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
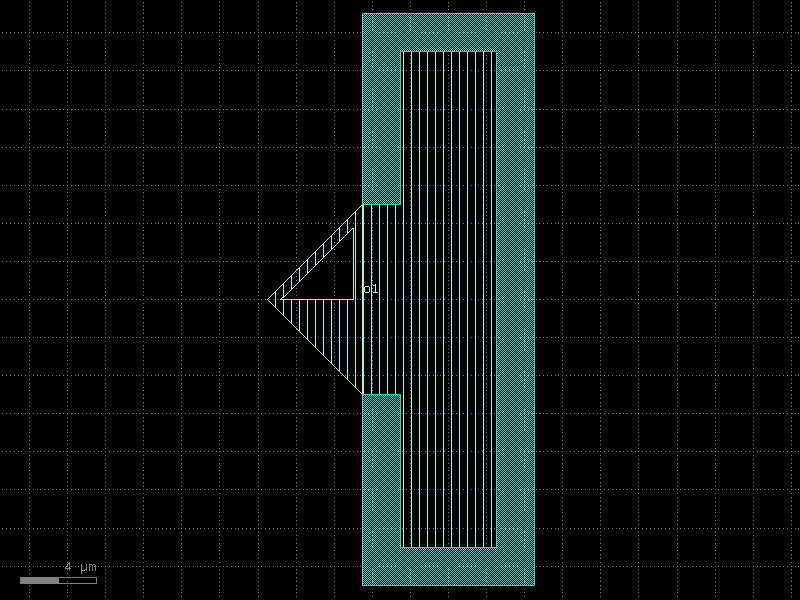
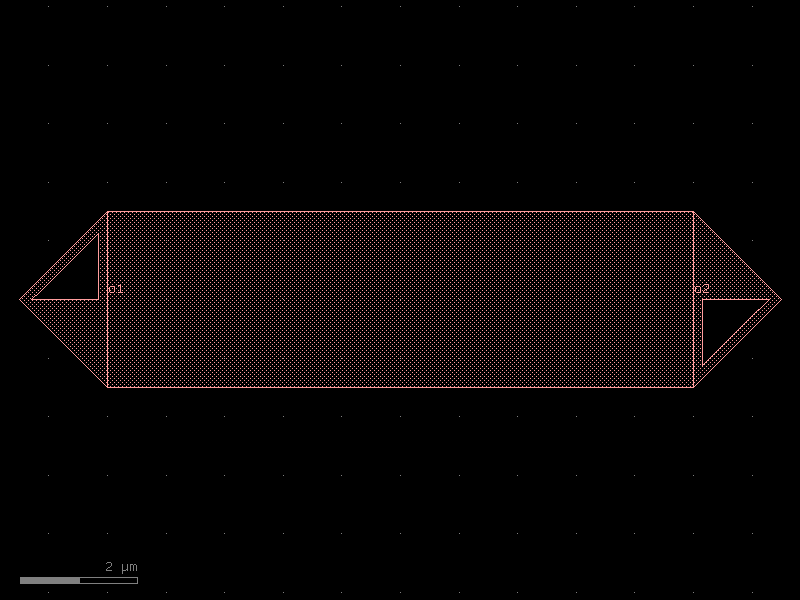
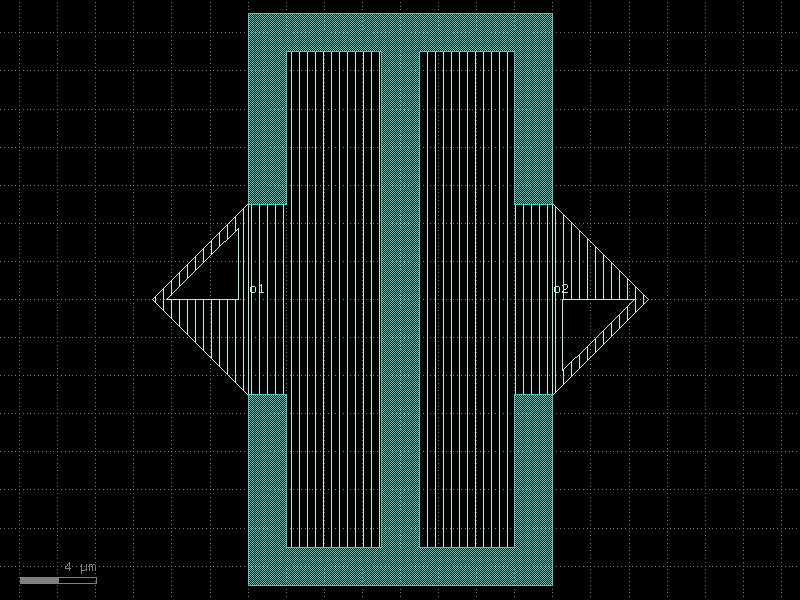
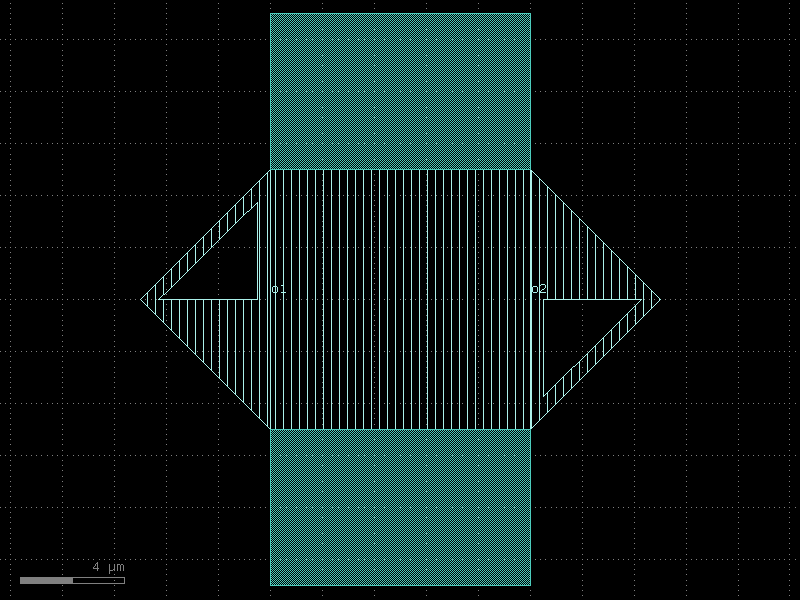
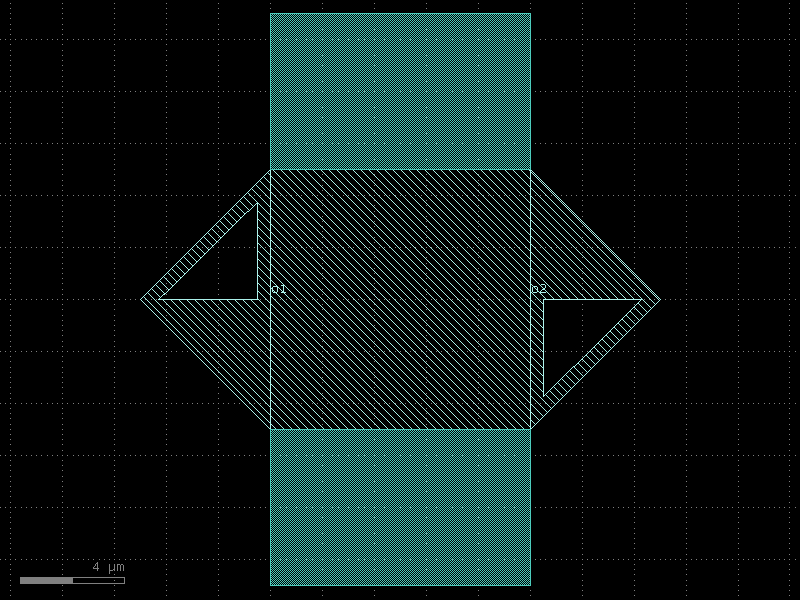
interdigital_capacitor#
- qpdk.cells.interdigital_capacitor(fingers=4, finger_length=20.0, finger_gap=2.0, thickness=5.0, etch_layer='M1_ETCH', etch_bbox_margin=2.0, cross_section='cpw', half=False)[source]#
Generate an interdigital capacitor component with ports on both ends.
An interdigital capacitor consists of interleaved metal fingers that create a distributed capacitance. This component creates a planar capacitor with two sets of interleaved fingers extending from opposite ends.
See for example [LeiZhuW00].
Note
finger_length=0effectively provides a parallel plate capacitor. The capacitance scales approximately linearly with the number of fingers and finger length.- Parameters:
fingers (int) – Total number of fingers of the capacitor (must be >= 1).
finger_length (float) – Length of each finger in μm.
finger_gap (float) – Gap between adjacent fingers in μm.
thickness (float) – Thickness of fingers and the base section in μm.
etch_layer (LayerSpec | None) – Optional layer for etching around the capacitor.
etch_bbox_margin (float) – Margin around the capacitor for the etch layer in μm.
cross_section (CrossSectionSpec) – Cross-section for the short straight from the etch box capacitor.
half (bool) – If True, creates a single-sided capacitor (half of the interdigital capacitor).
- Returns:
- A gdsfactory component with the interdigital capacitor geometry
and two ports (‘o1’ and ‘o2’) on opposing sides.
