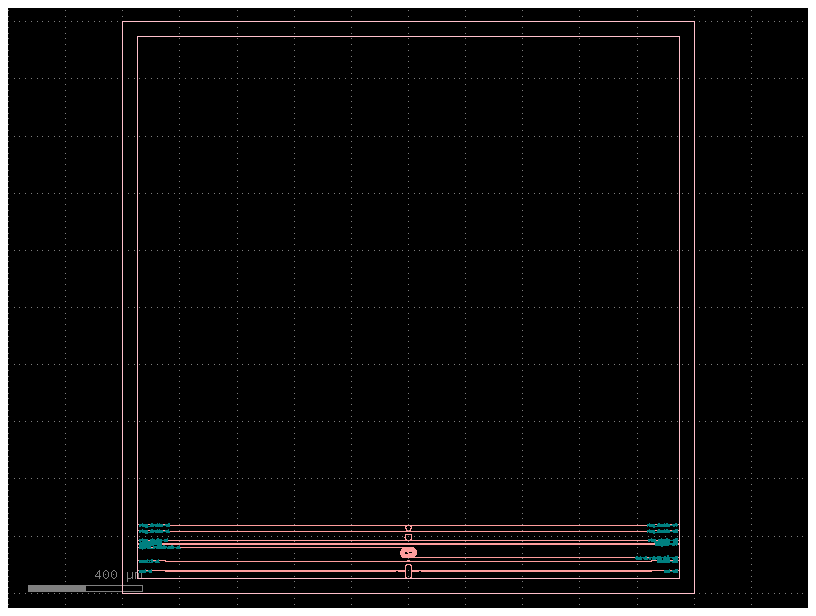
Routing to IO#
Routing electrical#
For routing low speed DC electrical ports you can use sharp corners instead of smooth bends.
You can also define port.orientation = None to ignore the port orientation for low speed DC ports.
For single route between ports you can use get_route_electrical
get_route_electrical#
get_route_electrical has bend = wire_corner with a 90deg bend corner.
from functools import partial
import gdsfactory as gf
from gdsfactory.generic_tech import get_generic_pdk
from gdsfactory.samples.big_device import big_device
gf.config.rich_output()
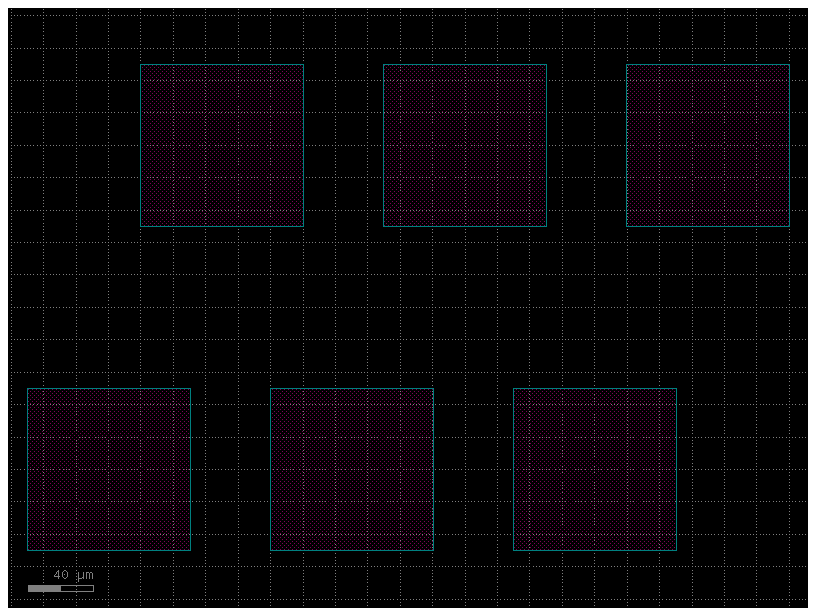
c = gf.Component("pads")
pt = c << gf.components.pad_array(orientation=270, columns=3)
pb = c << gf.components.pad_array(orientation=90, columns=3)
pt.move((70, 200))
c.plot()
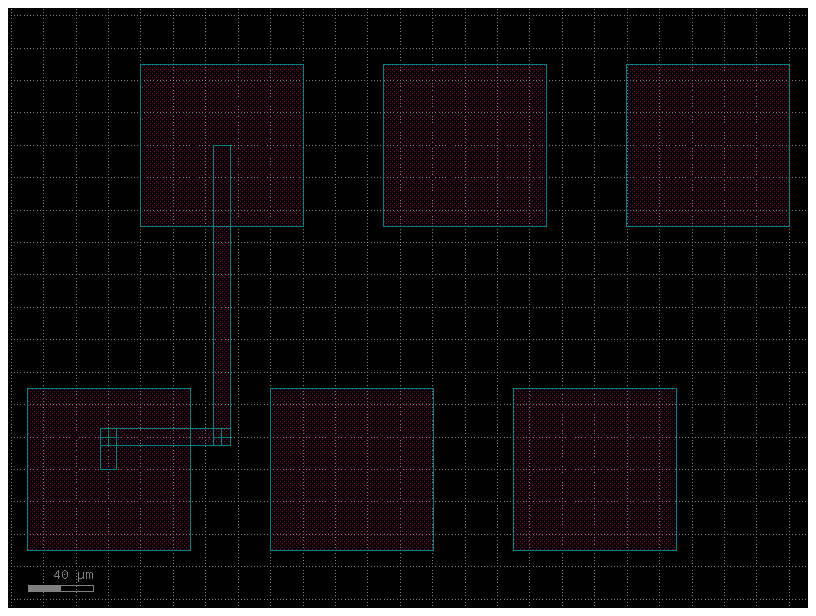
c = gf.Component("pads_with_routes_with_bends")
pt = c << gf.components.pad_array(orientation=270, columns=3)
pb = c << gf.components.pad_array(orientation=90, columns=3)
pt.move((70, 200))
route = gf.routing.get_route_electrical(
pt.ports["e11"], pb.ports["e11"], bend="bend_euler", radius=30
)
c.add(route.references)
