gdsfactory.routing.route_single#
- gdsfactory.routing.route_single(component, port1, port2, cross_section=None, layer=None, bend='bend_euler', straight='straight', start_straight_length=0.0, end_straight_length=0.0, waypoints=None, steps=None, port_type=None, allow_width_mismatch=False, radius=None, route_width=None, auto_taper=True, on_error=None, layer_transitions=None)[source]#
Returns a Manhattan Route between 2 ports.
Deprecated since version Use:
route_bundle()with single ports instead.The references are straights, bends and tapers.
- Parameters:
component (Component) – to place the route into.
port1 (Port) – start port.
port2 (Port) – end port.
cross_section (CrossSectionSpec | None) – spec.
layer (LayerSpec | None) – layer spec.
bend (ComponentSpec) – bend spec.
straight (ComponentSpec) – straight spec.
start_straight_length (float) – length of starting straight.
end_straight_length (float) – length of end straight.
waypoints (WayPoints | None) – optional list of points to pass through.
steps (Sequence[Step] | None) – optional list of steps to pass through. Each step is a dict with keys: x (absolute), y (absolute), dx (relative), dy (relative). Use x/y to set an absolute coordinate and dx/dy to shift relative to the current position.
port_type (str | None) – port type to route.
allow_width_mismatch (bool) – allow different port widths.
radius (float | None) – bend radius. If None, defaults to cross_section.radius.
route_width (float | None) – width of the route in um. If None, defaults to cross_section.width.
auto_taper (bool) – add auto tapers.
on_error (Literal['error'] | None) – what to do on error. If error, raises an error. If None ignores the error.
layer_transitions (LayerTransitions | None) – dictionary of layer transitions to use for the routing when auto_taper=True.
- Return type:
ManhattanRoute
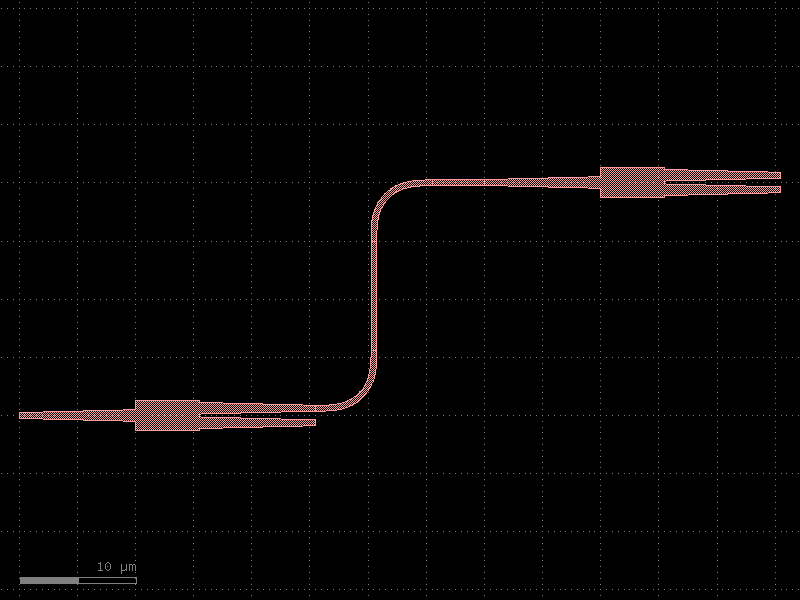
import gdsfactory as gf c = gf.Component() mmi1 = c << gf.components.mmi1x2() mmi2 = c << gf.components.mmi1x2() mmi2.move((40, 20)) gf.routing.route_single(c, mmi1.ports["o2"], mmi2.ports["o1"], radius=5, cross_section="strip") c.plot()
(
Source code,png,hires.png,pdf)