Schematic#
A schematic is a graph representation of your circuit.
For complex circuits, a schematic allows you to create symbols and hierarchy levels to represent your circuit.
Having a schematic allows you to also ensure that your layout matches you schematic (design intent).
There are many schematic capturing tools out there:
Qucs-s: for RF.
Xschem: for analog circuits.
Lumerical interconnect: for photonic circuits.
These tools allow you to create schematics with either your mouse or by code.
gdsfactory also allows you to create complex Schematics directly from python with a very simple interface.
import gdsfactory as gf
import yaml
from functools import partial
gf.gpdk.PDK.activate()
@gf.schematic_cell
def my_schematic(x: float = 108.5, y: float = 53.1) -> gf.Schematic:
"""Returns a schematic with two rings connected by a waveguide."""
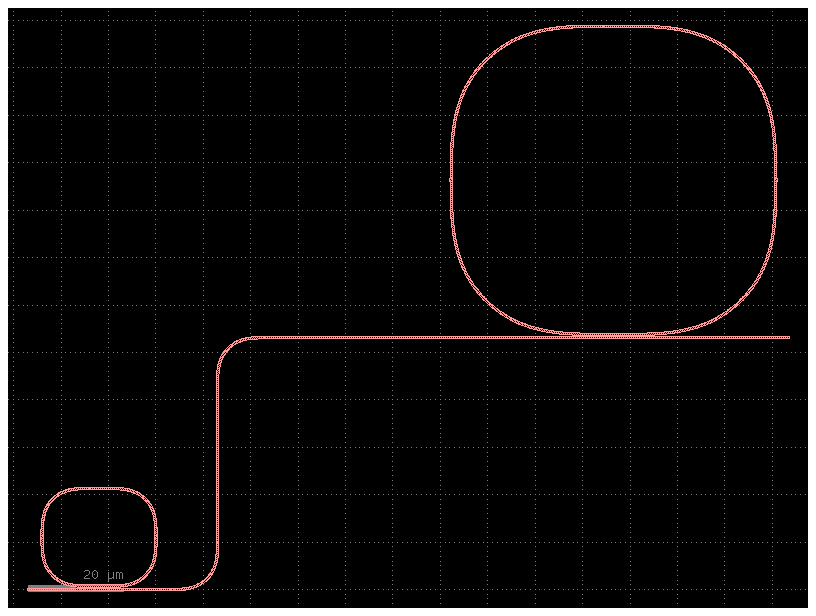
s = gf.Schematic()
r1 = s.create_inst(name="r1", component="ring_single")
r1.place(x=0, y=0)
r2 = s.create_inst(name="r2", component="ring_single", settings={"radius": 32.2})
r2.place(x=x, y=y)
s.add_route(
name="r1-r2",
start_ports=[r1.ports["o2"]],
end_ports=[r2.ports["o1"]],
routing_strategy="route_bundle",
)
return s
c = my_schematic()
c.plot()
@gf.schematic_cell(
factories=gf.get_factories.get_cells("gdsfactory"),
routing_strategies=gf.get_active_pdk().routing_strategies
or {
"route_bundle": partial(
gf.routing.route_bundle, layer=gf.get_layer((1, 0)), route_width=1
)
},
)
def my_schematic(x: float = 108.5, y: float = 53.1) -> gf.Schematic:
"""Returns a schematic with two rings connected by a waveguide."""