c.plot()
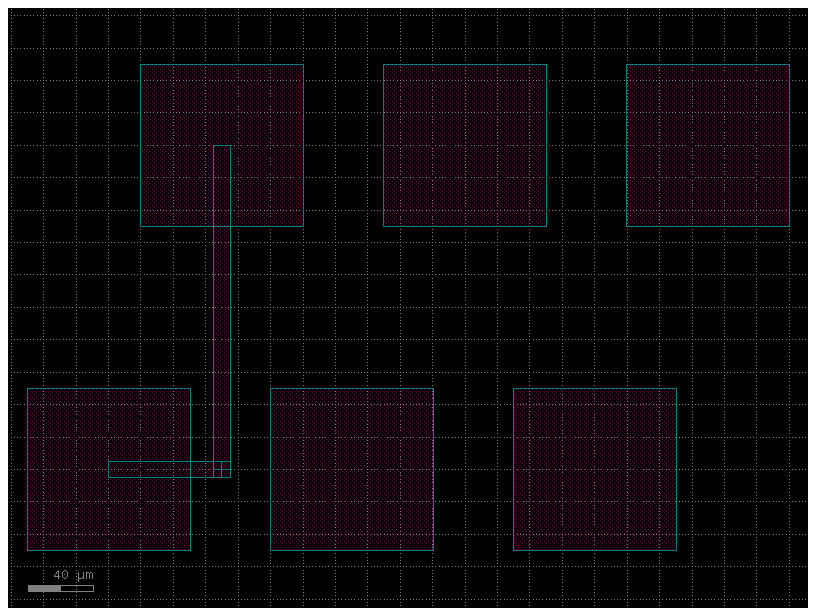
c = gf.Component("pads_with_routes_with_wire_corners")
pt = c << gf.components.pad_array(orientation=270, columns=3)
pb = c << gf.components.pad_array(orientation=90, columns=3)
pt.move((70, 200))
route = gf.routing.get_route_electrical(
pt.ports["e11"], pb.ports["e11"], bend="wire_corner"
)
c.add(route.references)
c.plot()

c = gf.Component("pads_with_routes_with_wire_corners_no_orientation")
pt = c << gf.components.pad_array(orientation=None, columns=3)
pb = c << gf.components.pad_array(orientation=None, columns=3)
pt.move((70, 200))
route = gf.routing.get_route_electrical(
pt.ports["e11"], pb.ports["e11"], bend="wire_corner"
)
c.add(route.references)
c.plot()
c = gf.Component("multi-layer")
columns = 2
ptop = c << gf.components.pad_array(columns=columns)
pbot = c << gf.components.pad_array(orientation=90, columns=columns)
ptop.movex(300)
ptop.movey(300)
route = gf.routing.get_route_electrical_multilayer(
ptop.ports["e11"],
pbot.ports["e11"],
end_straight_length=100,
)
c.add(route.references)
c.plot()
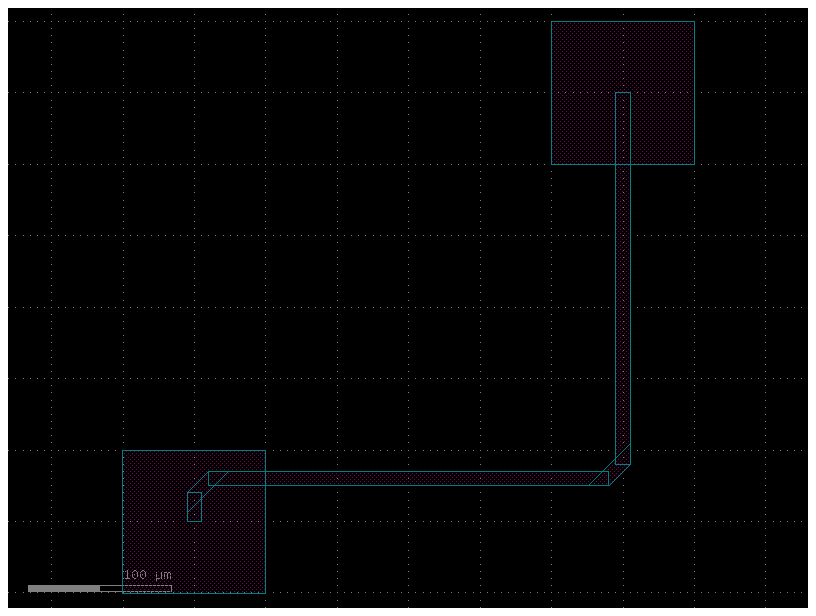
There is also bend = wire_corner45 for 45deg bend corner with parametrizable “radius”:
