FDFD mode solver#
We also have a FDFD mode solver.
Materials#
You can define materials as a material spec (float, string, tuple[string,string]).
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import gplugins.tidy3d as gt
nm = 1e-3
print(gt.materials.MaterialSpecTidy3d)
float | int | str | tidy3d.components.medium.Medium | tidy3d.components.medium.CustomMedium | tidy3d.components.medium.PoleResidue | tuple[float, float] | tuple[str, str]
gt.materials.get_index(
3.4
) # get the index of a material with a given refractive index float
3.4
# get the index of a material with a name string, for the case that the refractive index has only one variant
gt.materials.get_index("AlxOy")
1.7830851366538996
# get the index of a material with a name string, for the case that the refractive index has more than one variant
gt.materials.get_index(("cSi", "Li1993_293K"))
3.4750055639285913
Waveguides#
Guided Electromagnetic modes are the ones that have an effective index larger than the cladding of the waveguide
Here is a waveguide of Silicon (n=3.4) surrounded by SiO2 (n=1.44) cladding
For a 220 nm height x 450 nm width the effective index is 2.466
For defining the waveguide materials you can use a float indicating the refractive index.
strip = gt.modes.Waveguide(
wavelength=1.55,
core_width=0.5,
core_thickness=0.22,
slab_thickness=0.0,
core_material=3.47,
clad_material=1.44,
)
strip.plot_index()
<matplotlib.collections.QuadMesh at 0x7f28d2fade10>
You can also use materials from the default materials.
strip = gt.modes.Waveguide(
wavelength=1.55,
core_width=0.5,
core_thickness=0.22,
slab_thickness=0.0,
core_material="si",
clad_material="sio2",
)
strip.plot_index()
<matplotlib.collections.QuadMesh at 0x7f28d2eb2290>
strip.plot_grid()
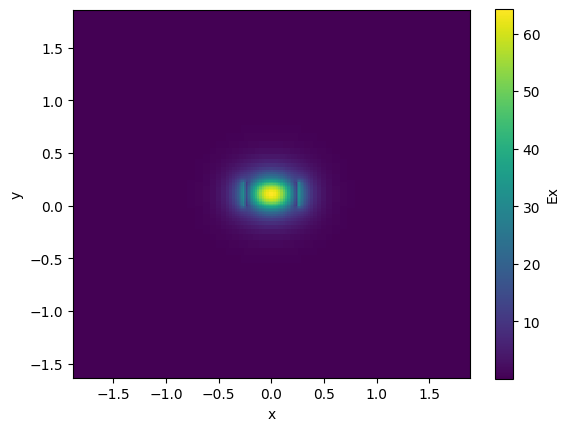
strip.plot_field(field_name="Ex", mode_index=0) # TE
10:37:48 UTC WARNING: The group index was not computed. To calculate group index, pass 'group_index_step = True' in the 'ModeSpec'.