- Return type:
Component
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
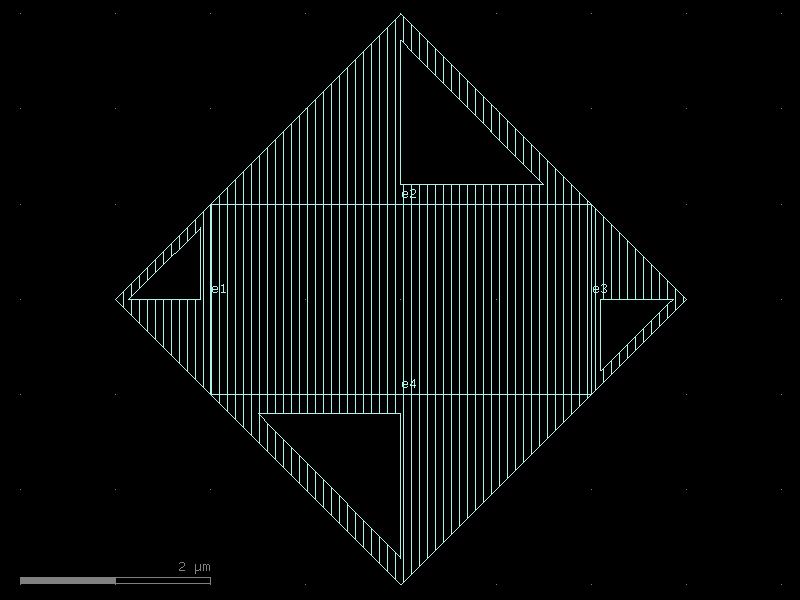
josephson_junction#
- qpdk.cells.josephson_junction(junction_overlap_displacement=1.8, wide_straight_length=8.3, narrow_straight_length=0.5, taper_length=4.7, cross_section_wide=<function josephson_junction_cross_section_wide>, cross_section_narrow=<function josephson_junction_cross_section_narrow>, layer_patch=<LayerMapQPDK.JJ_PATCH: 51>, size_patch=(1.5, 1.0))[source]#
Creates a single Josephson junction component.
A Josephson junction consists of two superconducting electrodes separated by a thin insulating barrier allowing tunnelling.
- Parameters:
junction_overlap_displacement (float) – Displacement of the overlap region in µm. Measured from the centers of the junction ports.
wide_straight_length (float) – Length of the wide straight section in µm.
narrow_straight_length (float) – Length of the narrow straight section in µm.
taper_length (float) – Length of the taper section in µm.
cross_section_wide (CrossSectionSpec) – Cross-section specification for the wide section.
cross_section_narrow (CrossSectionSpec) – Cross-section specification for the narrow section.
layer_patch (LayerSpec) – Layer for the patch that creates the overlap region.
size_patch (tuple[float, float]) – Size of the patch that creates the overlap region.
- Return type:
Component
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
josephson_junction_long#
- qpdk.cells.josephson_junction_long(**kwargs)[source]#
Josephson junction with wide_straight_length=12.
- Return type:
Component
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
launcher#
- qpdk.cells.launcher(straight_length=200.0, taper_length=100.0, cross_section_big=<function launcher_cross_section_big>, cross_section_small='cpw')[source]#
Generate an RF launcher pad for wirebonding or probe testing.
Creates a launcher component consisting of a straight section with large cross-section connected to a tapered transition down to a smaller cross-section. This design facilitates RF signal access through probes or wirebonds while maintaining good impedance matching.
The default dimensions are taken from [TSKivijarvi+25].
- Parameters:
straight_length (float) – Length of the straight, wirebond landing area, section in µm.
taper_length (float) – Length of the taper section in µm.
cross_section_big (CrossSectionSpec) – Cross-section specification for the large end of the launcher (probe/wirebond interface).
cross_section_small (CrossSectionSpec) – Cross-section specification for the small end of the launcher (circuit interface).
- Returns:
- A gdsfactory component containing the complete launcher
geometry with one output port (“o1”) at the small end.
- Return type:
Component
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
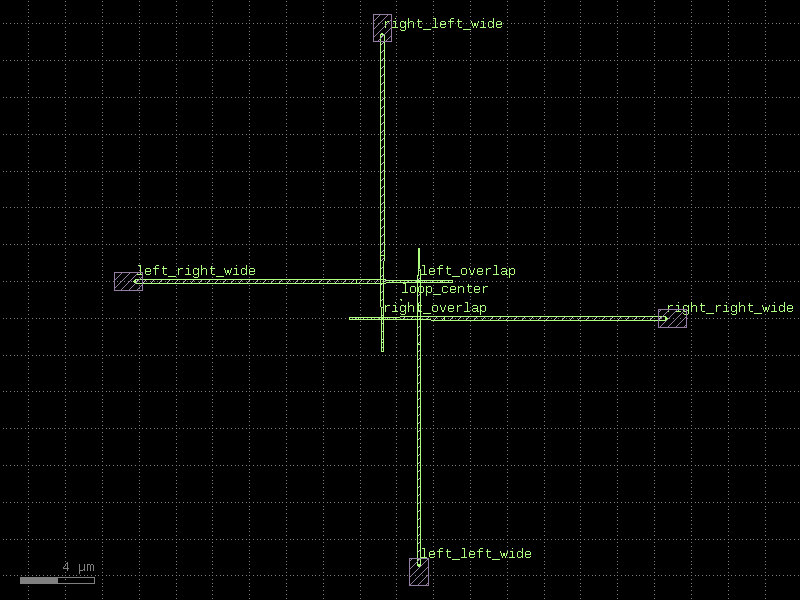
nxn#
- qpdk.cells.nxn(xsize=10.0, ysize=10.0, wg_width=10.0, layer=<LayerMapQPDK.M1_DRAW: 1>, wg_margin=0.0, north=1, east=1, south=1, west=1, cross_section=<function coplanar_waveguide>)[source]#
Returns an NxN junction with ports on each side.
- Parameters:
xsize (float) – Horizontal size of the junction in μm.
ysize (float) – Vertical size of the junction in μm.
wg_width (float) – Width of the waveguides in μm.
layer (tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum) – Layer specification.
wg_margin (float) – Margin from edge to waveguide in μm.
north (int) – Number of ports on the north side.
east (int) – Number of ports on the east side.
south (int) – Number of ports on the south side.
west (int) – Number of ports on the west side.
cross_section (CrossSection | str | dict[str, Any] | Callable[[...], CrossSection] | SymmetricalCrossSection | DCrossSection) – Cross-section specification.
- Return type:
Component
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
plate_capacitor#
- qpdk.cells.plate_capacitor(length=26.0, width=5.0, gap=7.0, etch_layer='M1_ETCH', etch_bbox_margin=2.0, cross_section='cpw')[source]#
Creates a plate capacitor.
A capacitive coupler consists of two metal pads separated by a small gap, providing capacitive coupling between circuit elements like qubits and resonators.
- Parameters:
length (float) – Length (vertical extent) of the capacitor pad in μm.
width (float) – Width (horizontal extent) of the capacitor pad in μm.
gap (float) – Gap between plates in μm.
etch_layer (LayerSpec | None) – Optional layer for etching around the capacitor.
etch_bbox_margin (float) – Margin around the capacitor for the etch layer in μm.
cross_section (CrossSectionSpec) – Cross-section for the short straight from the etch box capacitor.
- Returns:
A gdsfactory component with the plate capacitor geometry and two ports (‘o1’ and ‘o2’) on opposing sides.
- Return type:
Component
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)

plate_capacitor_single#
- qpdk.cells.plate_capacitor_single(length=26.0, width=5.0, etch_layer='M1_ETCH', etch_bbox_margin=2.0, cross_section='cpw')[source]#
Creates a single plate capacitor for coupling.
This is essentially half of a
plate_capacitor().- Parameters:
length (float) – Length (vertical extent) of the capacitor pad in μm.
width (float) – Width (horizontal extent) of the capacitor pad in μm.
etch_layer (LayerSpec | None) – Optional layer for etching around the capacitor.
etch_bbox_margin (float) – Margin around the capacitor for the etch layer in μm.
cross_section (CrossSectionSpec) – Cross-section for the short straight from the etch box capacitor.
- Returns:
A gdsfactory component with the plate capacitor geometry.