c = gf.Component("pads_with_routes_with_wire_corner45")
pt = c << gf.components.pad_array(orientation=270, columns=1)
pb = c << gf.components.pad_array(orientation=90, columns=1)
pt.move((300, 300))
route = gf.routing.get_route_electrical(
pt.ports["e11"], pb.ports["e11"], bend="wire_corner45", radius=30
)
c.add(route.references)
c.plot()
c = gf.Component("pads_with_routes_with_wire_corner45")
pt = c << gf.components.pad_array(orientation=270, columns=1)
pb = c << gf.components.pad_array(orientation=90, columns=1)
pt.move((300, 300))
route = gf.routing.get_route_electrical(
pt.ports["e11"], pb.ports["e11"], bend="wire_corner45", radius=100
)
c.add(route.references)
c.plot()

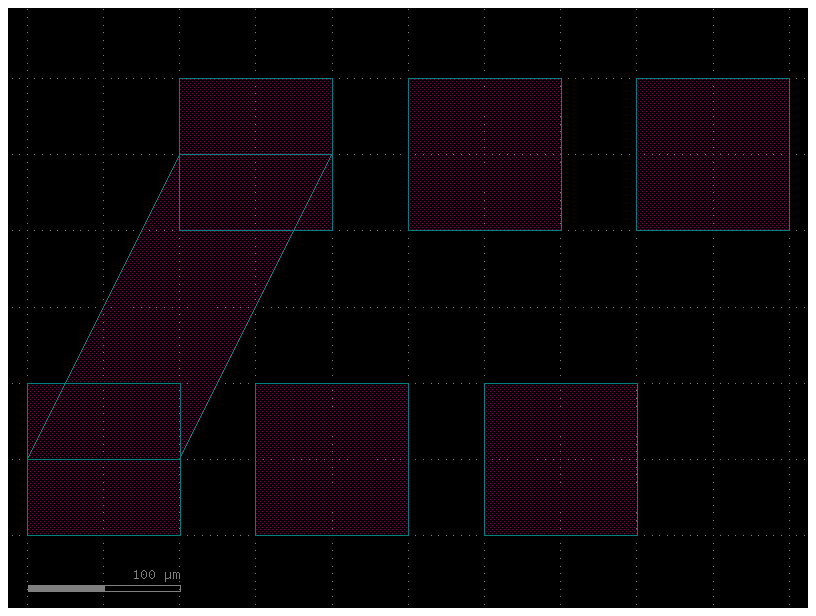
route_quad#
c = gf.Component("pads_route_quad")
pt = c << gf.components.pad_array(orientation=270, columns=3)
pb = c << gf.components.pad_array(orientation=90, columns=3)
pt.move((100, 200))
route = c << gf.routing.route_quad(pt.ports["e11"], pb.ports["e11"], layer=(49, 0))
c.plot()
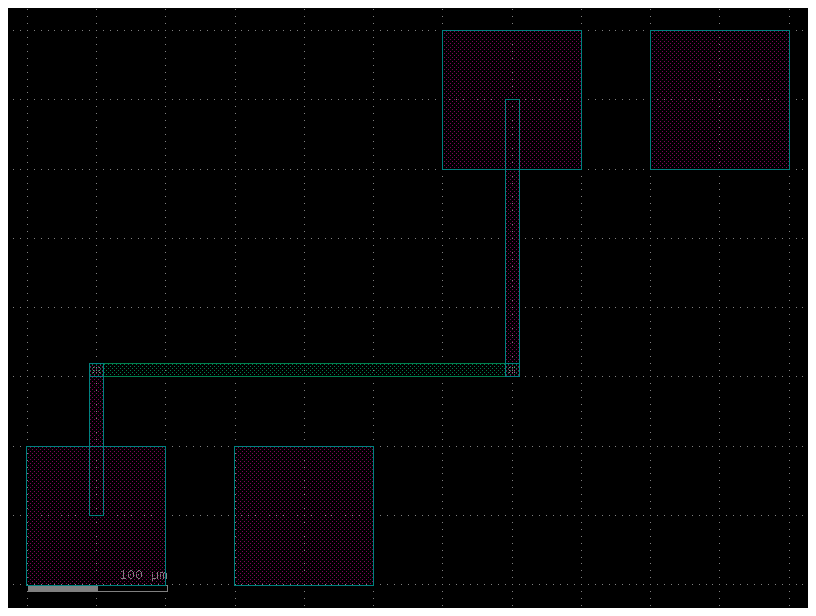
get_route_from_steps#
c = gf.Component("pads_route_from_steps")
pt = c << gf.components.pad_array(orientation=270, columns=3)