<matplotlib.collections.QuadMesh at 0x7f28d0bac250>
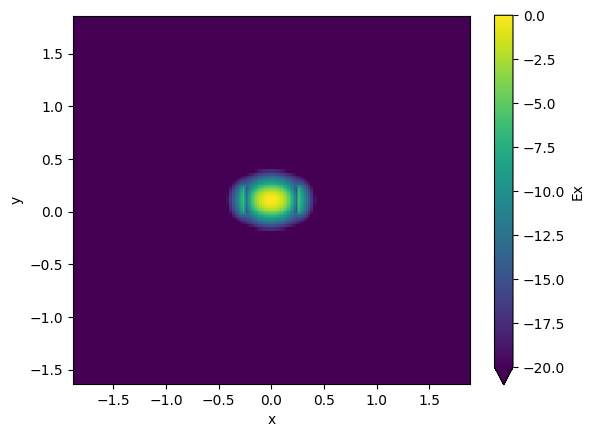
strip.plot_field(field_name="Ex", mode_index=0, value="dB") # TE
<matplotlib.collections.QuadMesh at 0x7f28d0b55710>
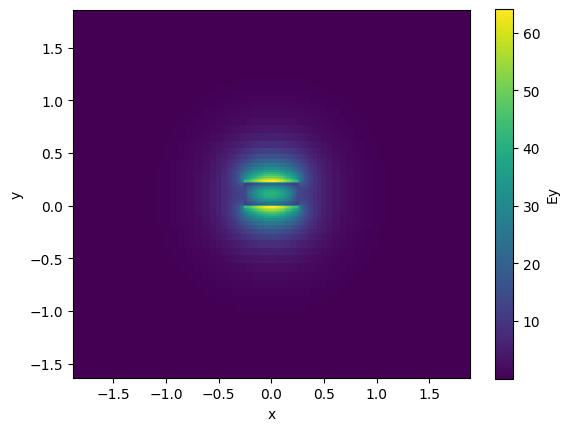
strip.plot_field(field_name="Ey", mode_index=1) # TM
<matplotlib.collections.QuadMesh at 0x7f28d0797a10>
print(strip.n_eff)
[2.51134734+4.42777628e-05j 1.86463643+2.09422901e-04j]
rib = gt.modes.Waveguide(
wavelength=1.55,
core_width=0.5,
core_thickness=0.22,
slab_thickness=0.15,
core_material="si",
clad_material="sio2",
)
rib.plot_index()
rib.n_eff
10:37:49 UTC WARNING: Mode field at frequency index 0, mode index 1 does not decay at the plane boundaries.
array([2.67427418+3.10179975e-05j, 2.50854925+4.47861102e-05j])
rib.plot_field(field_name="Ex", mode_index=0) # TE
<matplotlib.collections.QuadMesh at 0x7f28d04086d0>
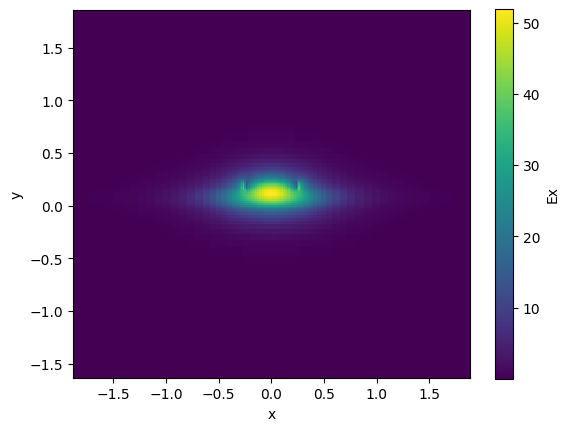
nitride = gt.modes.Waveguide(
wavelength=1.55,
core_width=1.0,
core_thickness=400 * nm,
slab_thickness=0.0,
core_material="sin",
clad_material="sio2",
)
nitride.plot_index()
nitride.n_eff
array([1.64461788+8.05914283e-05j, 1.57796343+1.42713312e-04j])
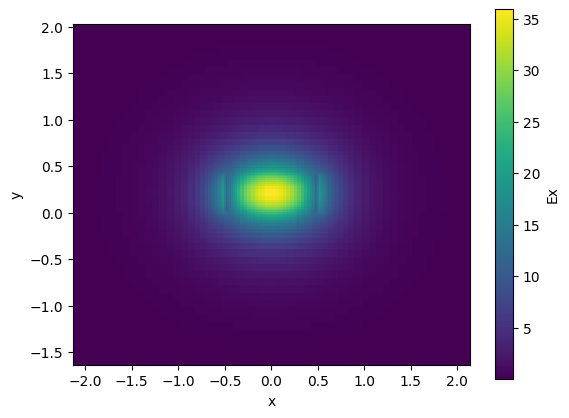
nitride.plot_field(field_name="Ex", mode_index=0) # TE
<matplotlib.collections.QuadMesh at 0x7f28d0df5810>
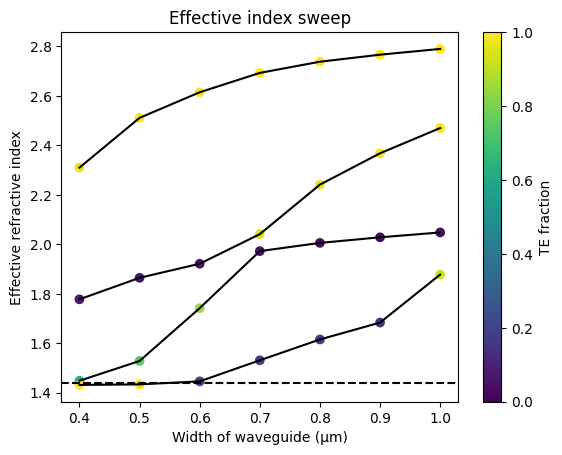
Sweep width#
You can sweep the waveguide width and compute the modes.