- Return type:
Component
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
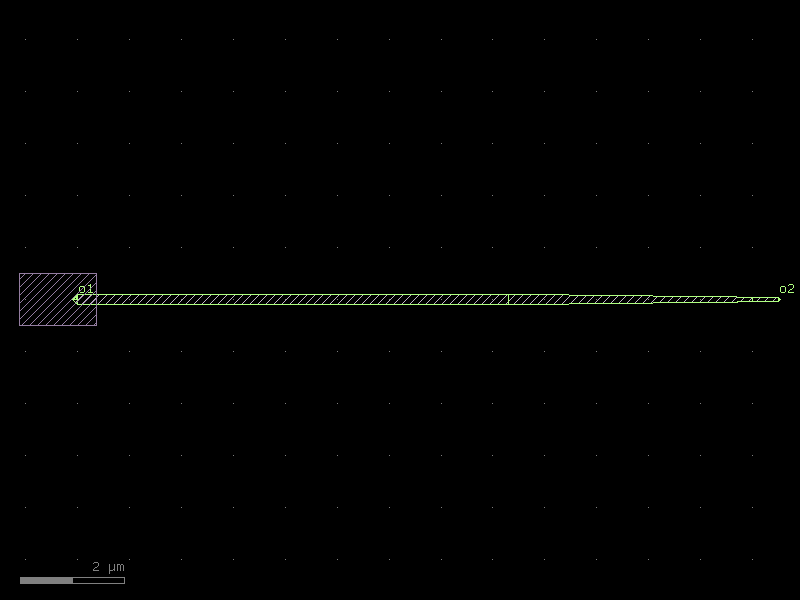

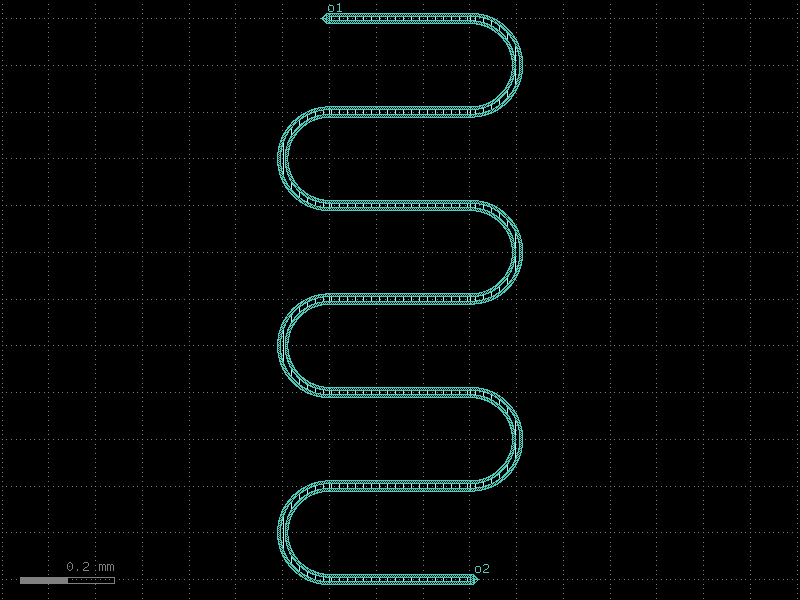
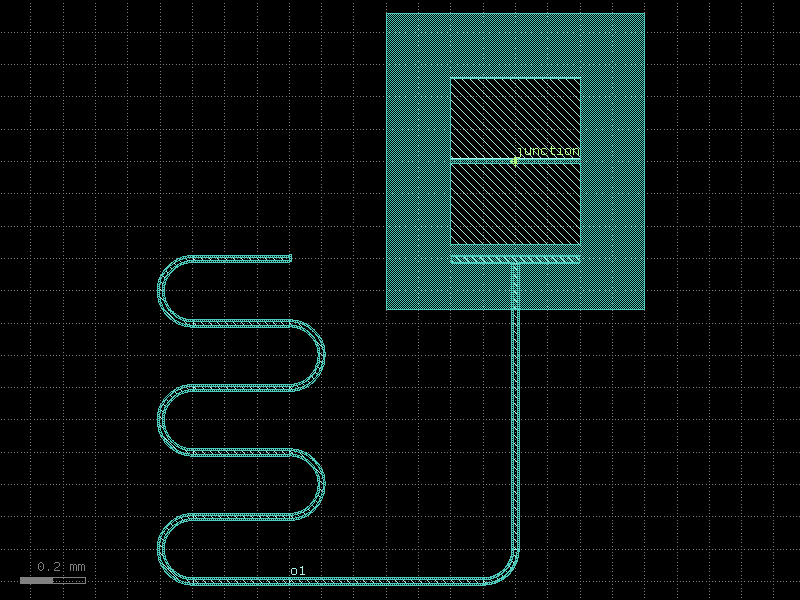
quarter_wave_resonator_coupled#
- qpdk.cells.quarter_wave_resonator_coupled(length=4000.0, meanders=6, bend_spec=<function bend_circular>, cross_section='cpw', *, start_with_bend=False, end_with_bend=False, open_start=True, open_end=False, cross_section_non_resonator='cpw', coupling_straight_length=200.0, coupling_gap=20.0)[source]#
Creates a quarter-wave resonator with a coupling waveguide.
Uses
resonator_coupled()as the basis but removes the shorted end port from the output ports.- Parameters:
length (float) – Length of the resonator in μm.
meanders (int) – Number of meander sections to fit the resonator in a compact area.
bend_spec (ComponentSpec) – Specification for the bend component used in meanders.
cross_section (CrossSectionSpec) – Cross-section specification for the resonator.
start_with_bend (bool) – If True, starts the resonator with a bend.
end_with_bend (bool) – If True, ends the resonator with a bend.
open_start (bool) – If True, adds an etch section at the start of the resonator.
open_end (bool) – If True, adds an etch section at the end of the resonator.
cross_section_non_resonator (CrossSectionSpec) – Cross-section specification for the coupling waveguide.
coupling_straight_length (float) – Length of the coupling waveguide section in μm.
coupling_gap (float) – Gap between the resonator and coupling waveguide in μm.
- Return type:
Component
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
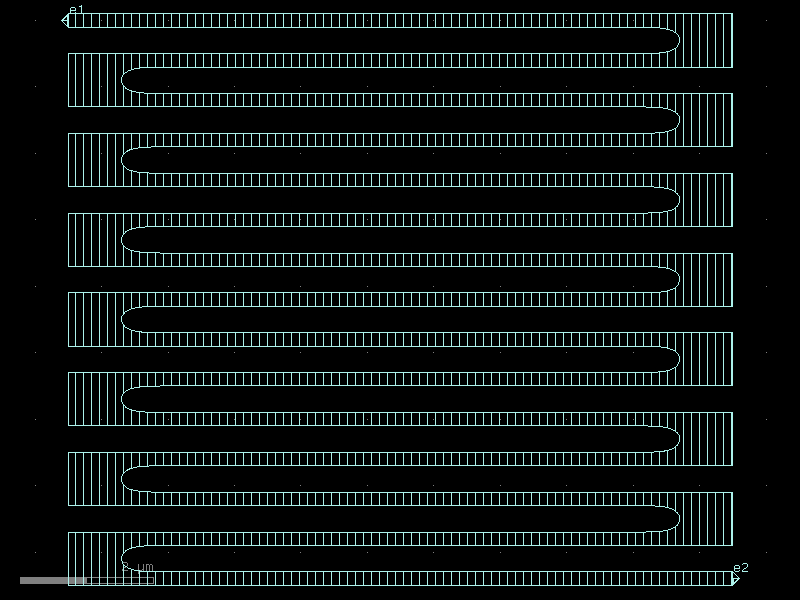

rectangle#
- qpdk.cells.rectangle(size=(4.0, 2.0), layer='M1_DRAW', centered=False, port_type='electrical', port_orientations=(180, 90, 0, -90))[source]#
Returns a rectangle.
- Parameters:
size (tuple[float, float]) – (tuple) Width and height of rectangle.
layer (tuple[int, int] | str | int | LayerEnum) – Specific layer to put polygon geometry on.
centered (bool) – True sets center to (0, 0), False sets south-west to (0, 0).
port_type (str | None) – optical, electrical.
port_orientations (tuple[int, ...] | list[int] | None) – list of port_orientations to add. None adds no ports.
- Return type:
Component
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)

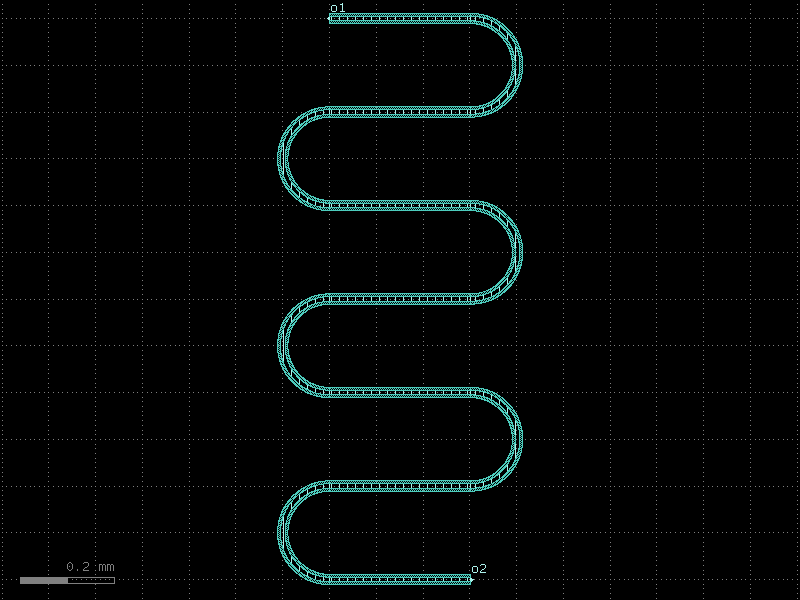
resonator#
- qpdk.cells.resonator(length=4000.0, meanders=6, bend_spec=<function bend_circular>, cross_section='cpw', *, start_with_bend=False, end_with_bend=False, open_start=True, open_end=False)[source]#
Creates a meandering coplanar waveguide resonator.
Changing open_start and open_end appropriately allows creating a shorted quarter-wave resonator or an open half-wave resonator.
See [MP12] for details
- Parameters:
length (float) – Length of the resonator in μm.
meanders (int) – Number of meander sections to fit the resonator in a compact area.
bend_spec (ComponentSpec) – Specification for the bend component used in meanders.
cross_section (CrossSectionSpec) – Cross-section specification for the resonator.
start_with_bend (bool) – If True, starts the resonator with a bend.
end_with_bend (bool) – If True, ends the resonator with a bend.
open_start (bool) – If True, adds an etch section at the start of the resonator.
open_end (bool) – If True, adds an etch section at the end of the resonator.
- Returns:
A gdsfactory component with meandering resonator geometry.
- Return type:
Component
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
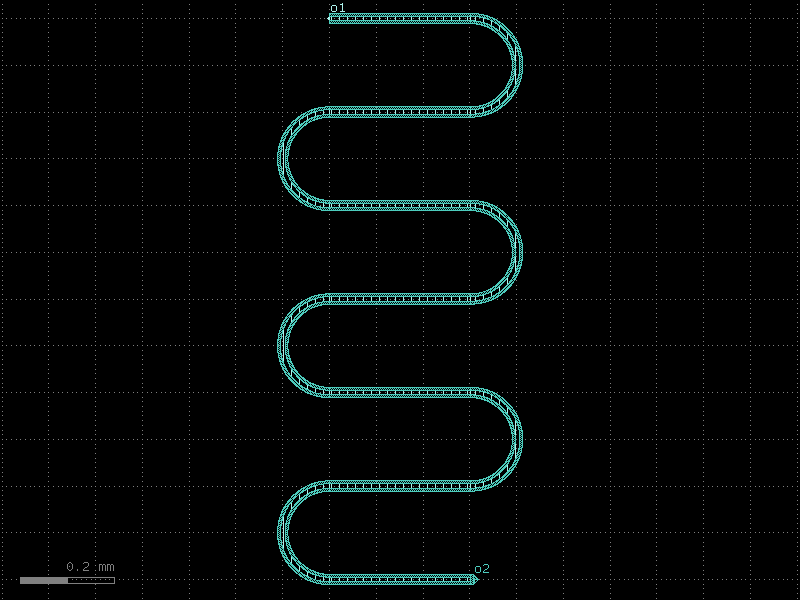
resonator_coupled#
- qpdk.cells.resonator_coupled(length=4000.0, meanders=6, bend_spec=<function bend_circular>, cross_section='cpw', *, start_with_bend=False, end_with_bend=False, open_start=True, open_end=False, cross_section_non_resonator='cpw', coupling_straight_length=200.0, coupling_gap=20.0)[source]#
Creates a meandering coplanar waveguide resonator with a coupling waveguide.