pb = c << gf.components.pad_array(orientation=90, columns=3)
pt.move((100, 200))
route = gf.routing.get_route_from_steps(
pb.ports["e11"],
pt.ports["e11"],
steps=[
{"y": 200},
],
cross_section="xs_metal_routing",
bend=gf.components.wire_corner,
)
c.add(route.references)
c.plot()
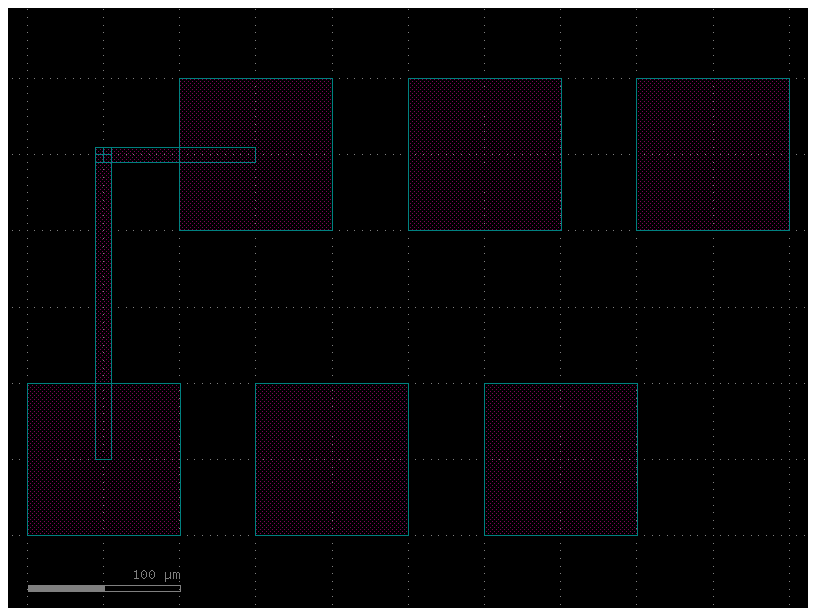
c = gf.Component("pads_route_from_steps_None_orientation")
pt = c << gf.components.pad_array(orientation=None, columns=3)
pb = c << gf.components.pad_array(orientation=None, columns=3)
pt.move((100, 200))
route = gf.routing.get_route_from_steps(
pb.ports["e11"],
pt.ports["e11"],
steps=[
{"y": 200},
],
cross_section="xs_metal_routing",
bend=gf.components.wire_corner,
)
c.add(route.references)
c.plot()
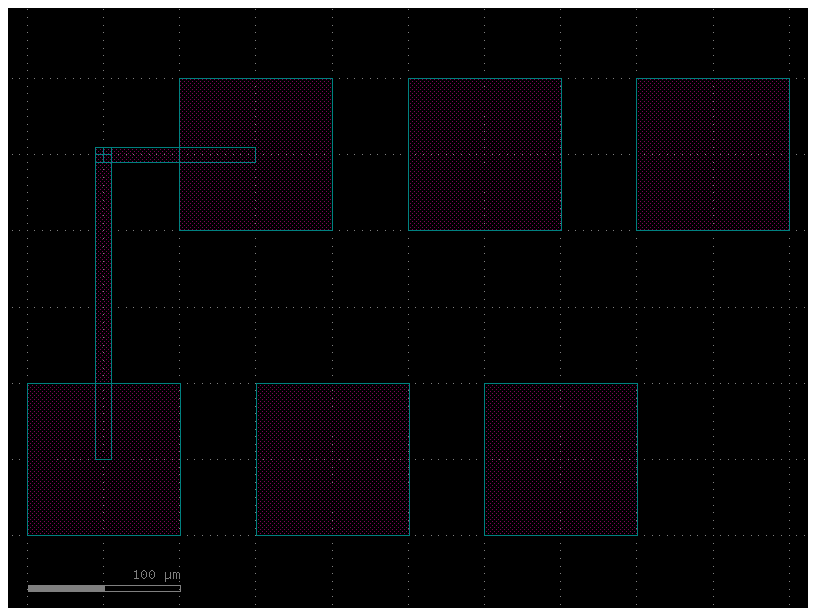
get_bundle_electrical#
For routing groups of ports you can use get_bundle that returns a bundle of routes using a bundle router (also known as bus or river router)
c = gf.Component("pads_bundle")
pt = c << gf.components.pad_array(orientation=270, columns=3)
pb = c << gf.components.pad_array(orientation=90, columns=3)
pt.move((100, 200))
routes = gf.routing.get_bundle_electrical(
pb.ports, pt.ports, end_straight_length=60, separation=30