s = gf.Schematic()
r1 = s.create_inst(name="r1", component="ring_single")
r1.place(x=0, y=0)
r2 = s.create_inst(name="r2", component="ring_single", settings={"radius": 32.2})
r2.place(x=x, y=y)
s.add_route(
name="r1-r2",
start_ports=[r1.ports["o2"]],
end_ports=[r2.ports["o1"]],
routing_strategy="route_bundle",
)
return s
c = my_schematic()
c.plot()

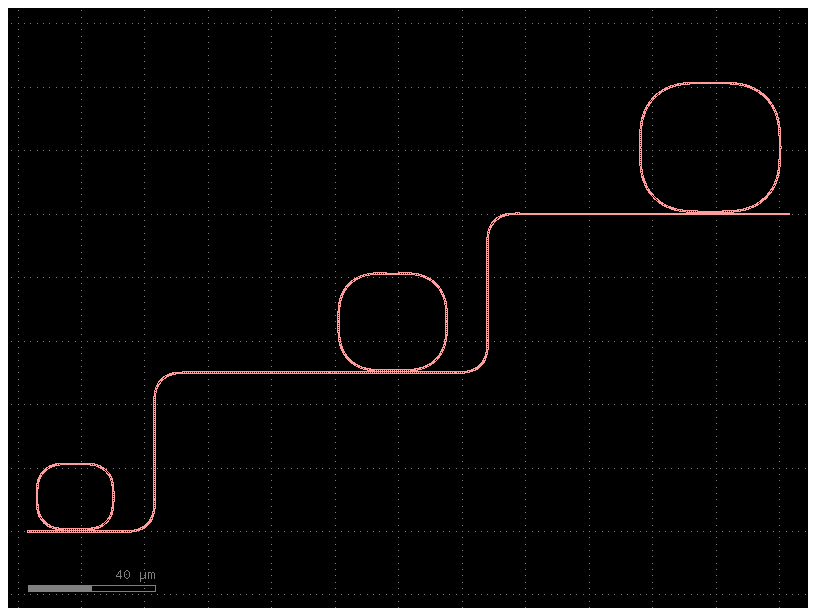
@gf.schematic_cell
def ring_array(n: int = 3, pitch_x: float = 100, pitch_y=50, radius: float = 10, radius_delta: float = 5) -> gf.Schematic:
"""Returns a schematic with n rings connected by a waveguide."""
s = gf.Schematic()
last_ring = None
for i in range(n):
r = s.create_inst(name=f"r{i}", component="ring_single", settings={"radius": radius+i*radius_delta})
r.place(x=i*pitch_x, y=i*pitch_y)
if last_ring is not None:
s.add_route(
name=f"r{i-1}-r{i}",
start_ports=[last_ring.ports["o2"]],
end_ports=[r.ports["o1"]],
routing_strategy="route_bundle",
)
last_ring = r
return s
c = ring_array()
c.plot()
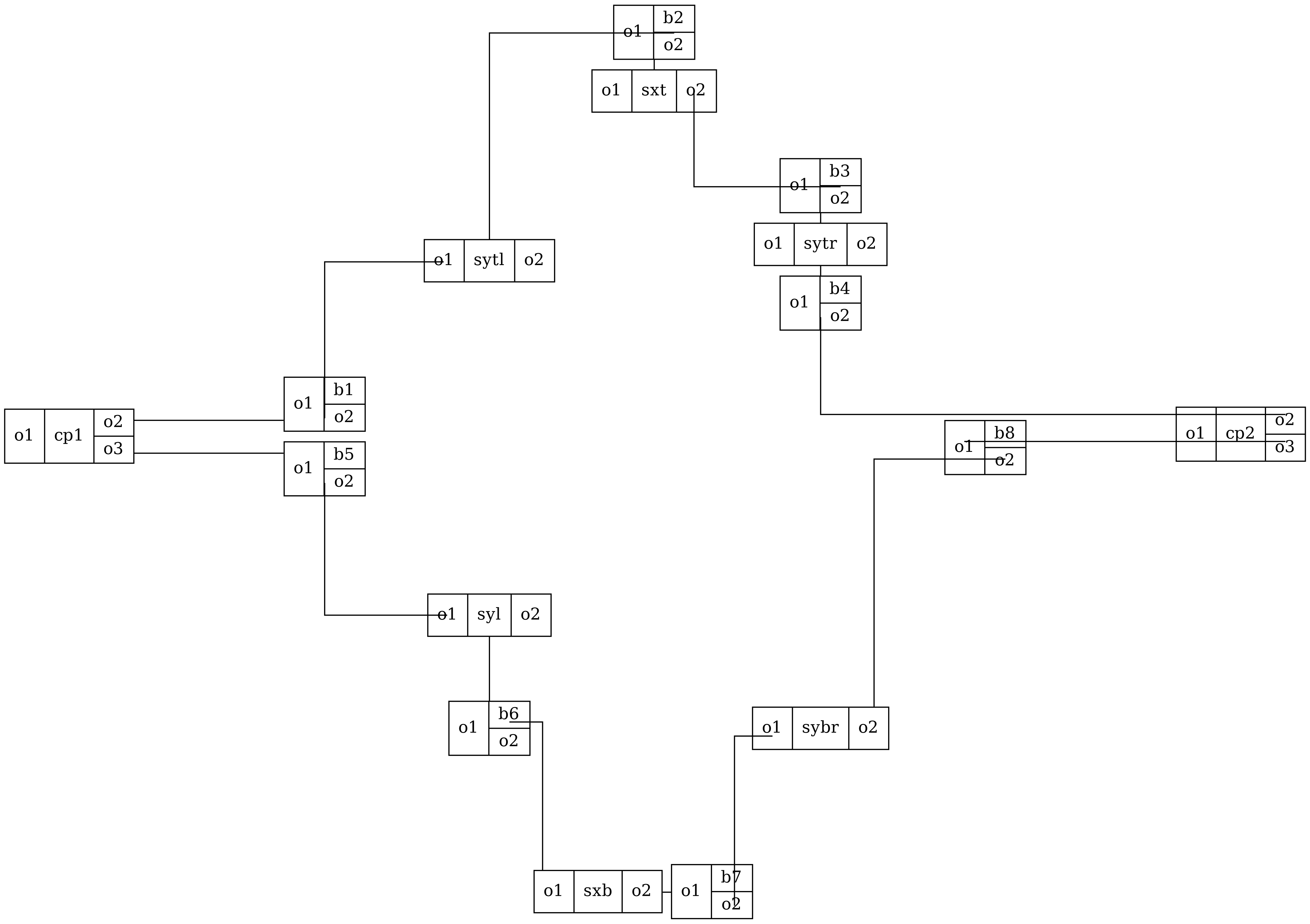
c = gf.c.mzi()
# .plot_netlist_graphviz(): This method reads the component's netlist and uses Graphviz (a graph visualization tool) to create a block diagram.
# interactive=False: This parameter specifies that the output should be a static image rather than an interactive plot.
c.plot_netlist_graphviz(interactive=False)