By increasing the waveguide width, the waveguide supports many more TE and TM modes. Where TE modes have a dominant Ex field and TM modes have larger Ey fields.
Notice that waveguides wider than 0.450 um support more than one TE mode. Therefore the maximum width for single mode operation is 0.450 um.
strip = gt.modes.Waveguide(
wavelength=1.55,
core_width=1.0,
slab_thickness=0.0,
core_material="si",
clad_material="sio2",
core_thickness=220 * nm,
num_modes=4,
)
w = np.linspace(400 * nm, 1000 * nm, 7)
n_eff = gt.modes.sweep_n_eff(strip, core_width=w)
fraction_te = gt.modes.sweep_fraction_te(strip, core_width=w)
for i in range(4):
plt.plot(w, n_eff.sel(mode_index=i).real, c="k")
plt.scatter(
w, n_eff.sel(mode_index=i).real, c=fraction_te.sel(mode_index=i), vmin=0, vmax=1
)
plt.axhline(y=1.44, color="k", ls="--")
plt.colorbar().set_label("TE fraction")
plt.xlabel("Width of waveguide (µm)")
plt.ylabel("Effective refractive index")
plt.title("Effective index sweep")
10:37:51 UTC WARNING: Mode field at frequency index 0, mode index 3 does not decay at the plane boundaries.
10:37:53 UTC WARNING: Mode field at frequency index 0, mode index 3 does not decay at the plane boundaries.
Text(0.5, 1.0, 'Effective index sweep')
Exercises
What is the maximum width to support a single TE mode at 1310 nm?
For a Silicon Nitride (n=2) 400nm thick waveguide surrounded by SiO2 (n=1.44), what is the maximum width to support a single TE mode at 1550 nm?
For two 500x220nm Silicon waveguides surrounded by SiO2, what is the coupling length (100% coupling) for 200 nm gap?
Group index#
You can also compute the group index for a waveguide.
nm = 1e-3
strip = gt.modes.Waveguide(
wavelength=1.55,
core_width=500 * nm,
slab_thickness=0.0,
core_material="si",
clad_material="sio2",
core_thickness=220 * nm,
num_modes=4,
group_index_step=10 * nm,
)
print(strip.n_group)
10:38:01 UTC WARNING: Mode field at frequency index 0, mode index 3 does not decay at the plane boundaries.
WARNING: Mode field at frequency index 1, mode index 3 does not decay at the plane boundaries.
WARNING: Mode field at frequency index 2, mode index 3 does not decay at the plane boundaries.