This component combines a resonator with a parallel coupling waveguide placed at a specified gap for proximity coupling. Similar to the design described in [BM18].
- Parameters:
length (float) – Length of the resonator in μm.
meanders (int) – Number of meander sections to fit the resonator in a compact area.
bend_spec (ComponentSpec) – Specification for the bend component used in meanders.
cross_section (CrossSectionSpec) – Cross-section specification for the resonator.
start_with_bend (bool) – If True, starts the resonator with a bend.
end_with_bend (bool) – If True, ends the resonator with a bend.
open_start (bool) – If True, adds an etch section at the start of the resonator.
open_end (bool) – If True, adds an etch section at the end of the resonator.
cross_section_non_resonator (CrossSectionSpec) – Cross-section specification for the coupling waveguide.
coupling_straight_length (float) – Length of the coupling waveguide section in μm.
coupling_gap (float) – Gap between the resonator and coupling waveguide in μm. Measured from edges of the center conductors.
- Returns:
A gdsfactory component with meandering resonator and coupling waveguide.
- Return type:
Component
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
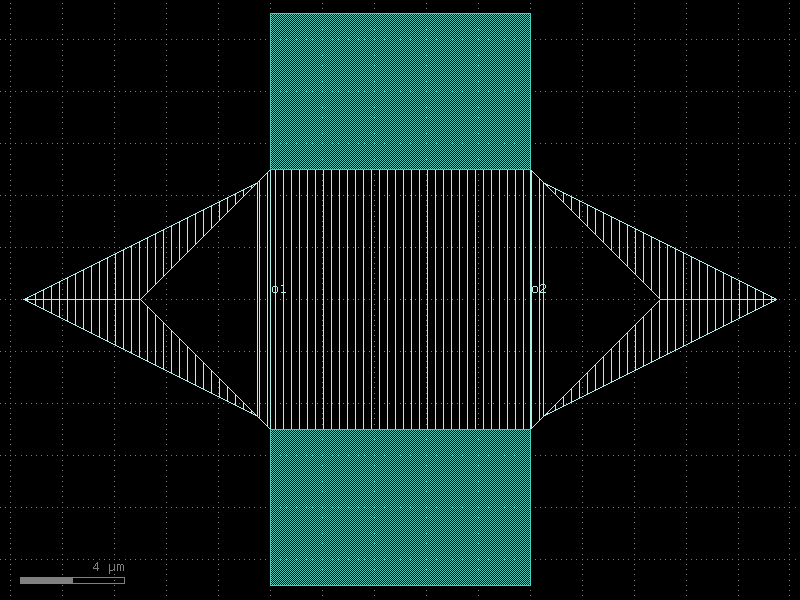
resonator_half_wave#
- qpdk.cells.resonator_half_wave(length=4000.0, meanders=6, bend_spec=<function bend_circular>, cross_section='cpw', *, start_with_bend=False, end_with_bend=False, open_start=True, open_end=True)#
Creates a meandering coplanar waveguide resonator.
Changing open_start and open_end appropriately allows creating a shorted quarter-wave resonator or an open half-wave resonator.
See [MP12] for details
- Parameters:
length (float) – Length of the resonator in μm.
meanders (int) – Number of meander sections to fit the resonator in a compact area.
bend_spec (ComponentSpec) – Specification for the bend component used in meanders.
cross_section (CrossSectionSpec) – Cross-section specification for the resonator.
start_with_bend (bool) – If True, starts the resonator with a bend.
end_with_bend (bool) – If True, ends the resonator with a bend.
open_start (bool) – If True, adds an etch section at the start of the resonator.
open_end (bool) – If True, adds an etch section at the end of the resonator.
- Returns:
A gdsfactory component with meandering resonator geometry.
- Return type:
Component
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
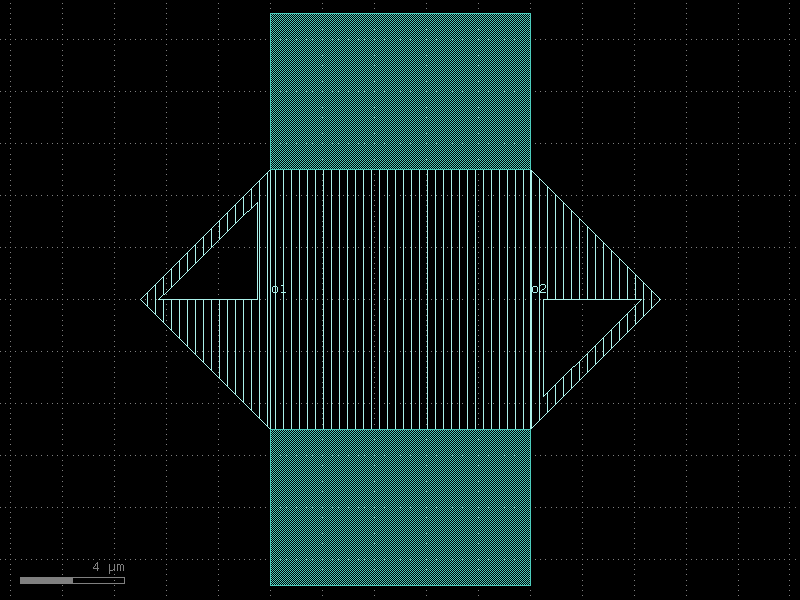
resonator_half_wave_bend_both#
- qpdk.cells.resonator_half_wave_bend_both(length=4000.0, meanders=6, bend_spec=<function bend_circular>, cross_section='cpw', *, start_with_bend=True, end_with_bend=True, open_start=True, open_end=True)#
Creates a meandering coplanar waveguide resonator.
Changing open_start and open_end appropriately allows creating a shorted quarter-wave resonator or an open half-wave resonator.
See [MP12] for details
- Parameters:
length (float) – Length of the resonator in μm.
meanders (int) – Number of meander sections to fit the resonator in a compact area.
bend_spec (ComponentSpec) – Specification for the bend component used in meanders.
cross_section (CrossSectionSpec) – Cross-section specification for the resonator.
start_with_bend (bool) – If True, starts the resonator with a bend.
end_with_bend (bool) – If True, ends the resonator with a bend.
open_start (bool) – If True, adds an etch section at the start of the resonator.
open_end (bool) – If True, adds an etch section at the end of the resonator.
- Returns:
A gdsfactory component with meandering resonator geometry.
- Return type:
Component
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
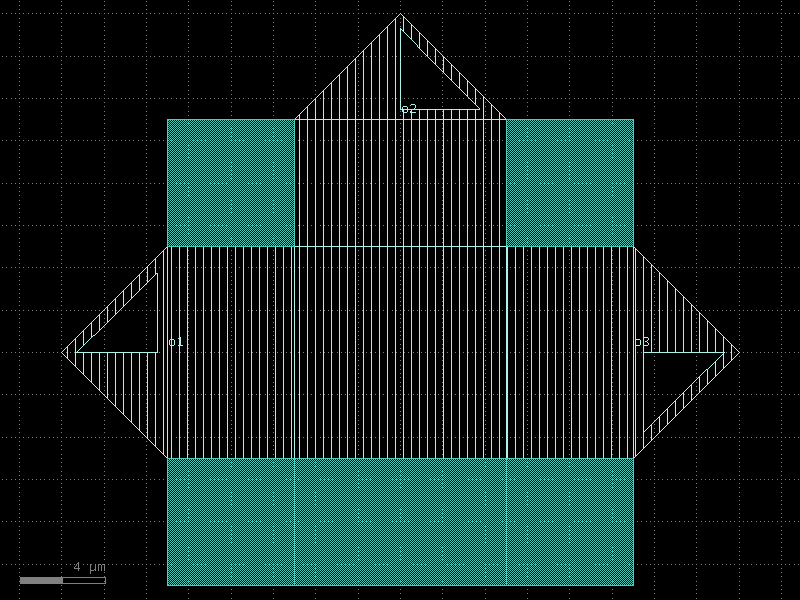
resonator_half_wave_bend_end#
- qpdk.cells.resonator_half_wave_bend_end(length=4000.0, meanders=6, bend_spec=<function bend_circular>, cross_section='cpw', *, start_with_bend=False, end_with_bend=True, open_start=True, open_end=True)#
Creates a meandering coplanar waveguide resonator.
Changing open_start and open_end appropriately allows creating a shorted quarter-wave resonator or an open half-wave resonator.
See [MP12] for details
- Parameters:
length (float) – Length of the resonator in μm.
meanders (int) – Number of meander sections to fit the resonator in a compact area.
bend_spec (ComponentSpec) – Specification for the bend component used in meanders.
cross_section (CrossSectionSpec) – Cross-section specification for the resonator.
start_with_bend (bool) – If True, starts the resonator with a bend.
end_with_bend (bool) – If True, ends the resonator with a bend.
open_start (bool) – If True, adds an etch section at the start of the resonator.
open_end (bool) – If True, adds an etch section at the end of the resonator.
- Returns:
A gdsfactory component with meandering resonator geometry.