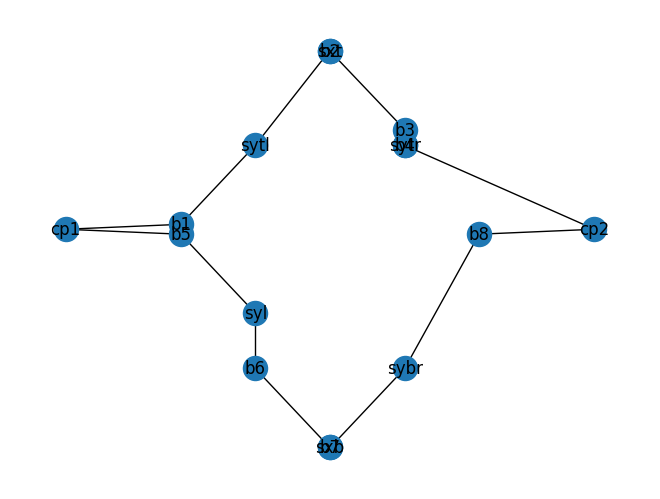
c.plot_netlist()
<networkx.classes.graph.Graph at 0x7f04b53e3d90>
Lets create a MZI lattice of 3 elements.
from kfactory.schematic import RegularArray
import gdsfactory as gf
@gf.cell
def splitter_tree_with_new_ports(**kwargs) -> gf.Component:
"""Returns a splitter tree with new ports."""
c = gf.c.splitter_tree(**kwargs).copy()
c.auto_rename_ports()
return c
pdk = gf.get_active_pdk()
pdk.register_cells(splitter_tree_new_ports=splitter_tree_with_new_ports)
@gf.schematic_cell(overwrite_existing=True) # for development
def lidar(n: int = 2**3, dbr_pitch: float = 3) -> gf.Schematic:
"""Returns a schematic with lidar array by a waveguide."""
s = gf.Schematic()
spt = s.create_inst(name="splitter", component='splitter_tree_new_ports', settings={'noutputs': n, 'spacing': (50, 50)})
dbr = s.create_inst(name="dbr", component='dbr', array=RegularArray(rows=n, column_pitch=0, row_pitch=dbr_pitch))
spt.place(x=0, y=0)
dbr.place(x=250+n*dbr_pitch, y=-n*dbr_pitch/2+dbr_pitch/2)
start_ports = [spt.ports[f"o{i+2}"] for i in range(n)]
end_ports = [dbr.ports["o1", 0, i] for i in range(n)]
s.add_route(
name="splitter_to_dbr",
start_ports=start_ports,
end_ports=end_ports,
routing_strategy="route_bundle",
radius=5,
separation=3,
sort_ports=True,
)
return s
c = lidar(n=2**4)
c.plot()