[4.17803969 4.08299706 2.71577378 1.50333028]
Bend modes#
You can compute bend modes specifying the bend radius.
strip_bend = gt.modes.Waveguide(
wavelength=1.55,
core_width=500 * nm,
core_thickness=220 * nm,
slab_thickness=0.0,
bend_radius=4,
core_material="si",
clad_material="sio2",
)
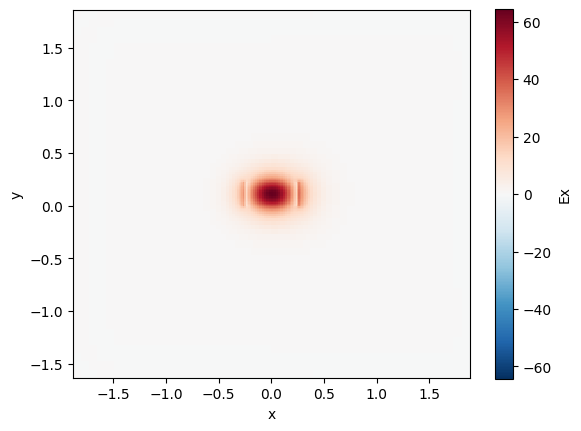
strip_bend.plot_field(field_name="Ex", mode_index=0) # TE
10:38:02 UTC WARNING: Mode field at frequency index 0, mode index 1 does not decay at the plane boundaries.
<matplotlib.collections.QuadMesh at 0x7f28d0cbc990>
Bend loss#
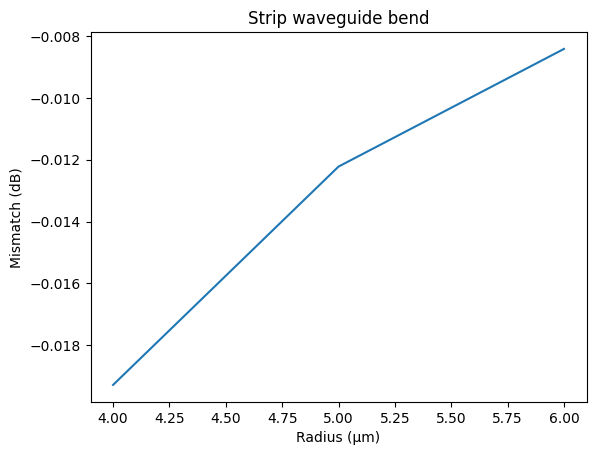
You can also compute the losses coming from the mode mismatch from the bend into a straight waveguide. To compute the bend loss due to mode mismatch you can calculate the mode overlap of the straight mode and the bent mode. Because there are two mode mismatch interfaces the total loss due to mode mismatch will be squared (from bend to straight and from straight to bend).

radii = np.arange(4, 7)
bend = gt.modes.Waveguide(
wavelength=1.55,
core_width=500 * nm,
core_thickness=220 * nm,
core_material="si",
clad_material="sio2",
num_modes=1,
bend_radius=radii.min(),
)
mismatch = gt.modes.sweep_bend_mismatch(bend, radii)
plt.plot(radii, 10 * np.log10(mismatch))
plt.title("Strip waveguide bend")
plt.xlabel("Radius (μm)")
plt.ylabel("Mismatch (dB)")
Text(0, 0.5, 'Mismatch (dB)')
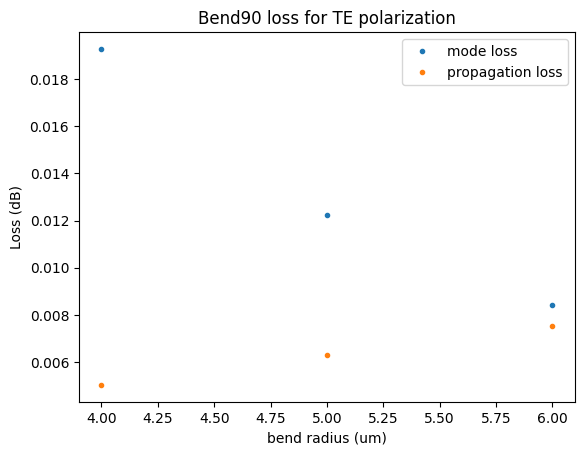
dB_cm = 2 # dB/cm
length = 2 * np.pi * radii * 1e-6
propagation_loss = dB_cm * length * 1e2
print(f"propagation_loss: {propagation_loss}")
plt.title("Bend90 loss for TE polarization")
plt.plot(radii, -10 * np.log10(mismatch), ".", label="mode loss")
plt.plot(radii, propagation_loss, ".", label="propagation loss")
plt.xlabel("bend radius (um)")
plt.ylabel("Loss (dB)")
plt.legend()
propagation_loss: [0.00502655 0.00628319 0.00753982]