- Return type:
Component
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
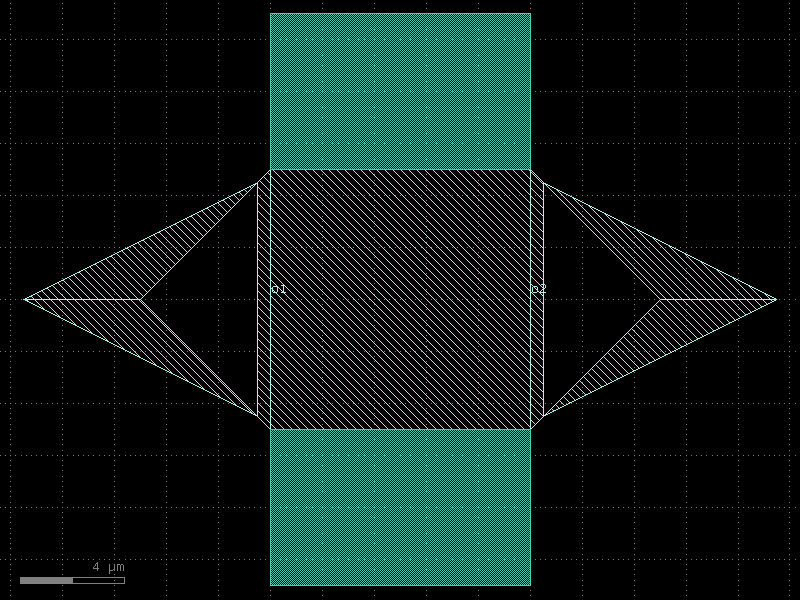
resonator_half_wave_bend_start#
- qpdk.cells.resonator_half_wave_bend_start(length=4000.0, meanders=6, bend_spec=<function bend_circular>, cross_section='cpw', *, start_with_bend=True, end_with_bend=False, open_start=True, open_end=True)#
Creates a meandering coplanar waveguide resonator.
Changing open_start and open_end appropriately allows creating a shorted quarter-wave resonator or an open half-wave resonator.
See [MP12] for details
- Parameters:
length (float) – Length of the resonator in μm.
meanders (int) – Number of meander sections to fit the resonator in a compact area.
bend_spec (ComponentSpec) – Specification for the bend component used in meanders.
cross_section (CrossSectionSpec) – Cross-section specification for the resonator.
start_with_bend (bool) – If True, starts the resonator with a bend.
end_with_bend (bool) – If True, ends the resonator with a bend.
open_start (bool) – If True, adds an etch section at the start of the resonator.
open_end (bool) – If True, adds an etch section at the end of the resonator.
- Returns:
A gdsfactory component with meandering resonator geometry.
- Return type:
Component
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
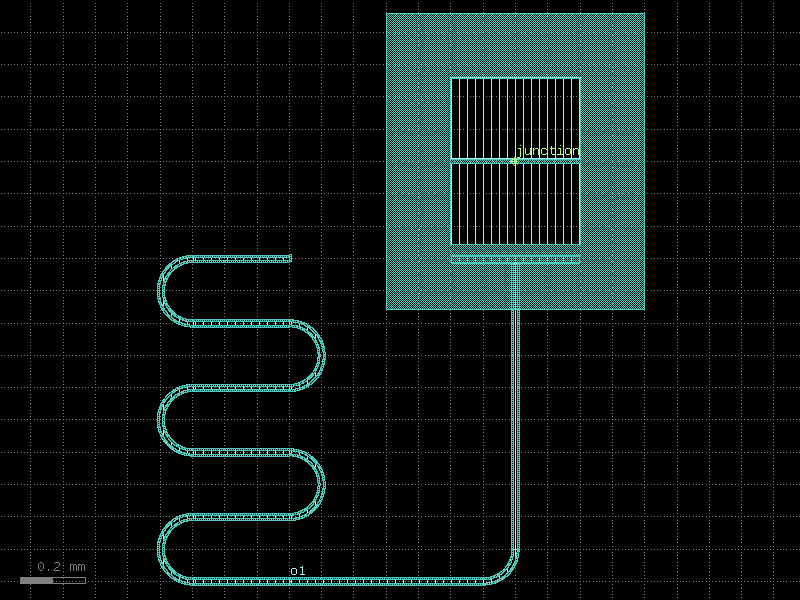
resonator_quarter_wave#
- qpdk.cells.resonator_quarter_wave(length=4000.0, meanders=6, bend_spec=<function bend_circular>, cross_section='cpw', *, start_with_bend=False, end_with_bend=False, open_start=False, open_end=True)#
Creates a meandering coplanar waveguide resonator.
Changing open_start and open_end appropriately allows creating a shorted quarter-wave resonator or an open half-wave resonator.
See [MP12] for details
- Parameters:
length (float) – Length of the resonator in μm.
meanders (int) – Number of meander sections to fit the resonator in a compact area.
bend_spec (ComponentSpec) – Specification for the bend component used in meanders.
cross_section (CrossSectionSpec) – Cross-section specification for the resonator.
start_with_bend (bool) – If True, starts the resonator with a bend.
end_with_bend (bool) – If True, ends the resonator with a bend.
open_start (bool) – If True, adds an etch section at the start of the resonator.
open_end (bool) – If True, adds an etch section at the end of the resonator.
- Returns:
A gdsfactory component with meandering resonator geometry.
- Return type:
Component
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
resonator_quarter_wave_bend_both#
- qpdk.cells.resonator_quarter_wave_bend_both(length=4000.0, meanders=6, bend_spec=<function bend_circular>, cross_section='cpw', *, start_with_bend=True, end_with_bend=True, open_start=False, open_end=True)#
Creates a meandering coplanar waveguide resonator.
Changing open_start and open_end appropriately allows creating a shorted quarter-wave resonator or an open half-wave resonator.
See [MP12] for details
- Parameters:
length (float) – Length of the resonator in μm.
meanders (int) – Number of meander sections to fit the resonator in a compact area.
bend_spec (ComponentSpec) – Specification for the bend component used in meanders.
cross_section (CrossSectionSpec) – Cross-section specification for the resonator.
start_with_bend (bool) – If True, starts the resonator with a bend.
end_with_bend (bool) – If True, ends the resonator with a bend.
open_start (bool) – If True, adds an etch section at the start of the resonator.
open_end (bool) – If True, adds an etch section at the end of the resonator.
- Returns:
A gdsfactory component with meandering resonator geometry.
- Return type:
Component
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
resonator_quarter_wave_bend_end#
- qpdk.cells.resonator_quarter_wave_bend_end(length=4000.0, meanders=6, bend_spec=<function bend_circular>, cross_section='cpw', *, start_with_bend=False, end_with_bend=True, open_start=False, open_end=True)#
Creates a meandering coplanar waveguide resonator.
Changing open_start and open_end appropriately allows creating a shorted quarter-wave resonator or an open half-wave resonator.
See [MP12] for details
- Parameters:
length (float) – Length of the resonator in μm.
meanders (int) – Number of meander sections to fit the resonator in a compact area.
bend_spec (ComponentSpec) – Specification for the bend component used in meanders.
cross_section (CrossSectionSpec) – Cross-section specification for the resonator.
start_with_bend (bool) – If True, starts the resonator with a bend.
end_with_bend (bool) – If True, ends the resonator with a bend.
open_start (bool) – If True, adds an etch section at the start of the resonator.
open_end (bool) – If True, adds an etch section at the end of the resonator.
- Returns:
A gdsfactory component with meandering resonator geometry.
- Return type:
Component
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
resonator_quarter_wave_bend_start#
- qpdk.cells.resonator_quarter_wave_bend_start(length=4000.0, meanders=6, bend_spec=<function bend_circular>, cross_section='cpw', *, start_with_bend=True, end_with_bend=False, open_start=False, open_end=True)#
Creates a meandering coplanar waveguide resonator.
Changing open_start and open_end appropriately allows creating a shorted quarter-wave resonator or an open half-wave resonator.
See [MP12] for details
- Parameters:
length (float) – Length of the resonator in μm.
meanders (int) – Number of meander sections to fit the resonator in a compact area.
bend_spec (ComponentSpec) – Specification for the bend component used in meanders.
cross_section (CrossSectionSpec) – Cross-section specification for the resonator.
start_with_bend (bool) – If True, starts the resonator with a bend.
end_with_bend (bool) – If True, ends the resonator with a bend.
open_start (bool) – If True, adds an etch section at the start of the resonator.
open_end (bool) – If True, adds an etch section at the end of the resonator.
- Returns:
A gdsfactory component with meandering resonator geometry.
- Return type:
Component
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
ring#
- qpdk.cells.ring(radius=10.0, width=0.5, angle_resolution=2.5, layer='WG', angle=360, distance_resolution=None)[source]#
Returns a ring.
- Parameters:
radius (float) – ring radius.
width (float) – of the ring.
angle_resolution (float) – max number of degrees per point.
layer (LayerSpec) – layer.
angle (float) – angular coverage of the ring
distance_resolution (float | None) – max distance between points. This is an alternate way to describe the resolution besides setting angle_resolution. If distance_resolution and angle_resolution are both set, distance_resolution determines the resolution.
- Return type:
Component
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
single_josephson_junction_wire#
- qpdk.cells.single_josephson_junction_wire(wide_straight_length=8.3, narrow_straight_length=0.5, taper_length=4.7, cross_section_wide=<function josephson_junction_cross_section_wide>, cross_section_narrow=<function josephson_junction_cross_section_narrow>, layer_patch=<LayerMapQPDK.JJ_PATCH: 51>, size_patch=(1.5, 1.0))[source]#
Creates a single wire to use in a Josephson junction.
- Parameters:
wide_straight_length (float) – Length of the wide straight section in µm.
narrow_straight_length (float) – Length of the narrow straight section in µm.
taper_length (float) – Length of the taper section in µm.
cross_section_wide (CrossSectionSpec) – Cross-section specification for the wide section.
cross_section_narrow (CrossSectionSpec) – Cross-section specification for the narrow section.
layer_patch (LayerSpec) – Layer for the patch that creates the overlap region.
size_patch (tuple[float, float]) – Size of the patch that creates the overlap region.
