gdsfactory.routing.get_route#
- gdsfactory.routing.get_route(input_port: Port, output_port: Port, bend: ComponentSpec = <function bend_euler>, with_sbend: bool = False, straight: ComponentSpec = <function straight>, taper: ComponentSpec | None = None, start_straight_length: float | None = None, end_straight_length: float | None = None, min_straight_length: float = 0.01, auto_widen: bool = False, auto_widen_minimum_length: float = 100, taper_length: float = 10, width_wide: float = 2, cross_section: None | CrossSectionSpec | MultiCrossSectionAngleSpec = 'xs_sc', **kwargs) Route[source]#
Returns a Manhattan Route between 2 ports.
The references are straights, bends and tapers. get_route is an automatic version of get_route_from_steps.
- Parameters:
input_port – start port.
output_port – end port.
bend – bend spec.
with_sbend – add sbend in case there are routing errors.
straight – straight spec.
taper – taper spec.
start_straight_length – length of starting straight.
end_straight_length – length of end straight.
min_straight_length – min length of straight for any intermediate segment.
auto_widen – auto widen the straights.
auto_widen_minimum_length – minimum length to auto widen.
taper_length – length of taper.
width_wide – width of the wider straight.
cross_section – spec.
kwargs – cross_section settings.
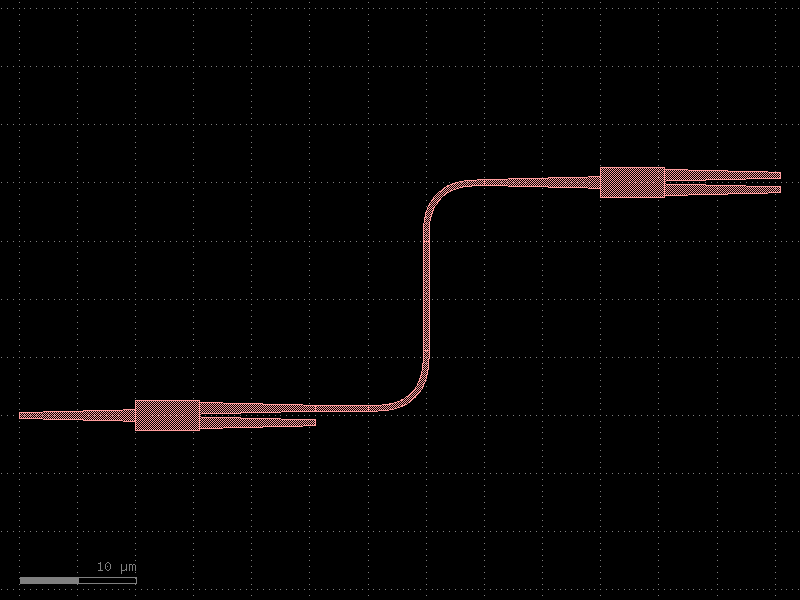
import gdsfactory as gf c = gf.Component('sample_connect') mmi1 = c << gf.components.mmi1x2() mmi2 = c << gf.components.mmi1x2() mmi2.move((40, 20)) route = gf.routing.get_route(mmi1.ports["o2"], mmi2.ports["o1"], radius=5) c.add(route.references) c.plot()
(
Source code,png,hires.png,pdf)