)
for route in routes:
c.add(route.references)
c.plot()
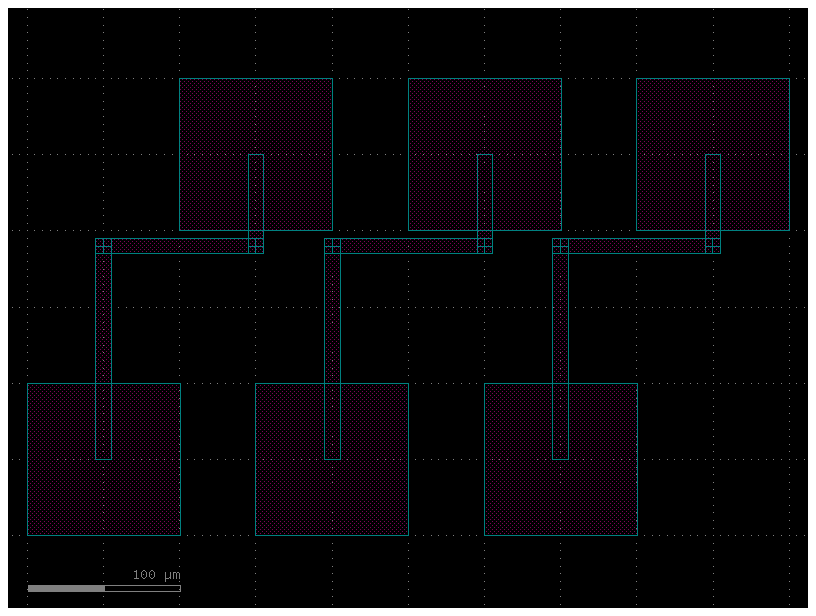
get_bundle_from_steps_electrical#
c = gf.Component("pads_bundle_steps")
pt = c << gf.components.pad_array(
partial(gf.components.pad, size=(30, 30)),
orientation=270,
columns=3,
spacing=(50, 0),
)
pb = c << gf.components.pad_array(orientation=90, columns=3)
pt.move((300, 500))
routes = gf.routing.get_bundle_from_steps_electrical(
pb.ports, pt.ports, end_straight_length=60, separation=30, steps=[{"dy": 100}]
)
for route in routes:
c.add(route.references)
c.plot()
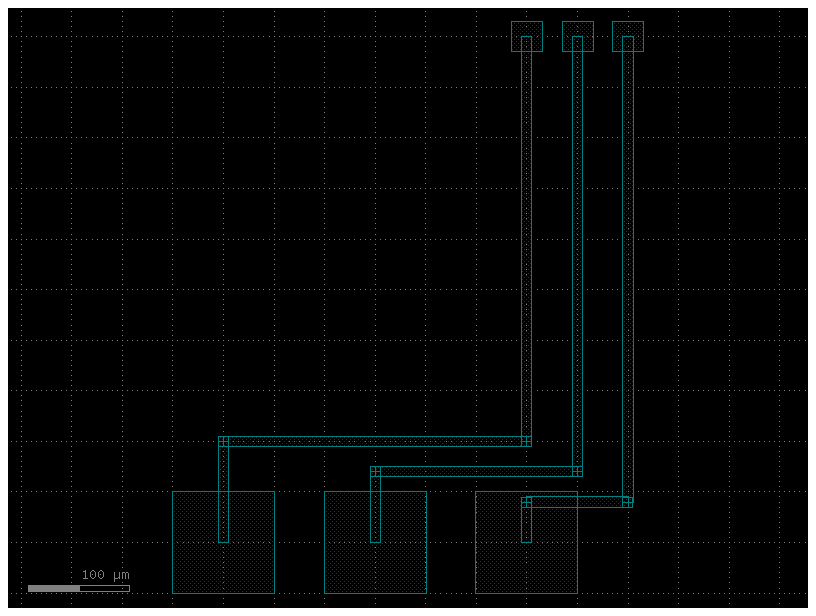
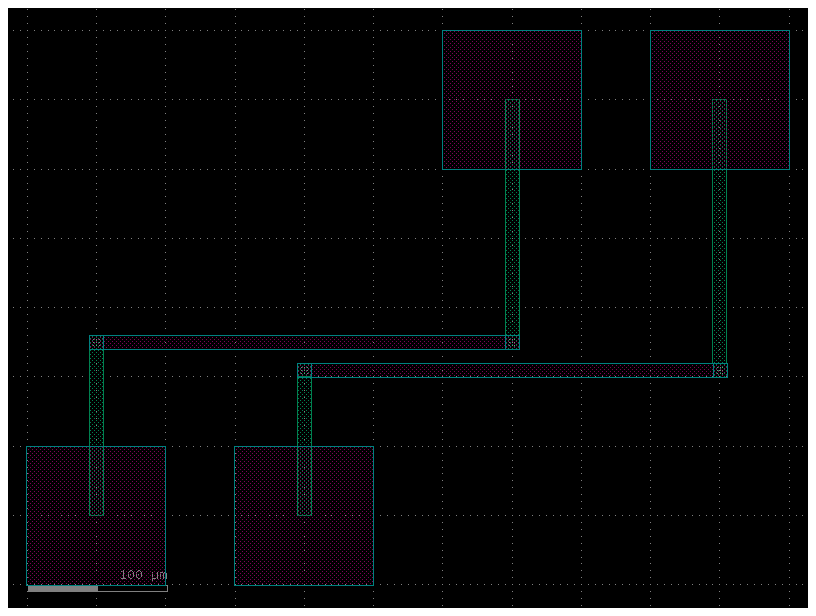
get_bundle_electrical_multilayer#
To avoid metal crossings you can use one metal layer.
c = gf.Component("get_bundle_multi_layer")
columns = 2
ptop = c << gf.components.pad_array(columns=columns)
pbot = c << gf.components.pad_array(orientation=90, columns=columns)
ptop.movex(300)
ptop.movey(300)
routes = gf.routing.get_bundle_electrical_multilayer(
ptop.ports, pbot.ports, end_straight_length=100, separation=20
)
for route in routes:
c.add(route.references)
c.plot()
Routing to pads#
You can also route to electrical pads.