- Return type:
Component
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
snspd#
- qpdk.cells.snspd(wire_width=0.2, wire_pitch=0.6, size=(10, 8), num_squares=None, turn_ratio=4, terminals_same_side=False, layer='M1_DRAW', port_type='electrical')[source]#
Creates an optimally-rounded SNSPD.
- Parameters:
wire_width (float) – Width of the wire.
wire_pitch (float) – Distance between two adjacent wires. Must be greater than width.
size (tuple[float, float]) – Float2 (width, height) of the rectangle formed by the outer boundary of the SNSPD.
num_squares (int | None) – int | None = None Total number of squares inside the SNSPD length.
turn_ratio (float) – float Specifies how much of the SNSPD width is dedicated to the 180 degree turn. A turn_ratio of 10 will result in 20% of the width being comprised of the turn.
terminals_same_side (bool) – If True, both ports will be located on the same side of the SNSPD.
layer (LayerSpec) – layer spec to put polygon geometry on.
port_type (str) – type of port to add to the component.
- Return type:
Component
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)

squid_junction#
- qpdk.cells.squid_junction(junction_spec=<function josephson_junction>, loop_area=4)[source]#
Creates a SQUID (Superconducting Quantum Interference Device) junction component.
A SQUID consists of two Josephson junctions connected in parallel, forming a loop.
See [CB04] for details.
- Parameters:
junction_spec (ComponentSpec) – Component specification for the Josephson junction component.
loop_area (float) – Area of the SQUID loop in µm². This does not take into account the junction wire widths.
- Return type:
Component
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)

squid_junction_long#
- qpdk.cells.squid_junction_long(**kwargs)[source]#
SQUID junction with josephson_junction_long.
- Return type:
Component
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
straight#
- qpdk.cells.straight(length=10.0, cross_section=<function coplanar_waveguide>, width=None, npoints=2)[source]#
Returns a straight waveguide.
- Parameters:
length (float) – Length of the straight waveguide in μm.
cross_section (CrossSection | str | dict[str, Any] | Callable[[...], CrossSection] | SymmetricalCrossSection | DCrossSection) – Cross-section specification.
width (float | None) – Optional width override in μm.
npoints (int) – Number of points for the waveguide.
- Return type:
Component
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
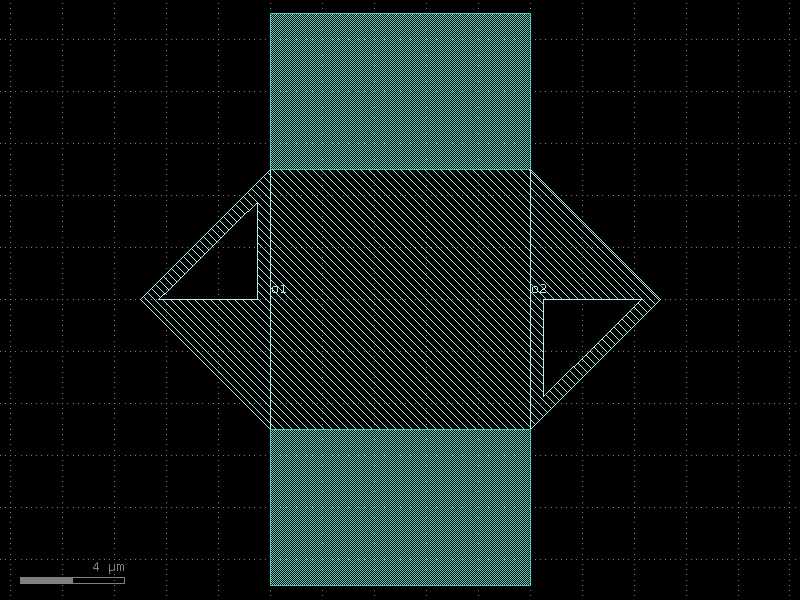
straight_all_angle#
- qpdk.cells.straight_all_angle(length=10.0, npoints=2, cross_section=<function coplanar_waveguide>, width=None)[source]#
Returns a Straight waveguide with offgrid ports.
- Parameters:
length (float) – Length of the straight waveguide in μm.
npoints (int) – Number of points for the waveguide.
cross_section (CrossSection | str | dict[str, Any] | Callable[[...], CrossSection] | SymmetricalCrossSection | DCrossSection) – Cross-section specification.
width (float | None) – Optional width override in μm.
- Return type:
ComponentAllAngle
o1 ──────────────── o2 length
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
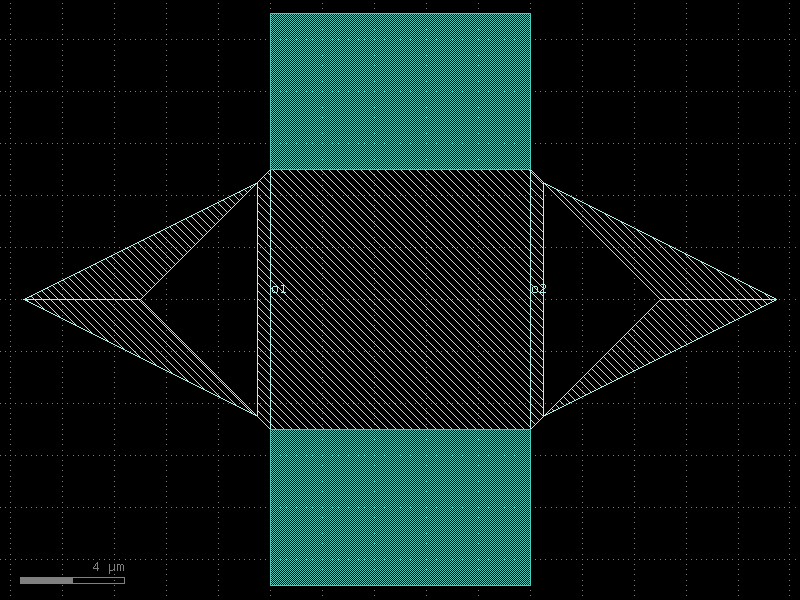
straight_double_open#
- qpdk.cells.straight_double_open(length=10.0, cross_section=<function coplanar_waveguide>, width=None, npoints=2)[source]#
Returns a straight waveguide with etched gaps at both ends.
Note
This may be treated as a \(\lambda/2\) straight resonator in some contexts.
- Parameters:
length (float) – Length of the straight waveguide in μm.
cross_section (CrossSection | str | dict[str, Any] | Callable[[...], CrossSection] | SymmetricalCrossSection | DCrossSection) – Cross-section specification.
width (float | None) – Optional width override in μm.
npoints (int) – Number of points for the waveguide.
- Return type:
Component
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
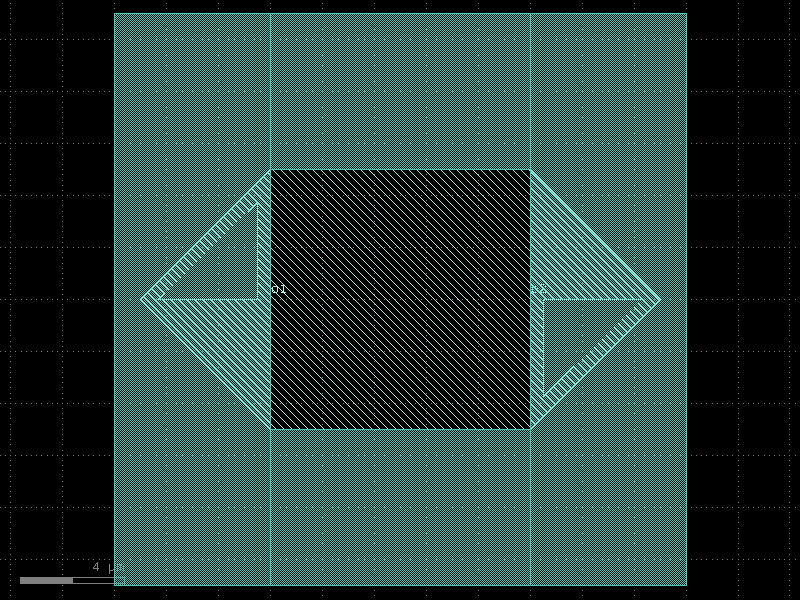
straight_open#
- qpdk.cells.straight_open(length=10.0, cross_section=<function coplanar_waveguide>, width=None, npoints=2)[source]#
Returns a straight waveguide with etched gap at one end.
- Parameters:
length (float) – Length of the straight waveguide in μm.
cross_section (CrossSection | str | dict[str, Any] | Callable[[...], CrossSection] | SymmetricalCrossSection | DCrossSection) – Cross-section specification.
width (float | None) – Optional width override in μm.
npoints (int) – Number of points for the waveguide.
- Return type:
Component
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
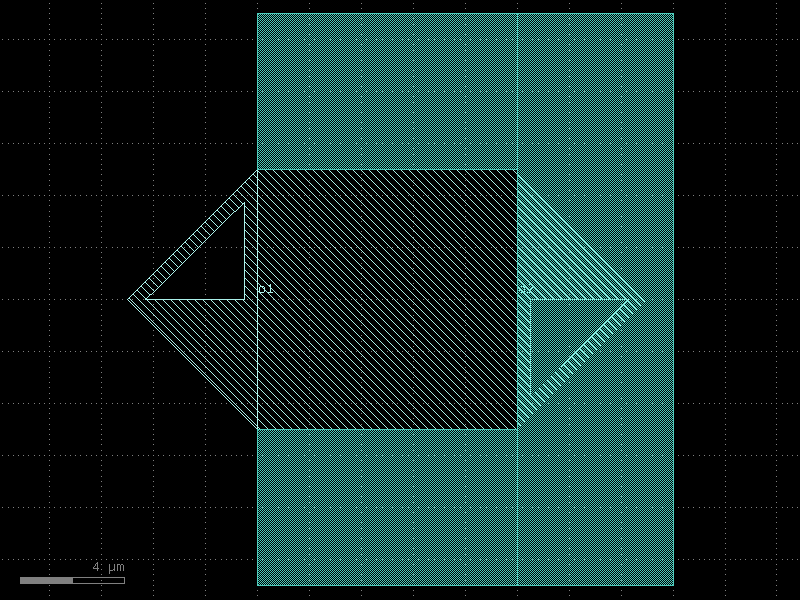
straight_shorted#
- qpdk.cells.straight_shorted(length=10.0, cross_section=<function coplanar_waveguide>, width=None, npoints=2)#
Returns a straight waveguide.