<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7f28cf279dd0>
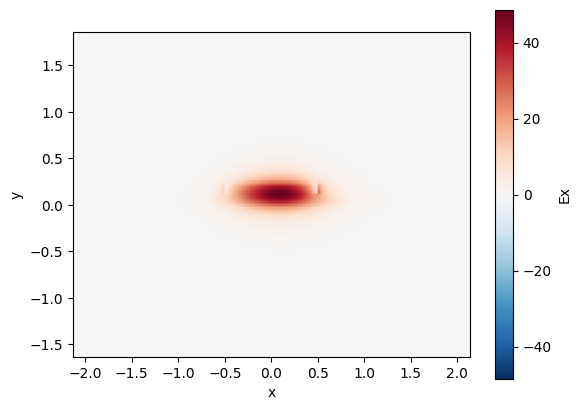
rib = gt.modes.Waveguide(
wavelength=1.55,
core_width=1000 * nm,
core_thickness=220 * nm,
slab_thickness=110 * nm,
bend_radius=15,
core_material="si",
clad_material="sio2",
)
rib.plot_field(field_name="Ex", mode_index=0) # TE
10:38:06 UTC WARNING: Mode field at frequency index 0, mode index 1 does not decay at the plane boundaries.
<matplotlib.collections.QuadMesh at 0x7f28cf24b790>
nitride_bend = gt.modes.Waveguide(
wavelength=1.55,
core_width=1000 * nm,
core_thickness=400 * nm,
slab_thickness=0.0,
bend_radius=30,
core_material="sin",
clad_material="sio2",
)
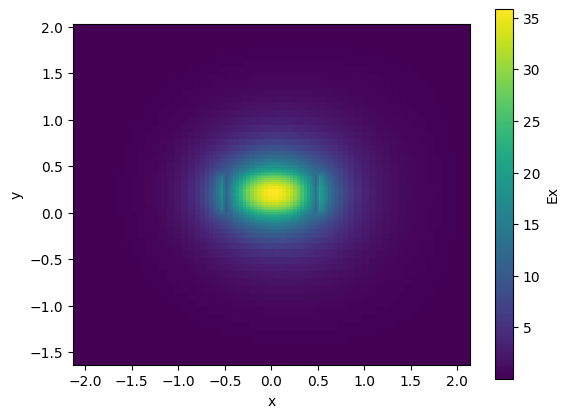
nitride_bend.plot_field(field_name="Ex", mode_index=0, value="abs") # TE
<matplotlib.collections.QuadMesh at 0x7f28ceb12290>
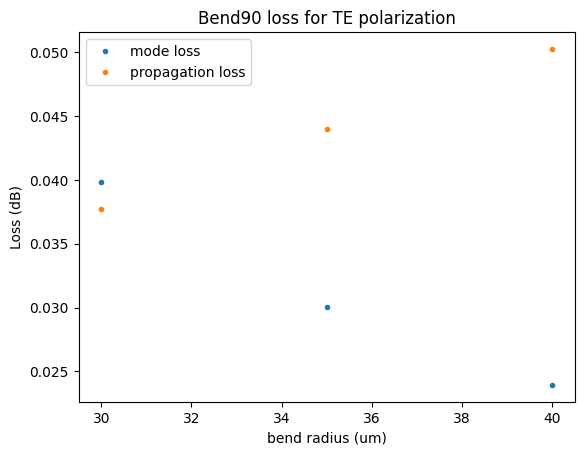
radii = np.array([30, 35, 40])
bend = gt.modes.Waveguide(
wavelength=1.55,
core_width=1000 * nm,
core_thickness=400 * nm,
core_material="sin",
clad_material="sio2",
num_modes=1,
bend_radius=radii.min(),
)
mismatch = gt.modes.sweep_bend_mismatch(bend, radii)
dB_cm = 2 # dB/cm
length = 2 * np.pi * radii * 1e-6
propagation_loss = dB_cm * length * 1e2
print(f"propagation_loss: {propagation_loss}")
plt.title("Bend90 loss for TE polarization")
plt.plot(radii, -10 * np.log10(mismatch), ".", label="mode loss")
plt.plot(radii, propagation_loss, ".", label="propagation loss")
plt.xlabel("bend radius (um)")
plt.ylabel("Loss (dB)")
plt.legend()
propagation_loss: [0.03769911 0.0439823 0.05026548]
<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7f28cf152190>
Exercises
For a 500nm wide 220nm thick Silicon waveguide surrounded by SiO2, what is the minimum bend radius to have less than 0.04dB loss for TE polarization at 1550nm?