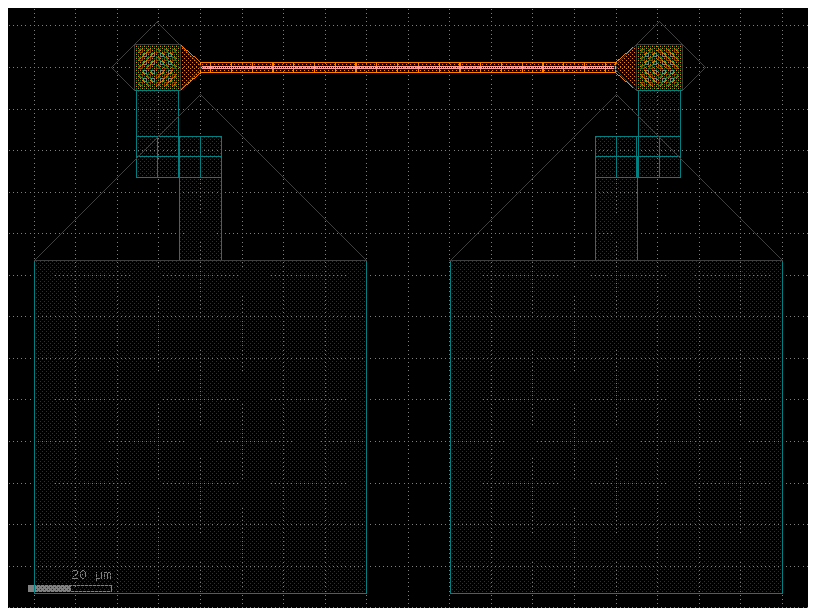
c = gf.components.straight_heater_metal(length=100.0)
cc = gf.routing.add_pads_bot(component=c, port_names=("l_e4", "r_e4"), fanout_length=50)
cc.plot()
c = gf.components.straight_heater_metal(length=100.0)
cc = gf.routing.add_pads_top(component=c)
cc.plot()
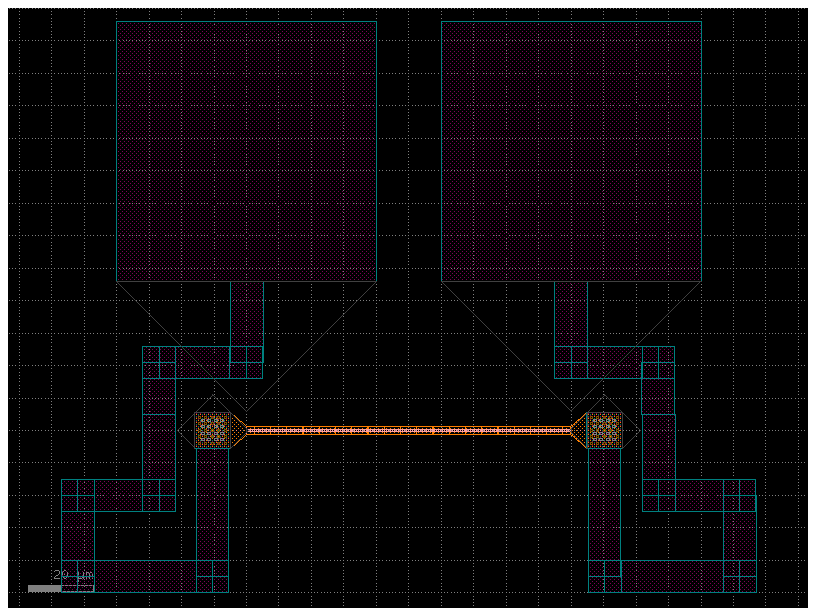
c = gf.components.straight_heater_metal(length=100.0)
cc = gf.routing.add_pads_top(component=c, port_names=("l_e2", "r_e2"))
cc.plot()
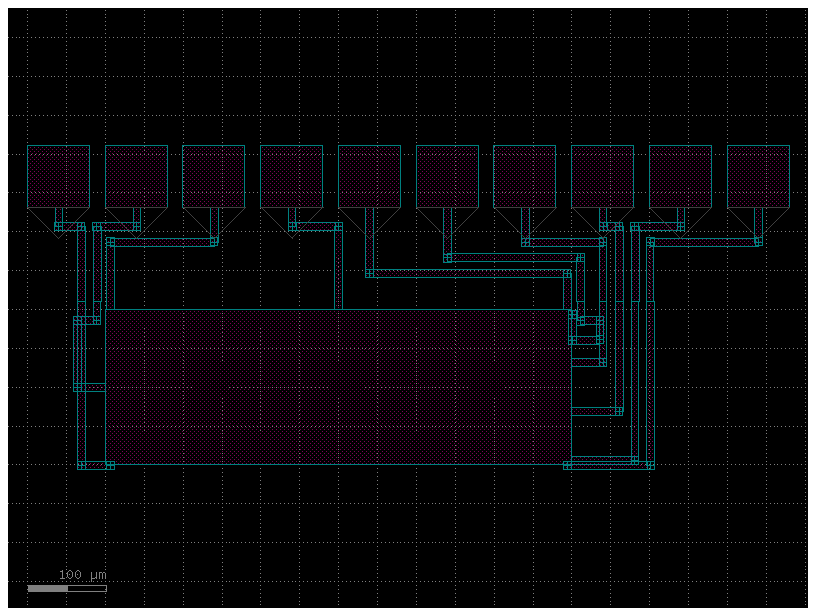
c = gf.c.nxn(
xsize=600,
ysize=200,
north=2,
south=3,
wg_width=10,
layer="M3",
port_type="electrical",
)
cc = gf.routing.add_pads_top(component=c)
cc.plot()