- Parameters:
length (float) – Length of the straight waveguide in μm.
cross_section (CrossSection | str | dict[str, Any] | Callable[[...], CrossSection] | SymmetricalCrossSection | DCrossSection) – Cross-section specification.
width (float | None) – Optional width override in μm.
npoints (int) – Number of points for the waveguide.
- Return type:
Component
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
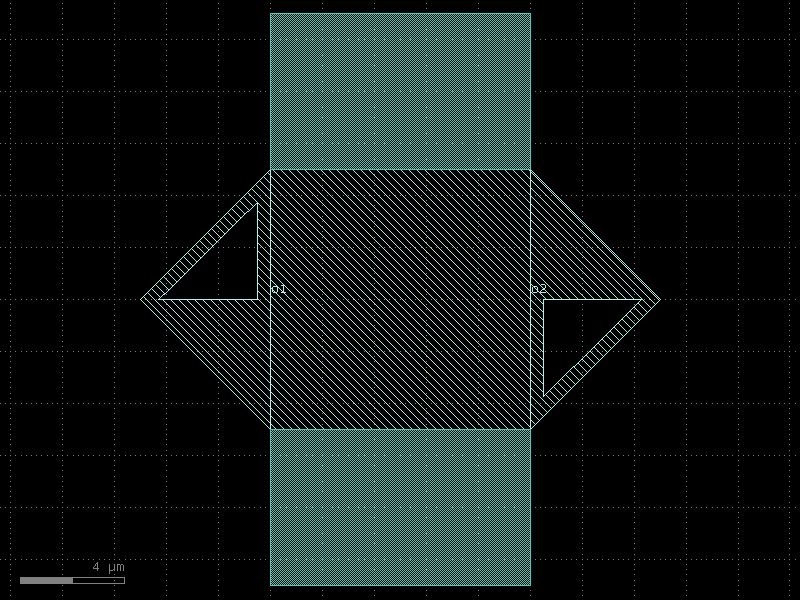
taper_cross_section#
- qpdk.cells.taper_cross_section(*, cross_section1='cpw', cross_section2='cpw', length=10, npoints=100, linear=False, width_type='sine')#
Returns taper transition between cross_section1 and cross_section2.
- Parameters:
cross_section1 (CrossSectionSpec) – start cross_section factory.
cross_section2 (CrossSectionSpec) – end cross_section factory.
length (float) – transition length.
npoints (int) – number of points.
linear (bool) – shape of the transition, sine when False.
width_type (str) – shape of the transition ONLY IF linear is False
- Return type:
Component
_____________________ / _______/______________________ / cross_section1 | cross_section2 ______\_______________________ \ \_____________________
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
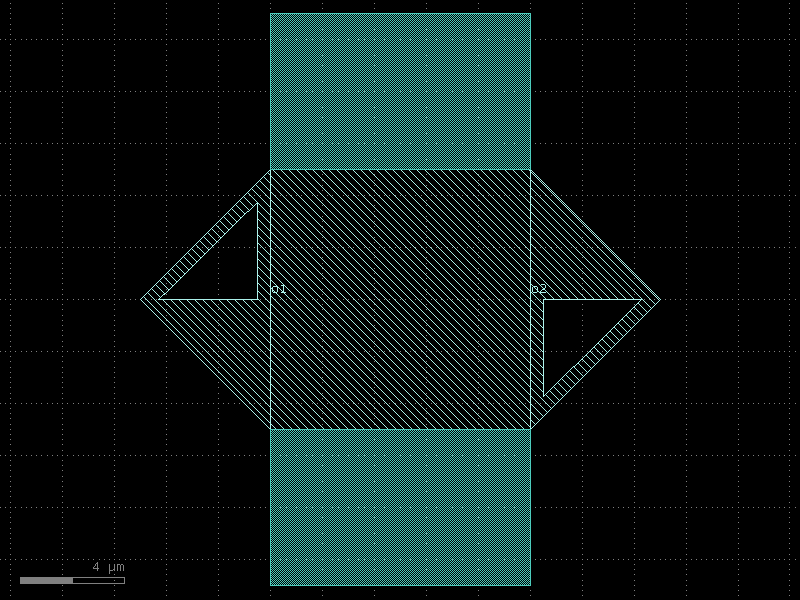
tee#
- qpdk.cells.tee(cross_section='cpw')[source]#
Returns a three-way tee waveguide.
- Parameters:
cross_section (CrossSection | str | dict[str, Any] | Callable[[...], CrossSection] | SymmetricalCrossSection | DCrossSection) – specification (CrossSection, string or dict).
- Return type:
Component
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
transform_component#
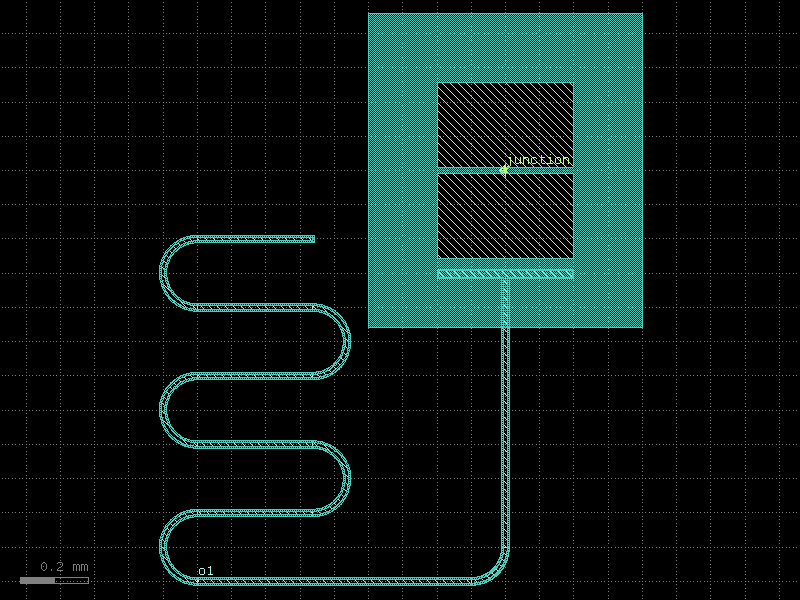
transmon_with_resonator#
- qpdk.cells.transmon_with_resonator(qubit='double_pad_transmon_with_bbox', resonator=functools.partial(<function resonator>, open_start=False, open_end=True, start_with_bend=True, length=4000, meanders=6), resonator_meander_start=(-900, -1200), resonator_length=5000.0, resonator_meanders=5, resonator_bend_spec='bend_circular', resonator_cross_section='cpw', resonator_open_start=False, resonator_open_end=True, coupler=functools.partial(<function plate_capacitor_single>, width=20, length=394), qubit_rotation=90, coupler_port='left_pad', coupler_offset=(-45, 0))[source]#
Returns a transmon qubit coupled to a quarter wave resonator.
- Parameters:
qubit (ComponentSpec) – Qubit component.
resonator (ComponentSpec) – Resonator component.
resonator_meander_start (tuple[float, float]) – (x, y) position of the start of the resonator meander.
resonator_length (float) – Length of the resonator in µm.
resonator_meanders (int) – Number of meander sections for the resonator.
resonator_bend_spec (ComponentSpec) – Specification for the bend component used in meanders.
resonator_cross_section (CrossSectionSpec) – Cross-section specification for the resonator.
resonator_open_start (bool) – If True, adds an etch section at the start of the resonator.
resonator_open_end (bool) – If True, adds an etch section at the end of the resonator.
coupler (ComponentSpec) – Coupler spec.
qubit_rotation (float) – Rotation angle for the qubit in degrees.
coupler_port (str) – Name of the qubit port to position the coupler relative to.
coupler_offset (tuple[float, float]) – (x, y) offset for the coupler position.
- Return type:
Component
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
transmon_with_resonator_and_probeline#
- qpdk.cells.transmon_with_resonator_and_probeline(qubit='double_pad_transmon_with_bbox', resonator=functools.partial(<function resonator>, open_start=False, open_end=True, start_with_bend=True, length=4000, meanders=6), resonator_meander_start=(-900, -1200), resonator_length=5000.0, resonator_meanders=5, resonator_bend_spec='bend_circular', resonator_cross_section='cpw', resonator_open_start=False, resonator_open_end=True, coupler=functools.partial(<function plate_capacitor_single>, width=20, length=394), qubit_rotation=90, coupler_port='left_pad', coupler_offset=(-45, 0), probeline_coupler=functools.partial(<function coupler_straight>, cross_section='cpw', gap=16), probeline_coupling_gap=16.0, probeline_coupling_length=None)[source]#
Returns a transmon qubit coupled to a quarter wave resonator and a probeline.