For a 500nm wide 220nm thick Silicon waveguide surrounded by SiO2, what is the minimum bend radius to have 99% power transmission for TM polarization at 1550nm?
Waveguide coupler#
You can also compute the modes of a waveguide coupler.
ore_width[0] core_width[1]
<-------> <------->
_______ _______ _
| | | | |
| | | |
| |_____| | | core_thickness
|slab_thickness |
|_____________________| |_
<----->
gap
c = gt.modes.WaveguideCoupler(
wavelength=1.55,
core_width=(500 * nm, 500 * nm),
gap=200 * nm,
core_thickness=220 * nm,
slab_thickness=100 * nm,
core_material="si",
clad_material="sio2",
)
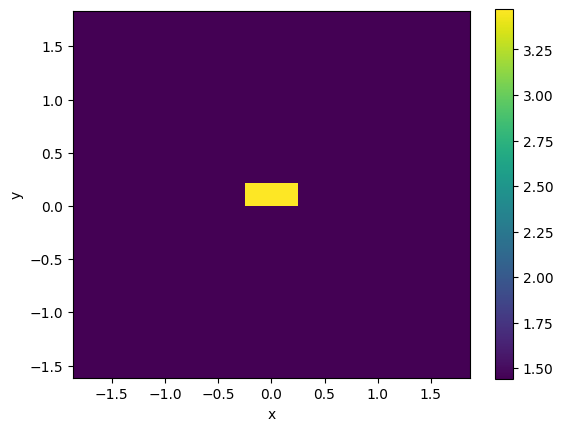
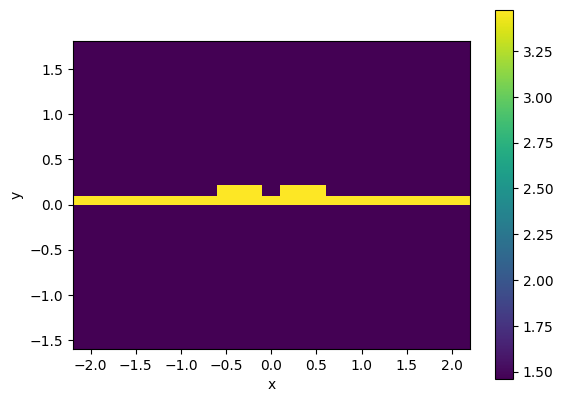
c.plot_index()
<matplotlib.collections.QuadMesh at 0x7f28ceb65210>
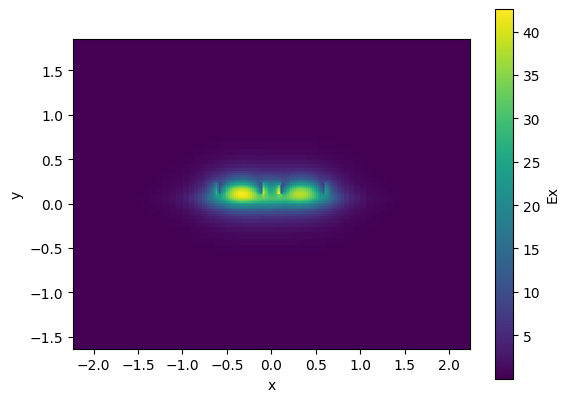
c.plot_field(field_name="Ex", mode_index=0) # even mode
<matplotlib.collections.QuadMesh at 0x7f28cea9e4d0>
c.plot_field(field_name="Ex", mode_index=1) # odd mode
<matplotlib.collections.QuadMesh at 0x7f28ceadfd50>
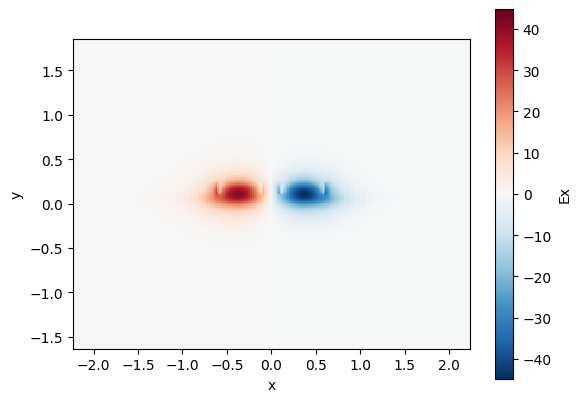
coupler = gt.modes.WaveguideCoupler(
wavelength=1.55,
core_width=(450 * nm, 450 * nm),
core_thickness=220 * nm,
core_material="si",
clad_material="sio2",
num_modes=4,
gap=0.1,
)
print("\nCoupler:", coupler)