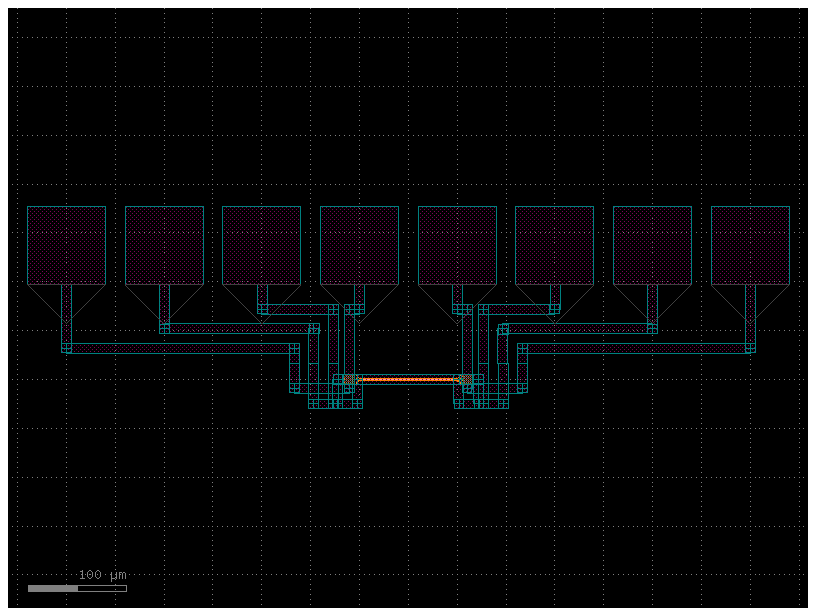
n = west = north = south = east = 10
spacing = 20
c = gf.components.nxn(
xsize=n * spacing,
ysize=n * spacing,
west=west,
east=east,
north=north,
south=south,
port_type="electrical",
wg_width=10,
)
c.plot()
cc = gf.routing.add_pads_top(component=c)
cc.plot()
Routing to optical terminations#
Route to Fiber Array#
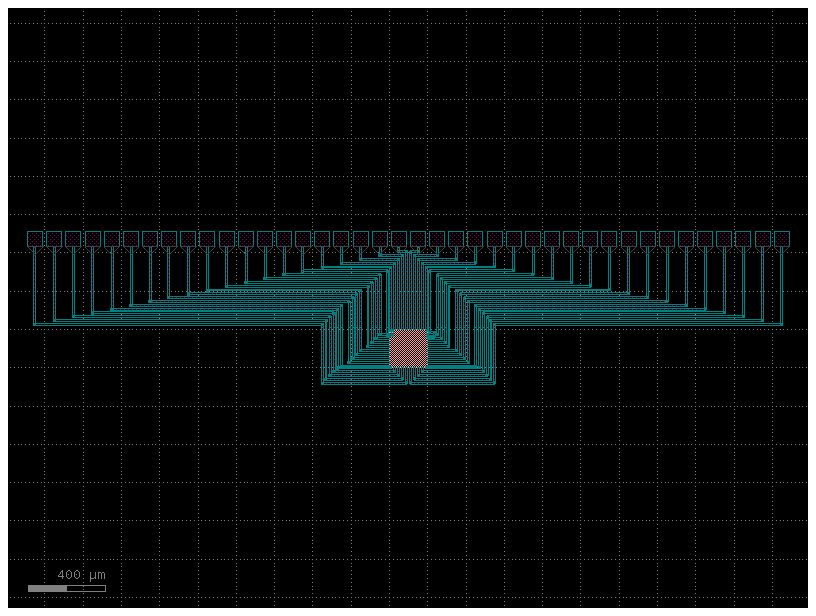
You can route to a fiber array.
component = big_device(nports=10)
c = gf.routing.add_fiber_array(component=component, radius=10.0, fanout_length=60.0)
c.plot()

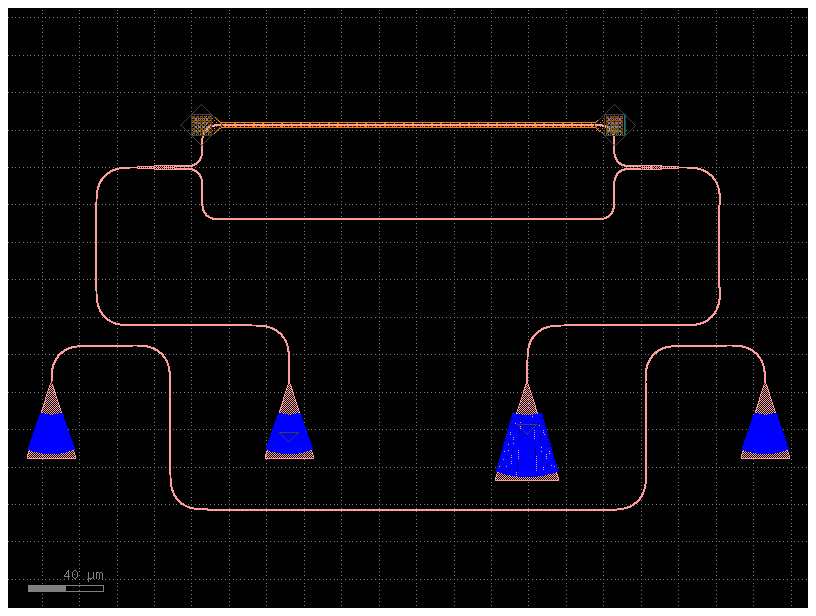
You can also mix and match TE and TM grating couplers. Notice that the TM polarization grating coupler is bigger.