Uses a
coupler_straight()to couple the resonator to a probeline. The coupling section is inserted at the start of the resonator meander, with one waveguide carrying the resonator signal and the other providing ports for probeline routing.- Parameters:
qubit (ComponentSpec) – Qubit component.
resonator (ComponentSpec) – Resonator component.
resonator_meander_start (tuple[float, float]) – (x, y) position of the start of the resonator meander.
resonator_length (float) – Length of the resonator in µm.
resonator_meanders (int) – Number of meander sections for the resonator.
resonator_bend_spec (ComponentSpec) – Specification for the bend component used in meanders.
resonator_cross_section (CrossSectionSpec) – Cross-section specification for the resonator.
resonator_open_start (bool) – If True, adds an etch section at the start of the resonator.
resonator_open_end (bool) – If True, adds an etch section at the end of the resonator.
coupler (ComponentSpec) – Coupler spec.
qubit_rotation (float) – Rotation angle for the qubit in degrees.
coupler_port (str) – Name of the qubit port to position the coupler relative to.
coupler_offset (tuple[float, float]) – (x, y) offset for the coupler position.
probeline_coupler (ComponentSpec) – Component spec for the probeline coupling section.
probeline_coupling_gap (float) – Gap between the resonator and probeline waveguides in the coupling section in µm.
probeline_coupling_length (float | None) – Length of the coupling section in µm.
- Return type:
Component
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
tsv#
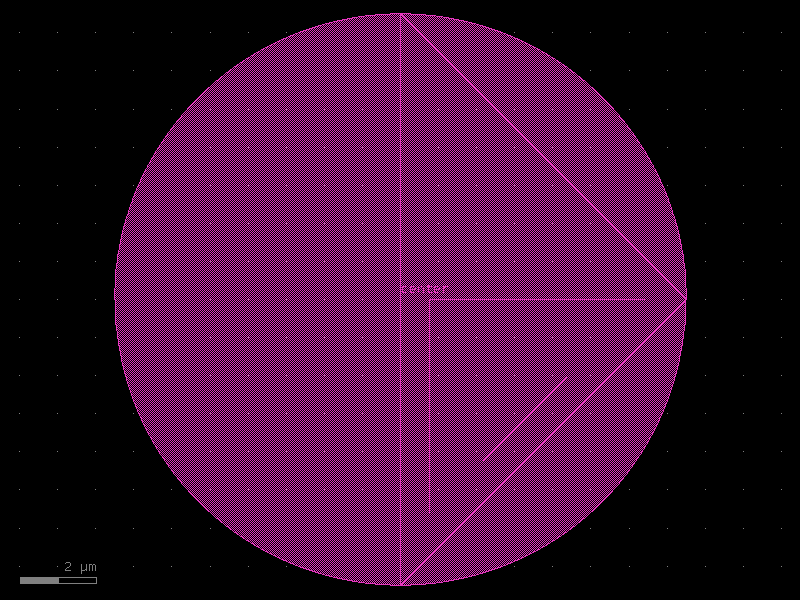
- qpdk.cells.tsv(diameter=15.0)[source]#
Creates a Through-silicon via (TSV) component for 3D integration.
See [YSM+20].
- Parameters:
diameter (float) – Diameter of the via in µm.
- Returns:
A gdsfactory Component representing the TSV.
- Return type:
Component
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
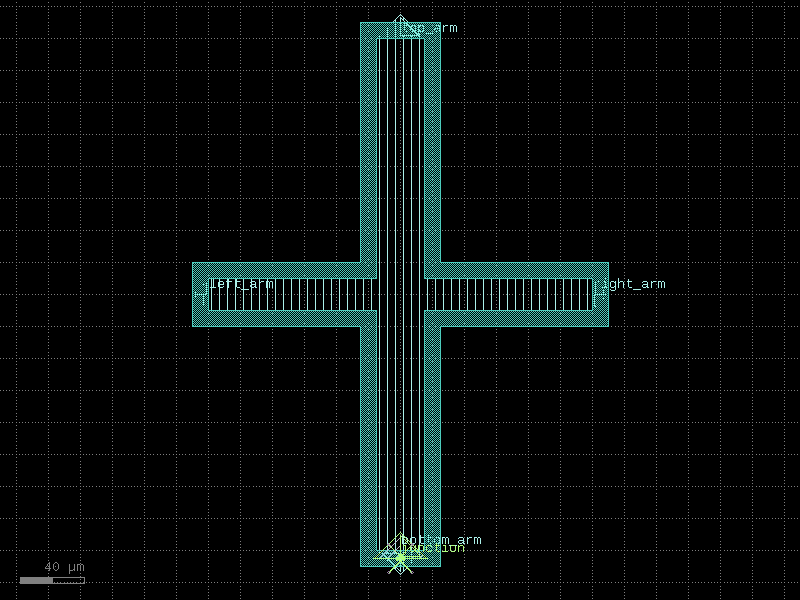
xmon_transmon#
- qpdk.cells.xmon_transmon(arm_width=(30.0, 20.0, 30.0, 20.0), arm_lengths=(160.0, 120.0, 160.0, 120.0), gap_width=10.0, junction_spec=<function squid_junction>, junction_displacement=None, layer_metal=<LayerMapQPDK.M1_DRAW: 1>, layer_etch=<LayerMapQPDK.M1_ETCH: 47>)[source]#
Creates an Xmon style transmon qubit with cross-shaped geometry.
An Xmon transmon consists of a cross-shaped capacitor pad with four arms extending from a central region, connected by a Josephson junction at the center. The design provides better control over the coupling to readout resonators and neighboring qubits through the individual arm geometries.
See [BKM+13] for details about the Xmon design.
- Parameters:
arm_width (tuple[float, float, float, float]) – Tuple of (top, right, bottom, left) arm widths in μm.
arm_lengths (tuple[float, float, float, float]) – Tuple of (top, right, bottom, left) arm lengths in μm. Computed from center to end of each arm.
gap_width (float) – Width of the etched gap around arms in μm.
junction_spec (ComponentSpec) – Component specification for the Josephson junction component.
junction_displacement (DCplxTrans | None) – Optional complex transformation to apply to the junction.
layer_metal (LayerSpec) – Layer for the metal pads.
layer_etch (LayerSpec) – Layer for the etched regions.
- Returns:
A gdsfactory component with the Xmon transmon geometry.
- Return type:
Component
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)

References#
R. Barends, J. Kelly, A. Megrant, D. Sank, E. Jeffrey, Y. Chen, Y. Yin, B. Chiaro, J. Mutus, C. Neill, P. O'Malley, P. Roushan, J. Wenner, T. C. White, A. N. Cleland, and John M. Martinis. Coherent Josephson Qubit Suitable for Scalable Quantum Integrated Circuits. Physical Review Letters, 111(8):080502, August 2013. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.111.080502.
Ilya Besedin and Alexey P Menushenkov. Quality factor of a transmission line coupled coplanar waveguide resonator. EPJ Quantum Technology, 5(1):2, December 2018. doi:10.1140/epjqt/s40507-018-0066-3.
John Clarke and Alex I. Braginski. The SQUID Handbook. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2004. ISBN 978-3-527-40229-8.
Jens Koch, Terri M. Yu, Jay Gambetta, A. A. Houck, D. I. Schuster, J. Majer, Alexandre Blais, M. H. Devoret, S. M. Girvin, and R. J. Schoelkopf. Charge-insensitive qubit design derived from the Cooper pair box. Physical Review A, 76(4):042319, October 2007. doi:10.1103/PhysRevA.76.042319.
Xuegang Li, Junhua Wang, Yao-Yao Jiang, Guang-Ming Xue, Xiaoxia Cai, Jun Zhou, Ming Gong, Zhao-Feng Liu, Shuang-Yu Zheng, Deng-Ke Ma, Mo Chen, Wei-Jie Sun, Shuang Yang, Fei Yan, Yi-Rong Jin, S. P. Zhao, Xue-Feng Ding, and Hai-Feng Yu. Cosmic-ray-induced correlated errors in superconducting qubit array. Nature Communications, 16(1):4677, May 2025. doi:10.1038/s41467-025-59778-z.
Xuegang Li, Yingshan Zhang, Chuhong Yang, Zhiyuan Li, Junhua Wang, Tang Su, Mo Chen, Yongchao Li, Chengyao Li, Zhenyu Mi, Xuehui Liang, Chenlu Wang, Zhen Yang, Yulong Feng, Kehuan Linghu, Huikai Xu, Jiaxiu Han, Weiyang Liu, Peng Zhao, Teng Ma, Ruixia Wang, Jingning Zhang, Yu Song, Pei Liu, Ziting Wang, Zhaohua Yang, Guangming Xue, Yirong Jin, and Haifeng Yu. Vacuum-gap transmon qubits realized using flip-chip technology. Applied Physics Letters, 119(18):184003, November 2021. doi:10.1063/5.0068255.
David M. Pozar. Microwave Engineering. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 4 edition, 2012. ISBN 978-0-470-63155-3.
D. Rosenberg, D. Kim, R. Das, D. Yost, S. Gustavsson, D. Hover, P. Krantz, A. Melville, L. Racz, G. O. Samach, S. J. Weber, F. Yan, J. L. Yoder, A. J. Kerman, and W. D. Oliver. 3D integrated superconducting qubits. npj Quantum Information, 3(1):42, October 2017. doi:10.1038/s41534-017-0044-0.
Mikko Tuokkola, Yoshiki Sunada, Heidi Kivijärvi, Jonatan Albanese, Leif Grönberg, Jukka-Pekka Kaikkonen, Visa Vesterinen, Joonas Govenius, and Mikko Möttönen. Methods to achieve near-millisecond energy relaxation and dephasing times for a superconducting transmon qubit. Nature Communications, 16(1):5421, July 2025. doi:10.1038/s41467-025-61126-0.
D. R. W. Yost, M. E. Schwartz, J. Mallek, D. Rosenberg, C. Stull, J. L. Yoder, G. Calusine, M. Cook, R. Das, A. L. Day, E. B. Golden, D. K. Kim, A. Melville, B. M. Niedzielski, W. Woods, A. J. Kerman, and W. D. Oliver. Solid-state qubits integrated with superconducting through-silicon vias. npj Quantum Information, 6(1):59, July 2020. doi:10.1038/s41534-020-00289-8.
Lei Zhu and Ke Wu. Accurate circuit model of interdigital capacitor and its application to design of new quasi-lumped miniaturized filters with suppression of harmonic resonance. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 48(3):347–356, March 2000. doi:10.1109/22.826833.