print("Effective indices:", coupler.n_eff)
print("Mode areas:", coupler.mode_area)
print("Coupling length:", coupler.coupling_length())
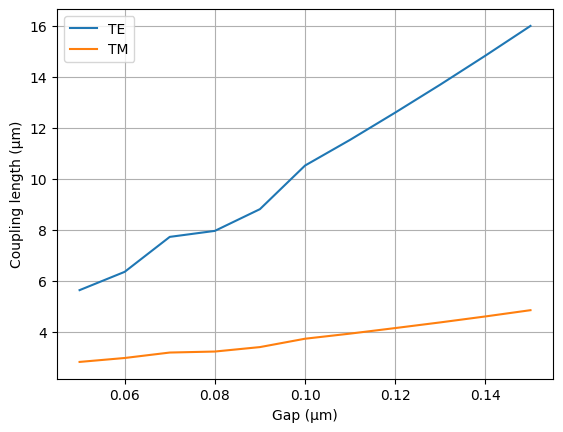
gaps = np.linspace(0.05, 0.15, 11)
lengths = gt.modes.sweep_coupling_length(coupler, gaps)
_, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1)
ax.plot(gaps, lengths)
ax.set(xlabel="Gap (μm)", ylabel="Coupling length (μm)")
ax.legend(["TE", "TM"])
ax.grid()
Coupler: WaveguideCoupler(wavelength=array(1.55), core_width=['0.45', '0.45'], core_thickness='0.22', core_material='si', clad_material='sio2', box_material=None, slab_thickness='0.0', clad_thickness=None, box_thickness=None, side_margin=None, sidewall_angle='0.0', sidewall_thickness='0.0', sidewall_k='0.0', surface_thickness='0.0', surface_k='0.0', bend_radius=None, num_modes='4', group_index_step='False', precision='double', grid_resolution='20', max_grid_scaling='1.2', cache_path='/home/runner/.gdsfactory/modes', overwrite='False', gap='0.1')
Effective indices: [2.4637647 +6.57552457e-05j 2.39007229+5.06214923e-05j
1.9225165 +1.99036730e-04j 1.71420814+2.37015740e-04j]
Mode areas: [0.31003254 0.33258301 0.57286555 0.59002858]
Coupling length: [10.5166863 3.72044606]