import gdsfactory as gf
c = gf.components.mzi_phase_shifter()
gcte = gf.components.grating_coupler_te
cc = gf.routing.add_fiber_array(
component=c,
optical_routing_type=2,
grating_coupler=[
gf.components.grating_coupler_te,
gf.components.grating_coupler_tm,
],
radius=20,
)
cc.plot()
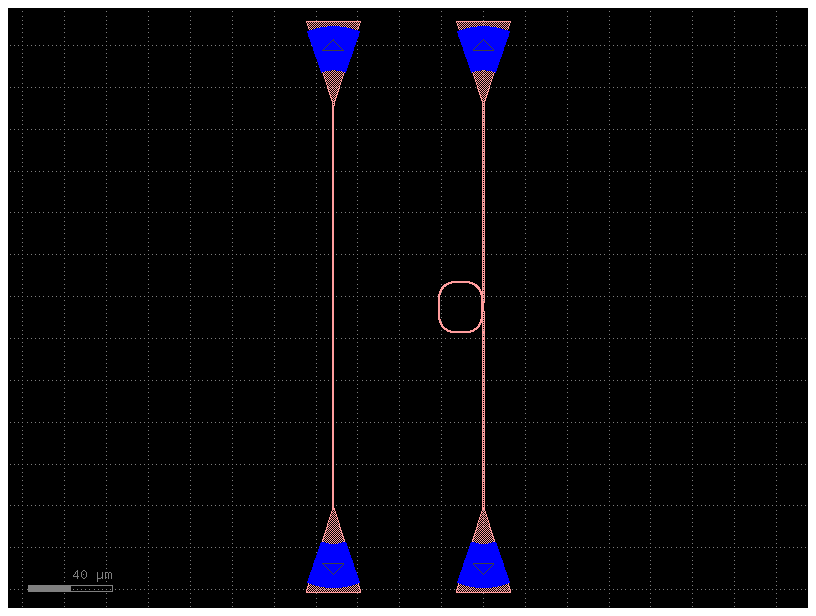
Route to Single fibers#
You can route to a single fiber input and single fiber output.
c = gf.components.ring_single()
cc = gf.routing.add_fiber_single(component=c)
cc.plot()
Route to edge couplers#
You can also route Edge couplers to a fiber array or to both sides of the chip.
For routing to both sides you can follow different strategies:
Place the edge couplers and route your components to the edge couplers.
Extend your component ports to each side.
Anything you imagine …
import numpy as np
import gdsfactory as gf
from gdsfactory.generic_tech import LAYER
@gf.cell
def sample_die(size=(2e3, 2e3), y_spacing: float = 10) -> gf.Component:
"""Returns a sample die
Args:
size: size of the die.
y_spacing: spacing between components.
Returns:
c: a sample die.
"""
c = gf.Component()
die = c << gf.c.rectangle(size=np.array(size), layer=LAYER.FLOORPLAN, centered=True)
die = c << gf.c.rectangle(
size=np.array(size) - 2 * np.array((50, 50)),
layer=LAYER.FLOORPLAN,
centered=True,
)
ymin = die.ymin
ec = gf.components.edge_coupler_silicon()
components = [
"mzi",
"mmi1x2",
"spiral_racetrack",
"coupler",
"ring_single",
"ring_double",
]
cells = gf.get_active_pdk().cells
for component in components:
function = cells[component]
ci = function()
ci = (
gf.routing.add_pads_top(
ci,
pad=gf.components.pad,
pad_spacing=150,
)
if ci.get_ports_list(port_type="electrical")
else ci
)
ref = c << ci
ref.ymin = ymin
ref.x = 0
ymin = ref.ymax + y_spacing
routes_left, ports_left = gf.routing.route_ports_to_side(
ref.get_ports_list(orientation=180),
cross_section="xs_sc",
side="west",
x=die.xmin + ec.xsize,
)
for route in routes_left:
c.add(route.references)
routes_right, ports_right = gf.routing.route_ports_to_side(
ref.get_ports_list(orientation=0),
cross_section="xs_sc",
x=die.xmax - ec.xsize,
side="east",
)
for route in routes_right:
c.add(route.references)
for port in ports_right:
ref = c << ec
ref.connect("o1", port)
text = c << gf.c.text(
text=f"{ci.name}-{port.name.split('_')[0]}", size=10, layer=LAYER.MTOP
)
text.xmax = ref.xmax - 10
text.y = ref.y
for port in ports_left:
ref = c << ec
ref.connect("o1", port)
text = c << gf.c.text(
text=f"{ci.name}-{port.name.split('_')[0]}", size=10, layer=LAYER.MTOP
)
text.xmin = ref.xmin + 10
text.y = ref.y
return c
c = sample_die()
gf.remove_from_cache(c.name)
c.show(show_ports=True) # show in klayout
c.plot() # plot in notebook
2025-01-19 23:49:28.965 | WARNING | gdsfactory.klive:show:49 - UserWarning: Could not connect to klive server. Is klayout open and klive plugin installed?